环境
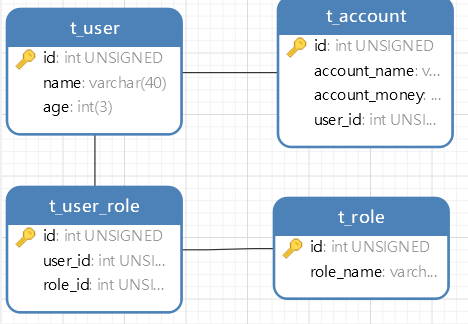
- 数据库表结构:
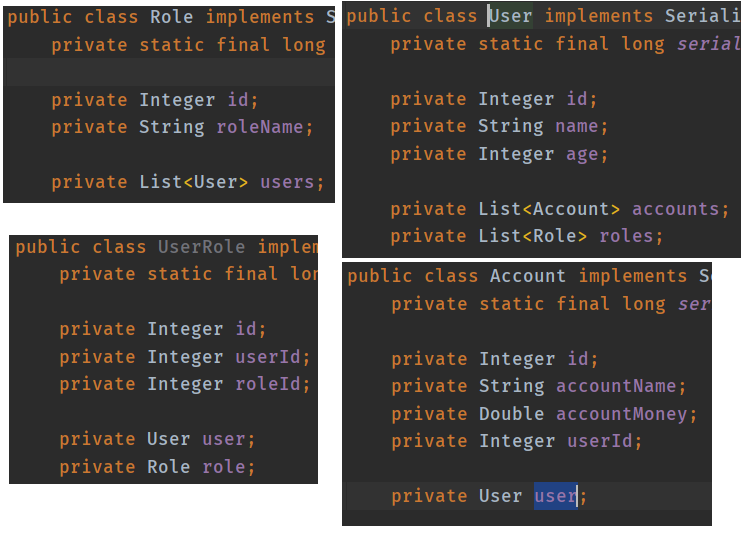
- 实体类结构:
resultMap
<resultMap id="唯一标识" type="返回结果的bean类型">
<id column="数据库字段名" property="bean中的属性名"/>
<result property="bean中的属性名" column="数据库字段名"/>
<association property="bean中的属性名(其他的bean对象)" fetchType="eager(立即加载)|lazy(延迟加载)"
javaType="属性的类型" column="传入方法中作为参数的列的列名"
select="cn.ann.mapper.UserMapper.getUserById(方法的完整路径名)"/>
<collection property="bean中的属性名(bean对象集合)" ofType="集合的泛型类型" fetchType="eager(立即加载)|lazy(延迟加载)" column="传入方法中作为参数的列的列名"
select="方法的完整路径名" resultMap="可以引用别的结果集映射配置"/>
</resultMap>- 注意: association 和 collection 中都可以配置自己的映射关系
- 关于 association 和 collection:
- association: 代表的是配置'一'的关系的映射
- collection: 代表的是配置'多'的关系的映射
- 个人感觉: 所谓的'一'和'多'其实指的是这个文件所映射的实体类中的属性是 对象 还是 集合 , 同时, 数据库中的表联系在Java中就可以同过这种方式来对应
mybatis中的一对一、一对多
正如"关于 association 和 collection"中所说, 在mybatis中只需要配置相应的结果映射就好了
一对一: 每个账户只能对应一个用户
解决方案一:
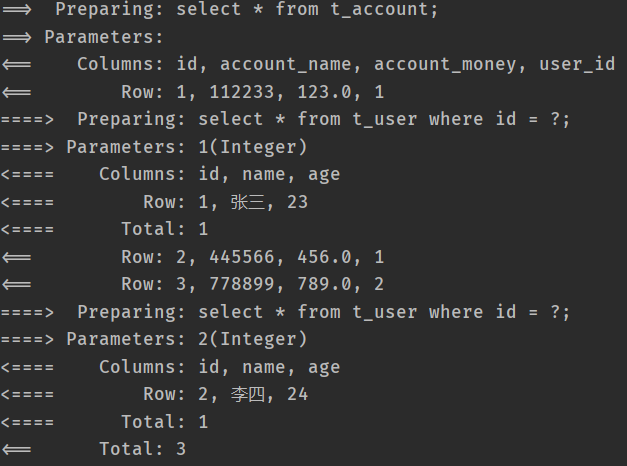
<resultMap id="accountAllMap" type="Account"> <id property="id" column="aid"/> <result property="accountName" column="account_name"/> <result property="accountMoney" column="account_money"/> <result property="userId" column="user_id"/> <association property="user" javaType="User"/> <!-- 因为user中的属性名和列名是一样的, 所以就没有配置结果的映射 --> </resultMap> <select id="getAccountById" resultMap="accountAllMap" parameterType="Integer"> select a.id as aid, a.account_name, a.account_money, u.* from t_account a right join t_user u on a.user_id = u.id where a.id = #{id} </select>- 此方案是一次性查出所有需要的数据, 然后封装
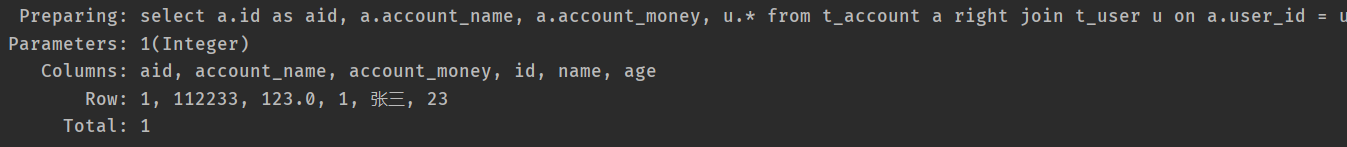
- 运行结果截图:

- sql截图:
- 解决方案二:
- AccountMapper:
<resultMap id="accountMap" type="Account"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result property="accountName" column="account_name"/> <result property="accountMoney" column="account_money"/> <result property="userId" column="user_id"/> <association property="user" fetchType="eager" column="user_id" select="cn.ann.mapper.UserMapper.getUserById"/> </resultMap> <select id="findAll" resultMap="accountMap"> select * from t_account; </select>- UserMapper:
<select id="getUserById" resultType="User" parameterType="Integer"> select * from t_user where id = #{id}; </select>- 此方案引用了UserMapper中的方法
- 运行结果截图:
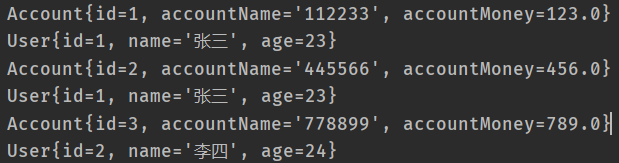
- sql截图:
- 比较上面两种方案, 我们可以发现:
- 方案1是一股脑查出所有数据, 且sql语句很长, 对于一对多的关系, 会非常浪费性能
- 方案2发送了多次sql语句, 在这样的前提下, 我们就可以设置立即加载或者是延时加载
- 立即加载: 就是在查询数据时将所有需要的数据都查出来
- 延时加载(按需加载): 在需要的时候再加载数据
- 多对一的表关系可以转化为mybatis的一对一
一对多: 一个用户可以有多个账户
此处演示方案二:
UserMapper.xml
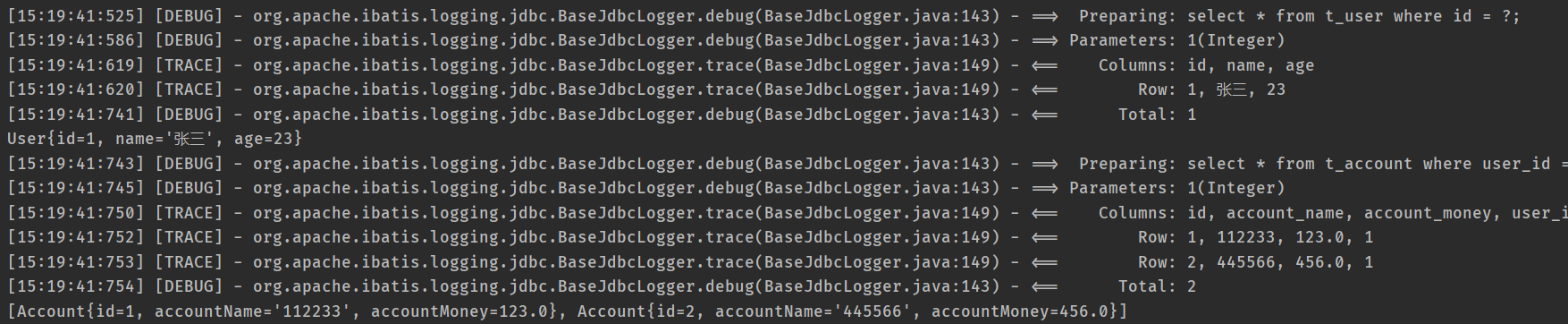
<resultMap id="userMap" type="user"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <collection property="accounts" ofType="account" fetchType="lazy" select="cn.ann.mapper.AccountMapper.getAccountsByUserId" column="id"/> </resultMap> <select id="getUserById" resultMap="userMap" parameterType="Integer"> select * from t_user where id = #{id}; </select>AccountMapper.xml
<select id="getAccountsByUserId" parameterType="Integer" resultType="account"> select * from t_account where user_id = #{userId} </select>- 运行结果截图: 此为延迟加载的效果
多对多的表关系可以转化为mybatis的一对多
延迟加载
- 延迟加载:即按需加载、懒加载,指的是加载数据时,并不加载全部的数据,数据在用到的时候才会去加载
- 立即加载:加载数据时,加载全部数据,一般一对一(多对一)的关联关系中使用立即加载,一对多的关系中使用延时加载
- mybatis开启延时加载:
开启全局延时加载:
<settings> <!-- 设置懒加载 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。否则,每个属性会按需加载; 3.4.1以后默认开启 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> <!-- 指定哪个对象的方法触发一次延迟加载。默认值: equals,clone,hashCode,toString --> <setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value=""/> </settings>- 为某个查询开启延时加载:
设置 collection 和 association 的属性fetchType- lazy: 懒加载(延时加载)
- eager: 立即加载