主要步骤:加载配置文件,实例化bean,填充bean属性,返回bean。
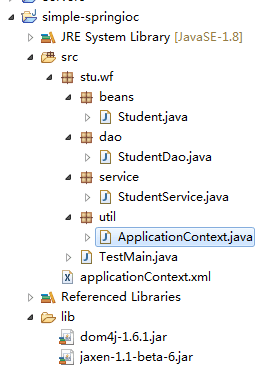
项目目录结构:
1.创建一个对象Student
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
2.创建StudentDao
public class StudentDao {
private String test;
public String getTest() {
return test;
}
public void setTest(String test) {
this.test = test;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
3.创建StudentService
public class StudentService {
//注入dao
private StudentDao studentDao;
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public StudentDao getStudentDao() {
return studentDao;
}
public void sayHello() {
studentDao.sayHello();
}
}
4.bean配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="student" class="stu.wf.beans.Student" scope="single">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="studentDao" class="stu.wf.dao.StudentDao" scope="single">
<property name="test" value="test"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="stu.wf.service.StudentService" scope="single">
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
5.最重要的逻辑处理ApplicationContext
public class ApplicationContext {
/**
* 保存单例bean
*/
private static Map<String, Object> singleBeans = new HashMap<>();
private static Document document = null;
private static ApplicationContext context = null;
public static ApplicationContext buildContext(String configPath) {
if(context == null) {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
document = reader.read(configPath);
instanceSingleBean();
context = new ApplicationContext();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return context;
}
/**
* 实例化所有单例bean 保存到singleBeans中
* @param document
* @throws Exception
*/
private static void instanceSingleBean()throws Exception{
String xpath = "//bean[@scope='single']";
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List <Element> elements = document.selectNodes(xpath);
for(Element element : elements) {
String classPath = element.attributeValue("class");
Object obj = Class.forName(classPath).newInstance();
singleBeans.put(classPath, obj);
}
}
public Object getBean(String beanId) {
Object resultObj = null;
String xpath = "//bean[@id='"+beanId+"']";
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Element> elements = document.selectNodes(xpath);
if(elements == null || elements.size()<1) {
throw new RuntimeException("beanId:"+beanId+" is error");
}else if(elements.size()>1) {
throw new RuntimeException("beanId:"+beanId+" not only one bean.");
}
Element element = elements.get(0);
String classPath = element.attributeValue("class");
resultObj = singleBeans.get(classPath);
try {
if(resultObj == null) {
resultObj = Class.forName(classPath).newInstance();
}
//填充bean属性 -- 简单依赖注入
initBean(resultObj,element);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return resultObj;
}
/**
* 填充bean屬性
* @param resultObj
* @param beanElement
* @throws Exception
* @throws SecurityException
*/
private void initBean(Object resultObj, Element beanElement) throws Exception, SecurityException {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Element> properTyElements = beanElement.elements("property");
if(properTyElements == null || properTyElements.size()<1) {
return ;
}
for(Element property : properTyElements) {
String fieldName = property.attributeValue("name");
String fieldValue = property.attributeValue("value");
String fieldRef = property.attributeValue("ref");
//对应的属性
Field field = resultObj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
String typeName = field.getType().getName();
if(fieldRef != null && !"".equals(fieldRef)) {
setPropertyRef(resultObj,field,fieldRef);
}else {
setProperTyValue(resultObj,field,typeName,fieldValue);
}
}
}
/**
* 简单判断,Integer String类型的属性
* @param resultObj
* @param field
* @param typeName
* @param fieldValue
* @throws Exception
*/
private void setProperTyValue(Object resultObj, Field field, String typeName, String fieldValue)throws Exception {
field.setAccessible(true);
if("java.lang.String".equals(typeName)){
field.set(resultObj, fieldValue);
}else if("java.lang.Integer".equals(typeName)){
field.set(resultObj, Integer.valueOf(fieldValue));
}
}
/**
* 处理属性也是个bean 依赖注入
* @param resultObj
* @param field
* @param fieldRef
* @throws Exception
*/
private void setPropertyRef(Object resultObj, Field field, String fieldRef) throws Exception{
String xPath="//bean[@id='"+fieldRef+"']";
Element beanElement = (Element) document.selectNodes(xPath).get(0);
String classPath = beanElement.attributeValue("class");
Object refObj = singleBeans.get(classPath);
if(refObj == null) {
refObj = Class.forName(classPath).newInstance();
}
//TODO 这里的引用refObj只是实例化了,本没有填充属性
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(resultObj, refObj);
}
}
6.测试类TestMain
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = ApplicationContext.buildContext("src/applicationContext.xml");
Student student = (Student)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("student:"+student);
StudentService studentService = (StudentService)context.getBean("studentService");
studentService.sayHello();
System.out.println("test:"+studentService.getStudentDao().getTest());
}
}
运行结果:
student:Student [id=1, name=张三]
hello world
test:null //并没有循环依赖注入,所有dao的属性为null
