An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
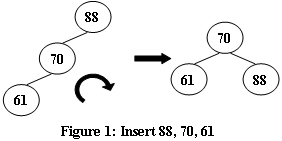 |
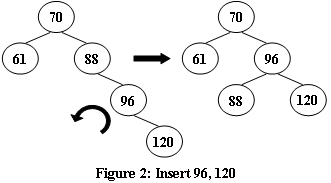 |
|---|---|
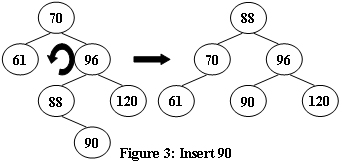 |
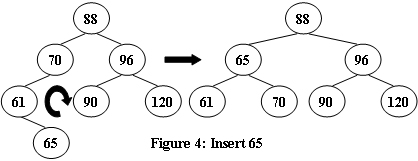 |
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 63 65
Sample Output 1:
70 63 88 61 65
YES
Sample Input 2:
8
88 70 61 96 120 90 65 68
Sample Output 2:
88 65 96 61 70 90 120 68 NO
毕竟是第一次做平衡二叉树,
平衡二叉树,一开始以为很难,最后看看也不过如此,我代码还是在平板上写的。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 using namespace std; 7 struct Node { 8 int val; 9 Node *left, *right; 10 } *tree; 11 int n, m; 12 13 Node *leftrotate(Node * tree) { 14 Node *temp = tree->left; 15 tree->left = temp->right; 16 temp->right = tree; 17 return temp; 18 } 19 20 Node *rightrotate(Node * tree) { 21 Node *temp = tree->right; 22 tree->right = temp->left; 23 temp->left = tree; 24 return temp; 25 } 26 27 Node *rightleftrotate(Node * tree) { 28 tree->left = rightrotate(tree->left); 29 return leftrotate(tree); 30 } 31 32 Node *leftrightrotate(Node * tree) { 33 tree->right = leftrotate(tree->right); 34 return rightrotate(tree); 35 } 36 37 38 int getlen(Node * root) { 39 if (root == NULL) 40 return 0; 41 return max(getlen(root->left), getlen(root->right)) + 1; 42 } 43 44 Node *insert(Node * tree, int val) { 45 if (tree == NULL) { 46 tree = new Node(); 47 tree->val = val; 48 } else if (val < tree->val) { 49 tree->left = insert(tree->left, val); 50 int ll = getlen(tree->left), rr = getlen(tree->right); 51 if (ll - rr >= 2) { 52 if (val < tree->left->val) 53 tree = leftrotate(tree); 54 else 55 tree = rightleftrotate(tree); 56 } 57 } else if (val > tree->val) { 58 tree->right = insert(tree->right, val); 59 int ll = getlen(tree->left), rr = getlen(tree->right); 60 if (rr - ll >= 2) { 61 if (val > tree->right->val) 62 tree = rightrotate(tree); 63 else 64 tree = leftrightrotate(tree); 65 } 66 } 67 return tree; 68 } 69 vector<int> v, vt; 70 void output(Node *root, int x){ 71 if(root != NULL){ 72 output(root->left, x<<1); 73 //cout <<root->val<<endl; 74 output(root->right, (x<<1)+1); 75 }else{ 76 v.push_back(x); 77 } 78 } 79 80 void levelout(Node *root){ 81 queue<Node*> q; 82 q.push(root); 83 Node *ans; 84 while(!q.empty()){ 85 ans = q.front(); 86 q.pop(); 87 vt.push_back(ans->val); 88 if(ans->left != NULL) 89 q.push(ans->left); 90 if(ans->right != NULL) 91 q.push(ans->right); 92 } 93 } 94 95 int main() { 96 cin >> n; 97 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 98 cin >> m; 99 tree = insert(tree, m); 100 } 101 levelout(tree); 102 for(int i = 0; i < vt.size(); i++){ 103 printf("%d%c",vt[i], i == vt.size()-1?'\n':' '); 104 } 105 output(tree,1); 106 sort(v.begin(), v.end()); 107 for(int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++){ 108 if(v[i-1]+1 != v[i]){ 109 cout << "NO" << endl; 110 return 0; 111 } 112 } 113 cout << "YES" << endl; 114 return 0; 115 }