文章目录
Author: CHEN, Yue
Organization: 浙江大学
Time Limit: 400 ms
Memory Limit: 64 MB
Code Size Limit: 16 KB
A1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree (30point(s))
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
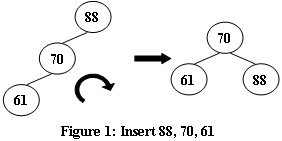 |
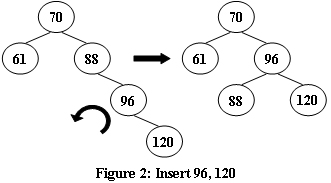 |
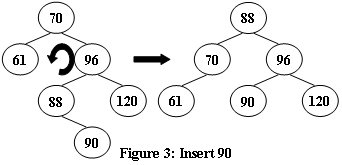 |
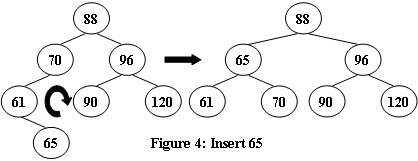 |
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 63 65
Sample Output 1:
70 63 88 61 65
YES
Sample Input 2:
8
88 70 61 96 120 90 65 68
Sample Output 2:
88 65 96 61 70 90 120 68
NO
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct NODE{
int data,num;
struct NODE *lchild,*rchild;
};
int maxNUM=-1;
vector<int> level;
int getHeight(NODE *root){
if(root==NULL) return 0;
return max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeight(root->rchild))+1;
}
NODE *lRotate(NODE *root){
NODE *temp=root->rchild;
root->rchild=temp->lchild;
temp->lchild=root;
return temp;
}
NODE *rRotate(NODE *root){
NODE *temp=root->lchild;
root->lchild=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=root;
return temp;
}
NODE *lrRotate(NODE *root){
root->lchild=lRotate(root->lchild);
return rRotate(root);
}
NODE *rlRotate(NODE *root){
root->rchild=rRotate(root->rchild);
return lRotate(root);
}
NODE *Insert(NODE *root,int x){
if(root==NULL){
root=new NODE;
root->data=x;
root->lchild=root->rchild=NULL;
}
else if(x<=root->data){
root->lchild=Insert(root->lchild,x);
if(getHeight(root->lchild)-getHeight(root->rchild)>=2){
if(x<root->lchild->data) root=rRotate(root);
else root=lrRotate(root);
}
}
else{
root->rchild=Insert(root->rchild,x);
if(getHeight(root->rchild)-getHeight(root->lchild)>=2){
if(x>root->rchild->data) root=lRotate(root);
else root=rlRotate(root);
}
}
return root;
}
void levelOrder(NODE *root){
queue<NODE*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
NODE *temp=q.front();
q.pop();
if(temp->num>maxNUM){
maxNUM=temp->num;
}
level.push_back(temp->data);
if(temp->lchild!=NULL){
q.push(temp->lchild);
temp->lchild->num=temp->num*2;
}
if(temp->rchild!=NULL){
q.push(temp->rchild);
temp->rchild->num=temp->num*2+1;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n,k;
cin>>n;
NODE *root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>k;
root=Insert(root,k);
}
root->num=1;
levelOrder(root);
for(int i=0;i<level.size();i++){
if(i==0) printf("%d",level[i]);
else printf(" %d",level[i]);
}
printf("\n");
if(maxNUM==n) printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
Analysis
-对一棵二叉平衡树进行逐个结点的插入操作。并输出其层序序列,以及判断其是否是完全二叉树。
