Props(属性)
组件创建的时候会使用很多参数来绘制,这些参数就是props。
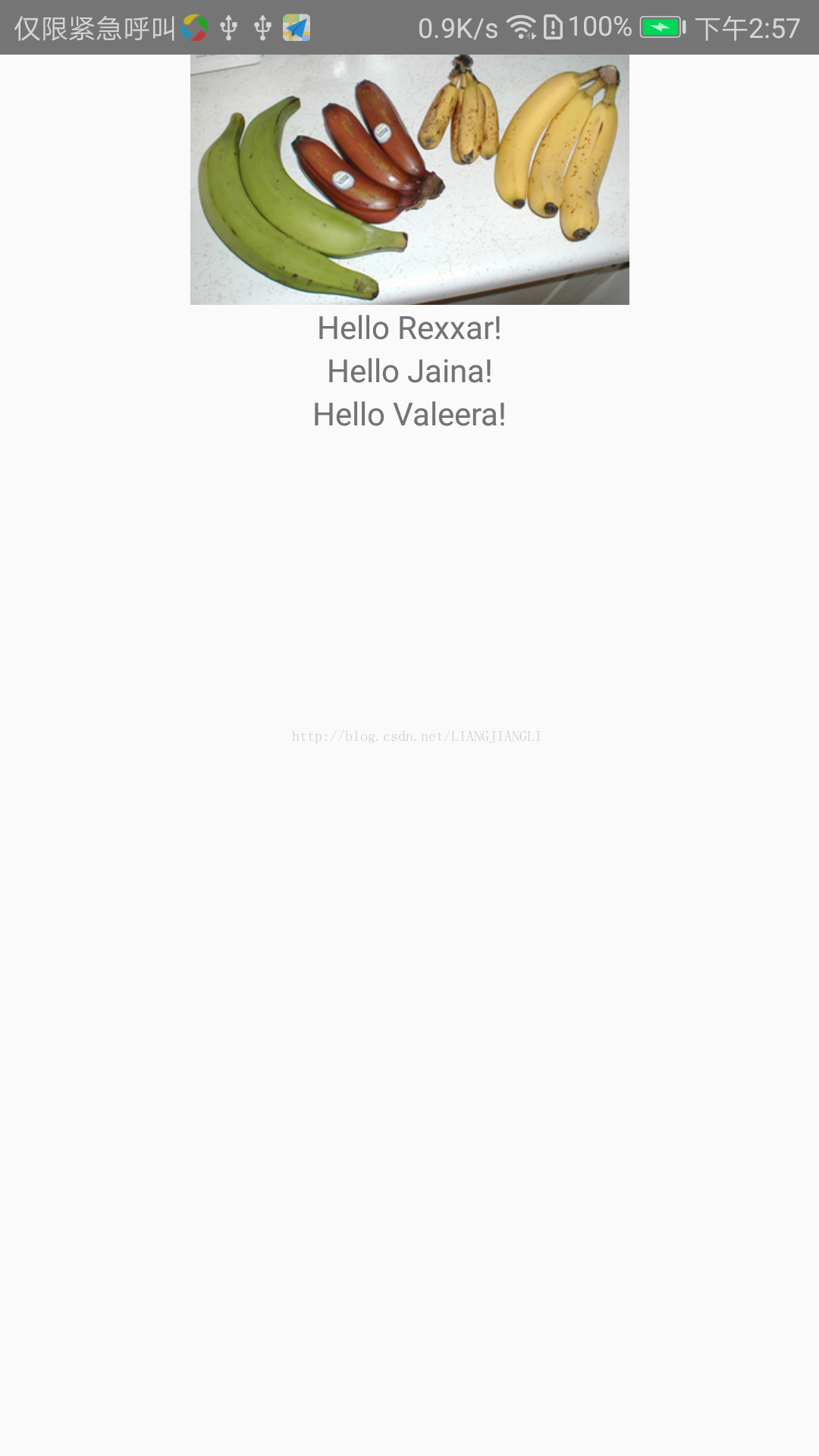
用法样例一:以Image为例,用prop来指定显示图片的地址,然后传给source
用法样例二:自定义的组件使用props
import React, {Component} from 'react'; import {AppRegistry, Image, Text, View} from 'react-native'; class Bananas extends Component { render() { //样例一 let pic = { uri: 'https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/de/Bananavarieties.jpg' }; return ( <View style={{alignItems: 'center'}}> <Image source={pic} style={{width: 193, height: 110}}/> <Greeting name='Rexxar'/> <Greeting name='Jaina'/> <Greeting name='Valeera'/> </View> ); } } //样例二 class Greeting extends Component { render() { return ( <Text>Hello {this.props.name}!</Text> ); } } AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => Bananas);
运行截图:
State (状态)
props是在父组件中指定,而且一经指定,在被指定的组件的生命周期中则不再改变。 对于需要改变的数据,我们需要使用state,一般state在构造
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, Text, View } from 'react-native'; class Blink extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { showText: true }; // 每1000毫秒对showText状态做一次取反操作 setInterval(() => { this.setState(previousState => { return { showText: !previousState.showText }; }); }, 1000); } render() { // 根据当前showText的值决定是否显示text内容 let display = this.state.showText ? this.props.text : ' '; return ( <Text>{display}</Text> ); } } class BlinkApp extends Component { render() { return ( <View> <Blink text='I love to blink' /> <Blink text='Yes blinking is so great' /> <Blink text='Why did they ever take this out of HTML' /> <Blink text='Look at me look at me look at me' /> </View> ); } } AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => BlinkApp);
style(样式)
样式名基本上是遵循了web上的CSS的命名,只是按照JS的语法要求使用了驼峰命名法。
style属性可以是一个普通的JavaScript对象。还可以传入一个数组——在数组后面的属性会覆盖前面的属性,这样你可以间接实现样式的继承。
用法样例:StyleSheet.create来集中定义组件的样式
import React, {Component} from 'react'; import {AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View} from 'react-native'; class LotsOfStyles extends Component { render() { return ( <View> <Text style={styles.red}>just red</Text> <Text style={styles.bigblue}>just bigblue</Text> <Text style={[styles.bigblue, styles.red]}>bigblue, then red</Text> <Text style={[styles.red, styles.bigblue]}>red, then bigblue</Text> </View> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ bigblue: { color: 'blue', fontWeight: 'bold', fontSize: 30, }, red: { color: 'red', }, }); AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => LotsOfStyles);
运行截图:
布局
Flex
flex相对于android布局的权重weight,flex:1代表撑满所有剩余的空间。如果父容器既没有固定的width和height,也没有设定flex,则父容器的尺寸为零。
Flexbox
使用flexbox规则来指定某个组件的子元素的布局
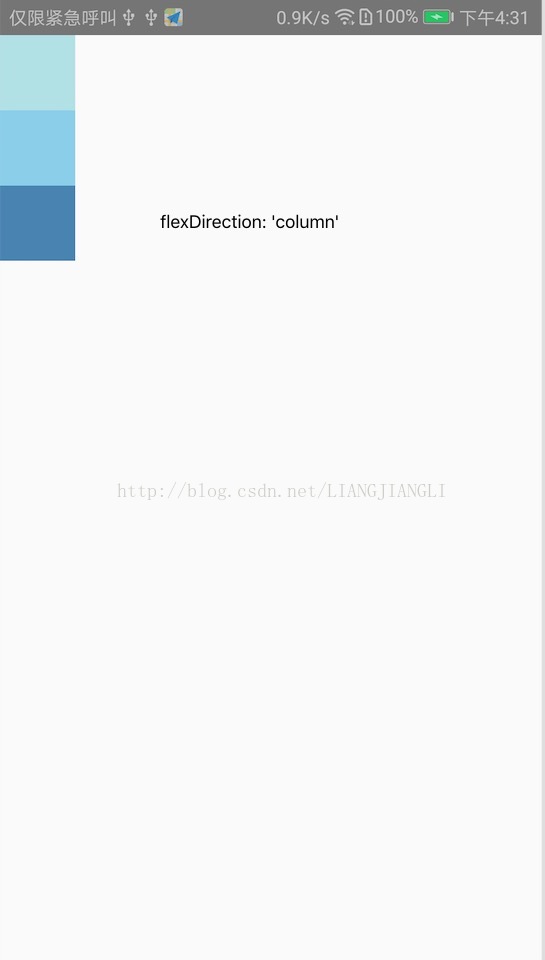
flexDirection 是指定主轴,子元素是沿着vertical轴(column),还是沿着horizontal轴(row)方向排列。
justifyContent 可以决定其子元素沿着主轴的排列方式。子元素是应该靠近主轴的起始端还是末尾段分布呢?亦或应该均匀分布?对应的这些可选项有:flex-start、center、flex-end、space-around以及space-between。
alignItems 可以决定其子元素沿着次轴(与主轴垂直的轴,比如若主轴方向为row,则次轴方向为column)的排列方式。子元素是应该靠近次轴的起始端还是末尾段分布呢?亦或应该均匀分布?对应的这些可选项有:flex-start、center、flex-end以及stretch。
注意:要使stretch选项生效的话,子元素在次轴方向上不能有固定的尺寸。以下面的代码为例:只有将子元素样式中的width: 50去掉之后,alignItems: 'stretch'才能生效。
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, View } from 'react-native'; class FlexDirectionBasics extends Component { render() { return ( // 尝试把`flexDirection`改为`row`看看 <View style={{flex: 1, flexDirection: 'column', justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center'}}> <View style={{width: 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'powderblue'}} /> <View style={{width: 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'skyblue'}} /> <View style={{width: 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'steelblue'}} /> </View> ); } }; AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => FlexDirectionBasics);
布局图解如下:
入门组件使用
TextInput
TextInput是一个允许用户输入文本的基础组件。它有一个名为onChangeText的属性,此属性接受一个函数,而此函数会在文本变化时被调用。另外还有一个名为onSubmitEditing的属性,会在文本被提交后(用户按下软键盘上的提交键)调用。
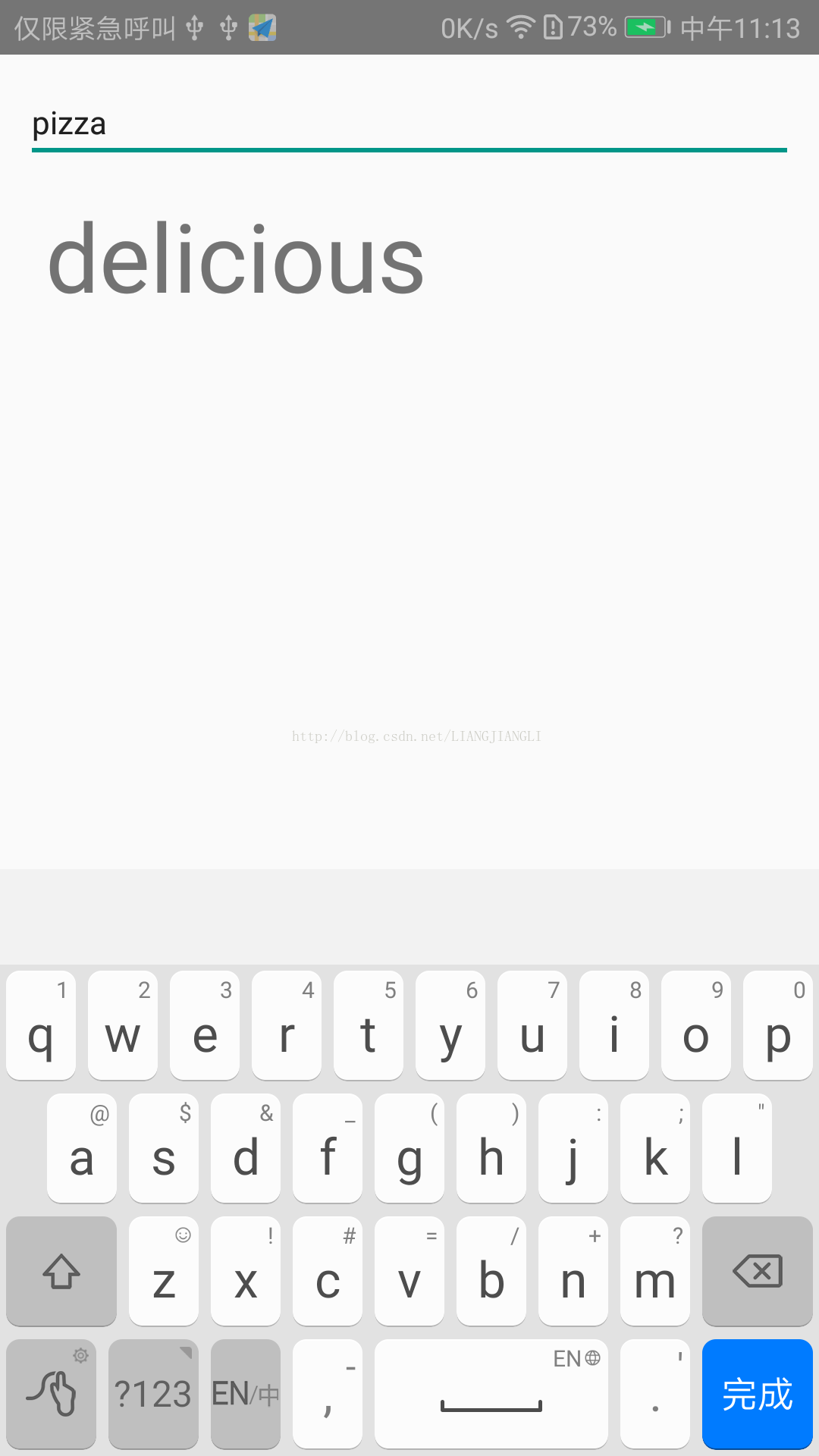
用法样例:监听用户输入,如果输入pizza单词就显示delicious,用户按下提交键后显示very delicious
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, Text, TextInput, View } from 'react-native'; class PizzaTranslator extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {text: ''}; } render() { let display = this.state.text === 'pizza' ? 'delicious' : this.state.text === 'finish' ? 'very delicious' : ' '; return ( <View style={{padding: 10}}> <TextInput style={{height: 40}} placeholder="Type here to translate!" onChangeText={(text) => this.setState({text})} multiline={false} onSubmitEditing={(event) => this.setState({text:'finish'})} /> <Text style={{padding: 10, fontSize: 42}}>{display}</Text> </View> ); } } AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => PizzaTranslator);
运行截图:
ScrollView
ScrollView不仅可以垂直滚动,还能水平滚动(通过horizontal属性来设置)。
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import{ AppRegistry, ScrollView, Image, Text } from 'react-native' class IScrolledDownAndWhatHappenedNextShockedMe extends Component { render() { return( <ScrollView> <Text style={{fontSize:96}}>Scroll me plz</Text> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Text style={{fontSize:96}}>If you like</Text> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Text style={{fontSize:96}}>Scrolling down</Text> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Text style={{fontSize:96}}>What's the best</Text> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Text style={{fontSize:96}}>Framework around?</Text> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Image source={require('../image/web.png')} /> <Text style={{fontSize:80}}>React Native</Text> </ScrollView> ); } } AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => IScrolledDownAndWhatHappenedNextShockedMe);
长列表
RN提供了几个适用于展示长列表数据的组件,一般而言我们会选用FlatList或是SectionList。
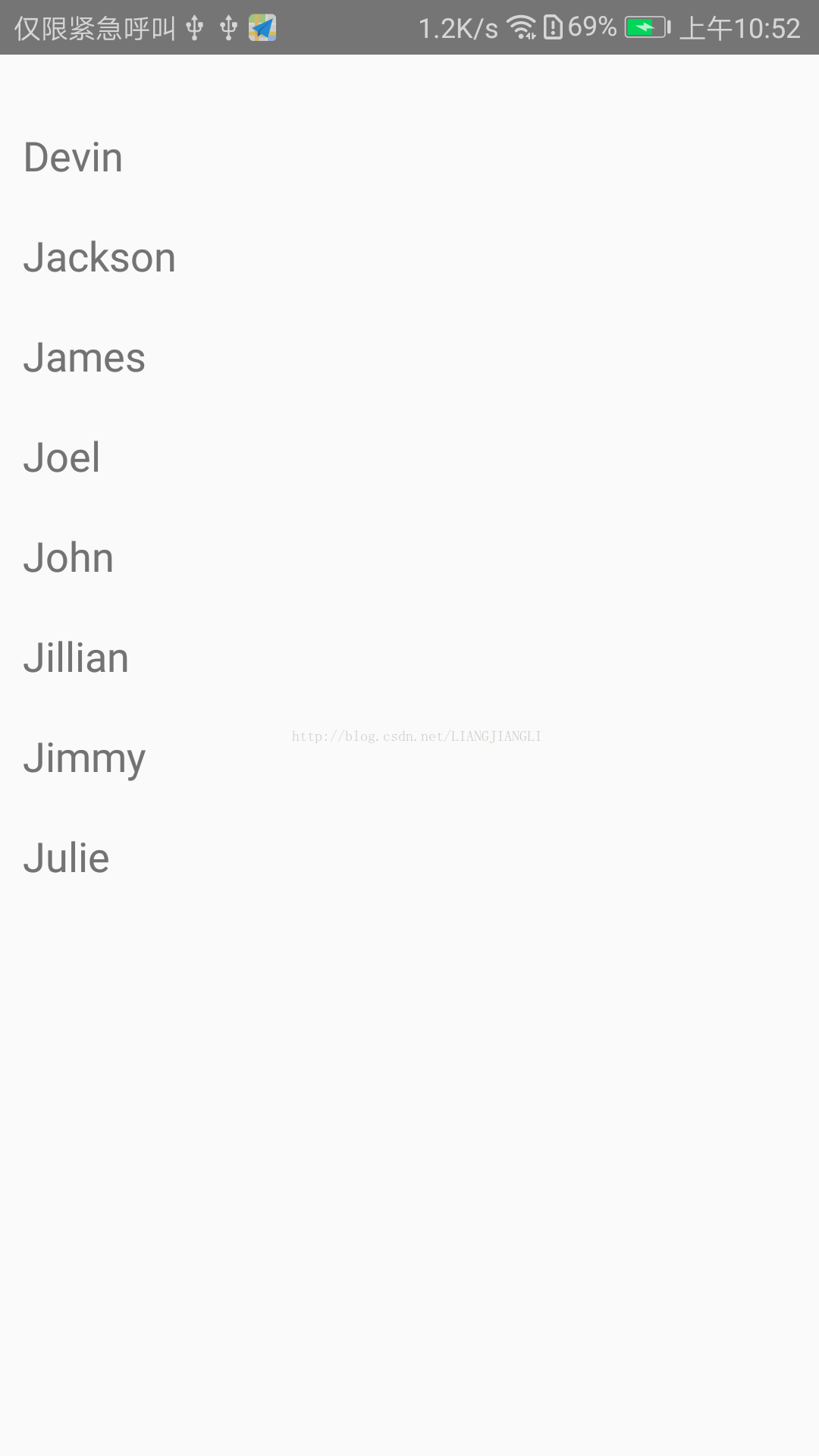
用法样例一:创建一个FlatList,使用data属性传入预设好的数据,然后通过renderItem渲染包含每一行数据的Text组件。
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, FlatList, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; export default class FlatListBasics extends Component { render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <FlatList data={[ {key: 'Devin'}, {key: 'Jackson'}, {key: 'James'}, {key: 'Joel'}, {key: 'John'}, {key: 'Jillian'}, {key: 'Jimmy'}, {key: 'Julie'}, ]} renderItem={({item}) => <Text style={styles.item}>{item.key}</Text>} /> </View> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, paddingTop: 22 }, item: { padding: 10, fontSize: 18, height: 44, }, }) AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => FlatListBasics);
运行截图:
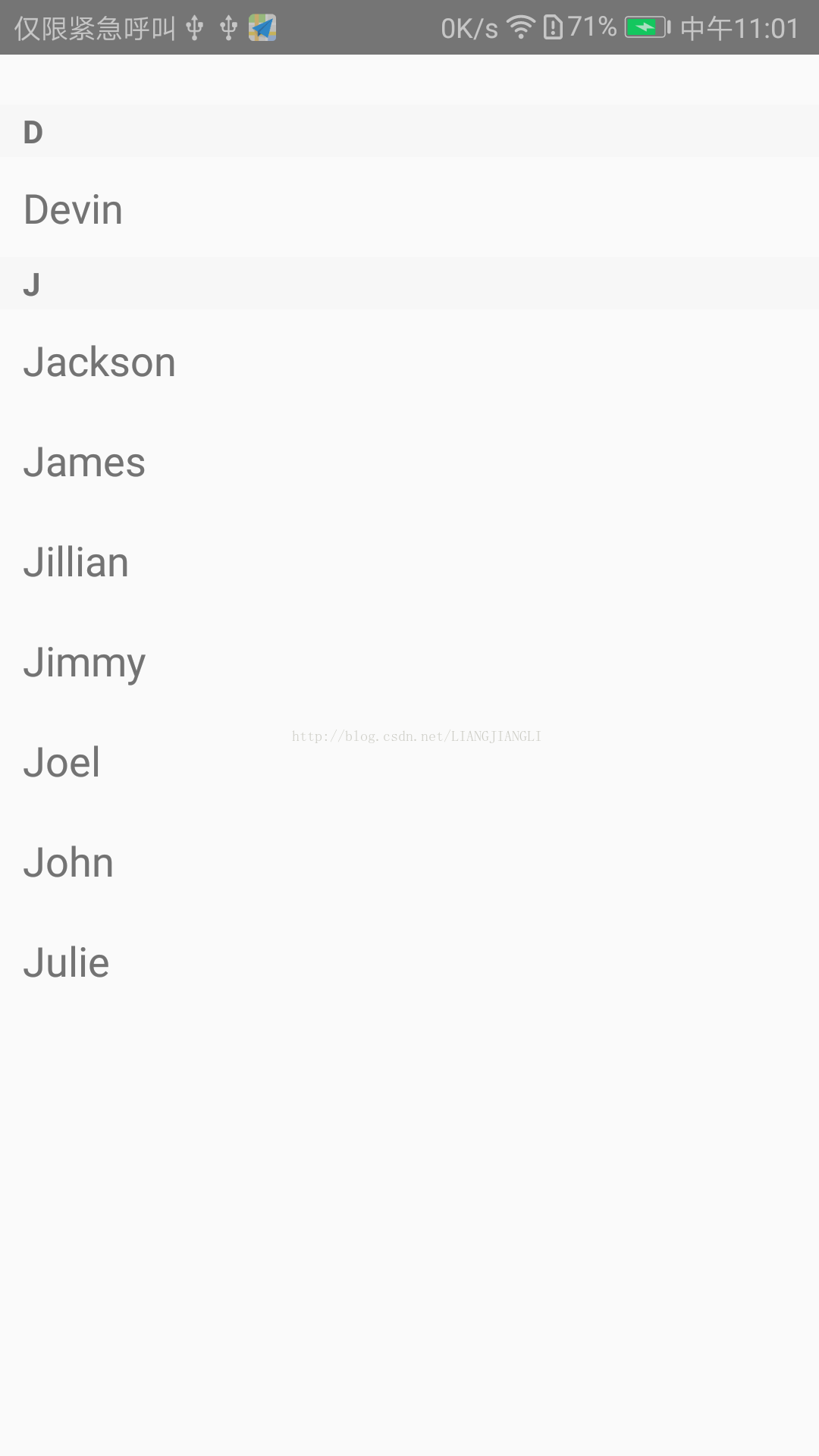
用法样例二:创建一个SectionList,使用属性sections预设好title和data数据,然后通过renderItem渲染包含每一行
data的Text组件,通过renderSectionHeader属性渲染title的Text组件。
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, SectionList, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; export default class SectionListBasics extends Component { render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <SectionList sections={[ {title: 'D', data: ['Devin']}, {title: 'J', data: ['Jackson', 'James', 'Jillian', 'Jimmy', 'Joel', 'John', 'Julie']}, ]} renderItem={({item}) => <Text style={styles.item}>{item}</Text>} renderSectionHeader={({section}) => <Text style={styles.sectionHeader}>{section.title}</Text>} /> </View> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, paddingTop: 22 }, sectionHeader: { paddingTop: 2, paddingLeft: 10, paddingRight: 10, paddingBottom: 2, fontSize: 14, fontWeight: 'bold', backgroundColor: 'rgba(247,247,247,1.0)', }, item: { padding: 10, fontSize: 18, height: 44, }, }) AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => SectionListBasics);
运行截图:
网络
使用Fecth
RN提供了web标准一致的Fetch API ,用于满足开发者访问网络的需求。
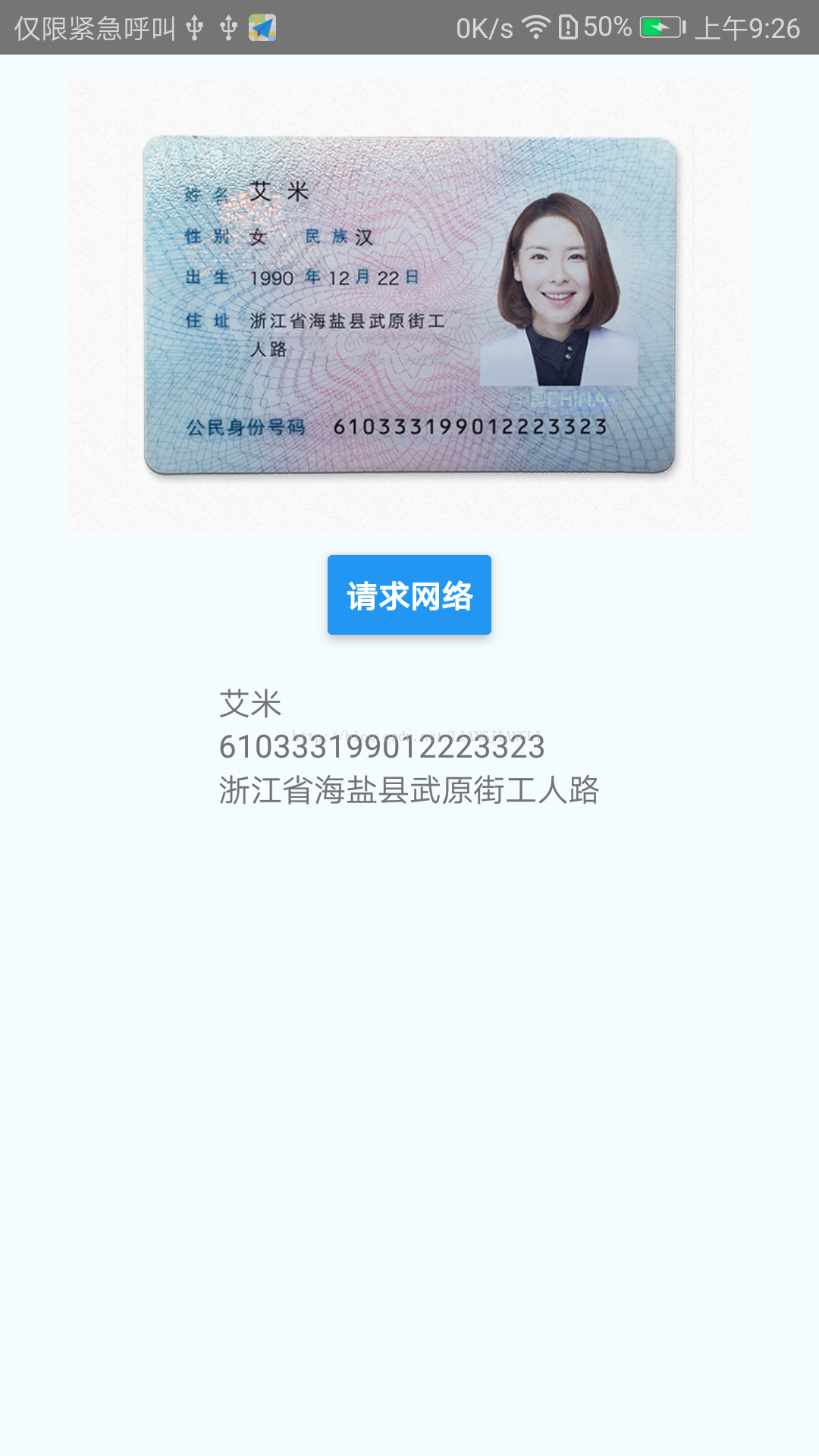
用法样例:通过网络请求腾讯优图身份证识别,获取身份证信息
import React, {Component} from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View, Image, Button } from 'react-native'; export default class AndroidIos extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { name: '', id: '', address: '', uri: 'https://opentest.youtu.qq.com/content/img/product/ocr/ocr_id_02.jpg?v=2.0' }; } onButtonPress = () => { //将网址作为参数传递给fetch fetch('http://api.youtu.qq.com/youtu/ocrapi/idcardocr', { //你可以指定header参数,或是指定使用POST方法,又或是提交数据等 method: 'POST', headers: { 'Accept': '*!/!*', 'Content-Type': 'text/json', 'user-agent': 'youtu-android-sdk', 'Authorization': 'Zp0X4NG2VfmukwMYipvy/Ipp0fNhPTEwMDg3NjAyJms' + '9QUtJRDF2ZlJPYndmYU1DdWVGQU90UkNHUGcxS1daUjdLRjFuJmU9MTUwMj' + 'k0MDQyNiZ0PTE1MDAzNDg0MjYmcj04MTMwNzQxOTgmdT04Mzk2NDMzOTg=', }, body: JSON.stringify({ 'app_id': '10087602', 'url': 'http://opentest.youtu.qq.com/content/img/product/ocr/ocr_id_02.jpg?v=2.0', 'card_type': 0, }) //处理服务器的响应数据 }).then((response) => response.json()) .then((responseJson) => { //var base64Icon = 'data:image/png;base64,' + responseJson.frontimage; this.setState({ name: responseJson.name, id: responseJson.id, address: responseJson.address, //uri: base64Icon }) }) .catch((error) => { console.warn('fetch error') }); }; render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Image source={{uri: this.state.uri}} style={styles.image}/> <Button title="请求网络" onPress={this.onButtonPress}/> <View style={styles.id}> <Text>{this.state.name}</Text> <Text>{this.state.id}</Text> <Text>{this.state.address}</Text> </View> </View> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, id: { flex: 1, flexDirection: 'column', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', marginTop: 20 }, image:{ height: 200, width: 300, margin: 10, }, }); AppRegistry.registerComponent('reactnativeapp', () => AndroidIos);
运行截图:
最后,我把上面的基础学习的代码放在了github上,
地址:https://github.com/Eric0liang/RNProject,
apk下载地址:https://github.com/Eric0liang/RNProject/blob/master/app-release.apk?raw=true
对于如何生产集成到android studio并生产apk,可以参考另一篇博客 《 React Native集成到现有Android Studio项目》