SqlSession会话创建过程
mybatis操作的时候跟数据库的每一次连接,都需要创建一个会话,我们用openSession()方法来创建。这个会话里面需要包含一个Executor用来执行 SQL。Executor又要指定事务类型和执行器的类型。
1.创建Transaction(两种方式)
| 属性 | 产生工厂类 | 产生事务 |
|---|---|---|
| JDBC | JbdcTransactionFactory | JdbcTransaction |
| MANAGED | ManagedTransactionFactory | ManagedTransaction |
- 如果配置的是 JDBC,则会使用Connection 对象的 commit()、rollback()、close()管理事务。
- 如果配置成MANAGED,会把事务交给容器来管理,比如 JBOSS,Weblogic。
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
public SqlSession openSession() {
//configuration中有默认赋值protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
2.创建Executor
//ExecutorType是SIMPLE,一共有三种SIMPLE(SimpleExecutor)、REUSE(ReuseExecutor)、BATCH(BatchExecutor)
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//xml中的development节点
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//type配置的是Jbdc所以生成的是JbdcTransactionFactory工厂类
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//Jdbc生成JbdcTransactionFactory生成JbdcTransaction
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//创建CachingExecutor执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//创建DefaultSqlSession属性包括 Configuration、Executor对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
获得Mapper对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
mapperRegistry.getMapper是从MapperRegistry的knownMappers里面取的,knownMappers里面存的是接口类型(interface mapper.UserMapper)和工厂类(MapperProxyFactory)。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
从knownMappers的Map里根据接口类型(interface mapper.UserMapper)取出对应的工厂类。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
这里通过JDK动态代理返回代理对象MapperProxy(org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy@6b2ea799)。
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//mapperInterface是interface mapper.UserMapper
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
执行SQL
User user = userMapper.getUserById(1);
调用invoke代理方法
由于所有的 Mapper 都是 MapperProxy 代理对象,所以任意的方法都是执行MapperProxy 的 invoke()方法。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//判断是否需要去执行SQL还是直接执行方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
//这里判断的是接口中的默认方法Default等
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//获取缓存,保存了方法签名和接口方法的关系
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
调用execute方法
咱们的例子用的是查询所以走的是else。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//根据命令类型走不行的操作command.getType()是select
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//将参数转换为SQL的参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
调用selectOne其实是selectList
selectone查询一个和查询多个其实是一样的。
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//从Configuration里的mappedStatements里根据key(id的全路径)获取MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
mappedStatements对象如图
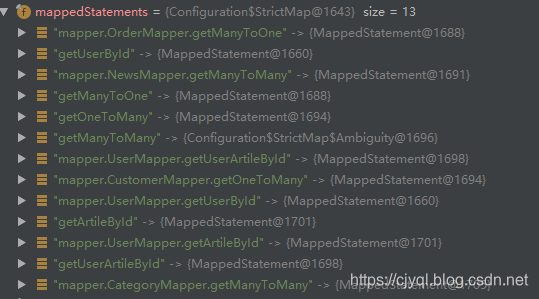
MappedStatement对象如图
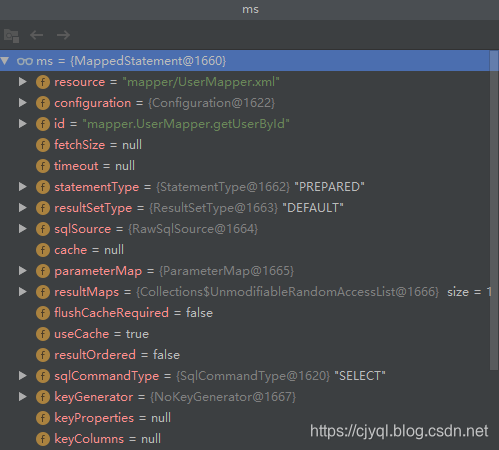
执行query方法
1.创建CacheKey
从 BoundSql 中获取SQL信息,创建 CacheKey。这个CacheKey就是缓存的Key。
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//取出sql语句
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
//key = -575461213:-771016147:mapper.UserMapper.getUserById:0:2147483647:select * from test_user where id = ?:1:development
//创建缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//使用缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
2.清空本地缓存
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//queryStack 用于记录查询栈,防止递归查询重复处理缓存
//flushCache=true 的时候,会先清理本地缓存(一级缓存)
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
//清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//如果没有缓存,会从数据库查询:queryFromDatabase()
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
//如果 LocalCacheScope == STATEMENT,会清理本地缓存
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
3.从数据库查询
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//先在缓存用占位符占位
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//执行Executor 的 doQuery(),默认是SimpleExecutor
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//执行查询后,移除占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//从新放入数据
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
1.执行doQuery
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//获取数据库连接
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//newStatementHandler生成StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//准备预处理语句statementHandler拦截器
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//执行StatementHandler的query
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
1.StatementHandler拦截器
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
2.创建StatementHandler
在 configuration.newStatementHandler()中,new 一个 StatementHandler,先得到 RoutingStatementHandler。
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
1.执行PreparedStatementHandler处理器
RoutingStatementHandler里面没有任何的实现,是用来创建基本的StatementHandler 的。这里会根据 MappedStatement里面的statementType决定StatementHandler的类型 。默认是PREPARED (STATEMENT 、 PREPARED 、CALLABLE)
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
2.ParameterHandler和resultSetHandler和Executor拦截器
StatementHandler 里面包含了处理参数的 ParameterHandler 和处理结果集的ResultSetHandler。
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.executor = executor;
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
generateKeys(parameterObject);
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
this.boundSql = boundSql;
//newParameterHandler里面是参数拦截器
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
//newResultSetHandler是返回结果的拦截器
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
//parameterHandler拦截器
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
//parameterHandler拦截器
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//Executor执行器
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
3.创建Statement
用 new 出来的 StatementHandler创建 Statement对象,prepareStatement()方法对语句进行预编译,处理参数
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
//从事务中获取数据库连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
//获取Statement
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//为Statement设置查询参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql());
Statement statement = null;
try {
//初始化Statement
statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
//设置查询超时时间
setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout);
setFetchSize(statement);
return statement;
} catch (SQLException e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) {
String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns();
if (keyColumnNames == null) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames);
}
} else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql);
} else {
//从数据库连接中获取statement
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
}
}
4.执行StatementHandler的query方法
RoutingStatementHandler 的 query()方法。delegate 委派,最终执行 PreparedStatementHandler 的 query()方法。
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
//执行PreparedStatement的execute方法
ps.execute();
//处理返回结果集
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
5.ResultSetHandler处理结果集
ResultSetHandler 只有一个实现类:DefaultResultSetHandler。也就是执行DefaultResultSetHandler类中的handleResultSets ()方法。
首先我们会先拿到第一个结果集,如果没有配置一个查询返回多个结果集的情况,一般只有一个结果集。如果下面的这个 while 循环我们也不用,就是执行一次。然后会调用 handleResultSet()方法。
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
= null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
