JDK1.8
ArrayList源码分析--jdk1.8
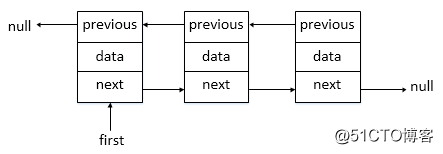
LinkedList源码分析--jdk1.8
HashMap源码分析--jdk1.8
AQS源码分析--jdk1.8
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer概述
1. AQS是一个基于FIFO队列,可以用于构建锁或者其他相关同步装置的基础框架。
2. AQS提供了双向链表。
3. AQS分为共享模式和独占模式。
4.AQS基于volatile内存可见性和CAS原子性操作实现线程间通信操作。
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer数据结构
数据结构是集合的精华所在,数据结构往往也限制了集合的作用和侧重点,了解各种数据结构是我们分析源码的必经之路。
AQS的数据结构如下:双向链表
AQS实现共享资源的访问控制基础:
1.state字段,即同步器状态字段。用于共享资源的访问控制
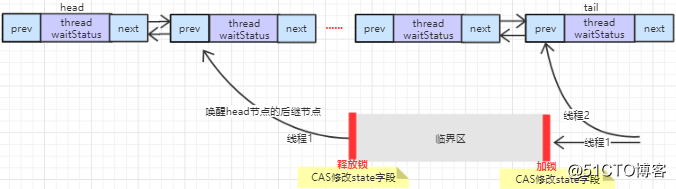
2.CLH队列,FIFO等待队列,存放竞争失败的线程。通常CLH队列是一个自旋队列,AQS以阻塞的方式实现
CLH队列的使用:
CLH扫盲
自旋锁
学习了解自旋锁之前先回顾一下互斥锁
互斥锁
线程在获取互斥锁的时候,如果发现锁已经被其它线程占有,那么线程就会惊醒休眠,然后在适当的时机(比如唤醒)在获取锁。
自旋锁
那么自旋锁顾名思义就是“自旋”。就是当一个线程在尝试获取锁失败之后,线程不会休眠或者挂起,而是一直在循环检测锁是否被其它线程释放。
区别
互斥锁就是开始开销要大于自旋锁。临界区持锁时间的大小并不会对互斥锁的开销造成影响,而自旋锁是死循环检测,加锁全程消耗cpu,起始开销虽然低于互斥锁,但是随着持锁时间,加锁的开销是线性增长。
适用的情况
互斥锁用于临界区持锁时间比较长的操作,比如下面这些情况都可以考虑临界区有IO操作
临界区代码复杂或者循环量大
临界区竞争非常激烈
单核处理器
自旋锁就主要用在临界区持锁时间非常短且CPU资源不紧张的情况下。当递归调用时有可能造成死锁。
线程(节点)队列
了解了自旋锁之后,在学习ReentrantLock的时候,一个线程在等待锁的时候会被封装成一个Node节点,然后加入一个队列中并检测前一个节点是否是头节点,并且尝试获取锁,如果获取锁成功就返回,否则就阻塞。直到上一个节点释放锁并唤醒它。这样看来似乎跟自旋没什么挂钩。这是因为AQS里面的CLH队列是CLH队列锁的一种变形。先来了解一下CLH队列锁
CLH队列锁
CLH(Craig, Landin, and Hagersten locks): 是一个自旋锁,能确保无饥饿性,提供先来先服务的公平性。
CLH锁也是一种基于链表的可扩展、高性能、公平的自旋锁,申请线程只在本地变量上自旋,它不断轮询前驱的状态,如果发现前驱释放了锁就结束自旋。http://www.2cto.com/kf/201412/363574.html这篇文章中有比较详细的图解。
AQS中的CLH队列
了解了自旋锁与CLH队列锁之后,在学习AQS中的CLH队列就比较简单了。AQS中的CLH队列主要是对CLH队列锁改动了两个地方
1.节点结构上做出改变。CLH队列锁的节点包含一个布尔类型locked的字段。如果要获取锁,就将这个locked设置为true。然后就不停的轮训前驱节点的locked是否释放了锁(这个过程我们就叫做自旋)。AQS的CLH队列在结构上引入了头节点,尾节点。并且拥有一个前节点与下一个节点的引用。
2.在等待获取锁的机制上由自旋改成了等待阻塞。
MCS
MSC与CLH最大的不同并不是链表是显示还是隐式,而是线程自旋的规则不同:CLH是在前趋结点的locked域上自旋等待,而MSC是在自己的
结点的locked域上自旋等待。正因为如此,它解决了CLH在NUMA系统架构中获取locked域状态内存过远的问题。
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
/*
* 提供了一个基于FIFO队列,可以用于构建锁或者其他相关同步装置的基础框架
* 双向链表
*/
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
/**
* 无参构造方法
*/
protected AbstractQueuedSynchronizer() { }
/**
* <pre>
* +------+ prev +-----+ +-----+
* head | | <---- | | <---- | | tail
* +------+ +-----+ +-----+
* </pre>
*/
static final class Node {
/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode 模式,分为共享与独占 共享模式 */
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode 独占模式 */
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled
* 结点状态 节点watiStatus的值
* CANCELLED,值为1,终态,该节点被取消由于超时或中断
* SIGNAL,值为-1,表示当前节点的后继节点包含的线程需要运行,也就是unpark,所以当前节点release或cancels时,必须unpark它的后继节点
* CONDITION,值为-2,表示当前节点在等待condition,也就是在condition队列中 该节点处于条件队列中,将不会被用于sync queue,直到节点状态被设置为0
* PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示当前场景下后续的acquireShared能够得以执行releaseShared应该被传播到其他节点
* 值为0,表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待着获取锁
* */
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */
static final int CONDITION = -2;
/**
* waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should
* unconditionally propagate
*/
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
/**
* Status field, taking on only the values:
* SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be)
* blocked (via park), so the current node must
* unpark its successor when it releases or
* cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must
* first indicate they need a signal,
* then retry the atomic acquire, and then,
* on failure, block.
* CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt.
* Nodes never leave this state. In particular,
* a thread with cancelled node never again blocks.
* CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue.
* It will not be used as a sync queue node
* until transferred, at which time the status
* will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has
* nothing to do with the other uses of the
* field, but simplifies mechanics.)
* PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated to other
* nodes. This is set (for head node only) in
* doReleaseShared to ensure propagation
* continues, even if other operations have
* since intervened.
* 0: None of the above
* 结点状态
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
/**
* 前驱结点
*/
volatile Node prev;
/**
* 后继结点
*/
volatile Node next;
/**
* 结点所对应的线程
*/
volatile Thread thread;
/**
* 下一个等待者
*/
Node nextWaiter;
/**
* 结点是否在共享模式下等待
*/
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
/**
* 获取前驱结点,若前驱结点为空,抛出异常
*/
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
// 保存前驱结点
Node p = prev;
if (p == null) // 前驱结点为空,抛出异常
throw new NullPointerException();
else // 前驱结点不为空,返回
return p;
}
// 无参构造函数
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
// 构造函数
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
// 构造函数
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
/**
* CLH队列中头结点
*/
private transient volatile Node head;
/**
* CLH队列中尾结点
*/
private transient volatile Node tail;
/**
* 同步状态
* 多线程同步获取资源成功,则state字段会自增;若有线程释放资源,则state字段自减。
* 信号量 记录该线程持有锁的次数。 该线程每次释放所 信号量 -1。 信号量为零 代表 锁被真正释放
*/
private volatile int state;
/**
* @return current state value
*/
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
/**
* @param newState the new state value
*/
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
/**
* 使用unsafe的cas比较并且交换,保证原子性
*/
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer继承和实现分析
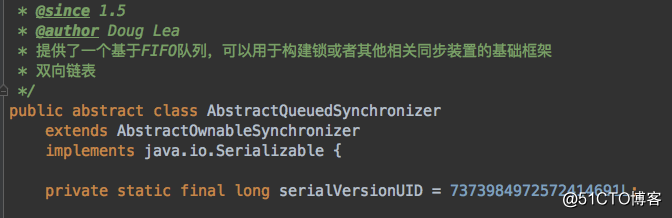
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
1. AbstractOwnableSynchronizer是一个抽象类,实现了Serializable接口,定义了独占模式,设置和获取独占模式下的线程Thread信息。
2.ArrayList实现了List<E>、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable接口
1)List<E>接口,ArrayList既然继承自AbstractList抽象类,而AbstractList已 经实现了List接口,那么ArrayList类为何还要再实现List接口呢?我们带着疑问往下看:
public class Demo1 extends ArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//返回[]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Demo1.class.getInterfaces()));
}
public class Demo2 implements Serializable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//返回[interface java.io.Serializable]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Demo2.class.getInterfaces()));
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Serializable c1 = new Demo1();//未显示实现接口
Serializable c2 = new Demo2();//显示实现接口
Serializable proxy2 = createProxy(c2);
proxy2.foo();
Serializable proxy1 = createProxy(c1);
proxy1.foo();
}
private static <T> T createProxy(final T obj) {
final InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
return method.invoke(obj, args);
}
};
//实现接口代理,Demo1报错,Demo2成功
//java.lang.ClassCastException: $Proxy1 cannot be cast to
//example.Test$Serializable
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj
.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler);
}可以看出这样这样设计是有道理的,因此,这并不是一个错误,很可能是作者Josh Bloch为了便于实现代理而精心设计的。
参考与:开发collection 的作者Josh说
2)RandomAccess接口,这是一个标记接口,一般此标记接口用于 List 实现,以表明它们支持快速(通常是恒定时间)的随机访问,该接口的主要目的是允许通用算法改变其行为,以便在应用于随机或顺序访问列表时提供良好的性能,实现了该接口的话使用普通的for循环来遍历,性能更高,而没有实现该接口的话,使用Iterator来迭代,这样性能更高,例如linkedList。所以这个标记性只是为了让我们知道我们用什么样的方式去获取数据性能更好
3)Cloneable接口,可以使用Object.Clone()方法。
4)Serializable接口,序列化接口,表明该类可以被序列化,什么是序列化?简单的说,就是能够从类变成字节流传输,反序列化,就是从字节流变成原来的类
ArrayList核心方法分析
1. add方法(4种重载实现)--增

1)add(E);//默认直接在末尾添加元素
/**
* 新增元素
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//赋值初始长度 或者扩容,新增元素,当前实际size+1的长度
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//添加元素
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 确保elemenData数组有合适的大小
* 如果元素为空,则复制长度默认为10 或者更大
* @author jiaxiaoxian
* @date 2019年2月12日
*/
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {//如果数组为空,则从size+1的值和默认值10中取最大的
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
/**
* 确保elemenData数组有合适的大小
* @author jiaxiaoxian
* @date 2019年2月12日
* 如果长度大于元素长度则扩容
*/
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//记录修改次数,迭代中不一致会触发fail-fast机制,因此在遍历中删除元素的正确做法应该是使用Iterator.remove()
modCount++;
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity); //扩容
}
/**
* 扩容
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 旧容量
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 新容量为旧容量的1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 新容量小于参数指定容量,修改新容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 新容量大于最大容量
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 指定新容量
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 拷贝扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
//如果小于0 就报错,如果大于最大值 则取最大值
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}2)add(int index, E element);//给指定下标,添加元素
/**
* 给指定下标,添加元素
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//判断下标是否越界
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//赋值初始长度 或者扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将源数组中从index位置开始后的size-index个元素统一后移一位
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
//赋值
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* 判断下标是否越界
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* src:源数组
* srcPos:源数组要复制的起始位置
* dest:目的数组
* destPos:目的数组放置的起始位置
* length:复制的长度
* 注意:src 和 dest都必须是同类型或者可以进行转换类型的数组
*/
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);3)addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);//添加Collection类型元素
/**
* 按照指定collection的迭代器所返回的元素顺序,将该collection中的所有元素添加到此列表的尾部
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
//将数组a[0,...,numNew-1]复制到数组elementData[size,...,size+numNew-1]
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}4)addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);//指定位置,添加Collection类型元素
/**
* 从指定的位置开始,将指定collection中的所有元素插入到此列表中,新元素的顺序为指定collection的迭代器所返回的元素顺序
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
//判断下标是否越界
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
//先将数组elementData[index,...,index+numMoved-1]复制到elementData[index+numMoved,...,index+2*numMoved-1]
//即,将源数组中从index位置开始的后numMoved个元素统一后移numNew位
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}总结:
正常情况下会扩容1.5倍,特殊情况下(新扩展数组大小已经达到了最大值)则只取最大值。
2.remove方法(4种重载实现)--删

1)remove(int index); //根据指定下标 删除元素
/**
* 根据指定下标 删除元素
*/
public E remove(int index) {
//判断索引是否越界
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
//获取旧元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//将数组elementData中index位置之后的所有元素向前移一位
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//将原数组最后一个位置置为null,由GC清理
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
} 2)remove(Object o); //根据指定元素 删除元素
/**
* 移除ArrayList中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在),ArrayList中允许存放重复的元素
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 由于ArrayList中允许存放null,因此下面通过两种情况来分别处理。
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
//私有的移除方法,跳过index参数的边界检查以及不返回任何值
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* 根据下标快速删除元素
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
//将数组elementData中index位置之后的所有元素向前移一位
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
/**
* 清空ArrayList,将全部的元素设为null,等待垃圾回收将这个给回收掉,所以叫clear
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
3)removeAll(Collection<?> c); //删除包含在指定容器c中的所有元素
/**
* 删除ArrayList中包含在指定容器c中的所有元素
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
//检查指定的对象c是否为空
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
/**
* 删除全部
* @author jiaxiaoxian
* @date 2019年2月12日
*/
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0; //读写双指针
boolean modified = false;
try {
for (; r < size; r++)
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) //判断指定容器c中是否含有elementData[r]元素
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r);
w += size - r;
}
if (w != size) {
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}4)removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter); //按照一定规则过滤(删除)集合中的元素
/**
* 按照一定规则过滤(删除)集合中的元素
* 如:idList.removeIf(id -> id == nul);
* 去掉 List idList 集合中id 为 null 的
* @param filter
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
// figure out which elements are to be removed
// any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage
// will leave the collection unmodified
int removeCount = 0;
final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E element = (E) elementData[i];
if (filter.test(element)) {
removeSet.set(i);
removeCount++;
}
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements
final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
if (anyToRemove) {
final int newSize = size - removeCount;
for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
elementData[j] = elementData[i];
}
for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
this.size = newSize;
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
return anyToRemove;
}总结:
remove函数用户移除指定下标的元素,此时会把指定下标到数组末尾的元素向前移动一个单位,并且会把数组最后一个元素设置为null,这样是为了方便之后将整个数组不被使用时,会被GC,可以作为小的技巧使用。
3.set方法--改
/**
* 覆盖指定下标元素
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
//判断索引是否越界
rangeCheck(index);
//获取旧元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//覆盖为新元素
elementData[index] = element;
//返回旧元素
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 判断下标是否越界
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}4.get方法--查
/**
* 返回指定索引的值
*/
public E get(int index) {
//判断索引是否越界
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* @author jiaxiaoxian
* @date 2019年2月12日
* 返回下标元素的 值
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}5.indexOf方法--查找下标
/**
* 查找下标, 如果为null,直接和null比较,返回下标
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 查找最后出现的下标,从大往下循环查找
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}6.clone方法--克隆
/**
* 复制,返回此ArrayList 的浅拷贝
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}7.trimToSize方法--删除冗余容量
/**
* 判断数据实际容量大小,删除自动增长后冗余的容量
* 该方法用于回收多余的内存。也就是说一旦我们确定集合不在添加多余的元素之后,调用 trimToSize() 方法会将实现集合的数组大小刚好调整为集合元素的大小。
* 注意:该方法会花时间来复制数组元素,所以应该在确定不会添加元素之后在调用
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}8.Itr内部类--类似Iterator,可以帮我们对List进行遍历,增删改查等
/**
* 实例化一个Itr对象,并返回
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* 内部类,类似Iterator,可以帮我们对List进行遍历,增删改查等
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return 下一个元素
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such 当前元素
int expectedModCount = modCount; //modCount,就是为了判断是否有多个线程访问修改
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} 9.ListItr内部类--继承了内部类Itr,还在此基础上增加了向前遍历,增加元素,更改元素内容等功能
/**
* 这个类继承了内部类Itr
* 除了拥有上一个类的功能,还增加了向前遍历,增加元素,更改元素内容等功能
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} 10.SubList内部类--基于ArrayList建一个子集类
/**
* 虽然这个类很长,其实里面的大部分方法调用都是ArrayList中的
* ListIterator在这个类中采用匿名内部类做了一点更改,不过也很类似
* 毕竟这个类就是根据ArrayList建一个子集类,就不赘述了
*/
private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
private final AbstractList<E> parent;
private final int parentOffset;
private final int offset;
int size;
SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.parent = parent;
this.parentOffset = fromIndex;
this.offset = offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E e) {
// 检验索引是否合法
rangeCheck(index);
//实现fail-fast机制 (迭代中不允许操作增删改)
checkForComodification();
// 旧值
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
// 赋新值
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
// 检验索引是否合法
rangeCheck(index);
//实现fail-fast机制 (迭代中不允许操作增删改)
checkForComodification();
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return this.size;
}
public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size++;
}
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size--;
return result;
}
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex,
parentOffset + toIndex);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size += cSize;
return true;
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
final int offset = this.offset;
return new ListIterator<E>() {
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
lastRet = cursor = i;
checkForComodification();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
/**
* 实现fail-fast机制
* 线程不安全 迭代中不允许修改
* @author jiaxiaoxian
* @date 2019年2月12日
*/
private void checkForComodification() {
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
return new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(ArrayList.this, offset,
offset + this.size, this.modCount);
}
}11.ArrayListSpliterator内部类--并行迭代,基于索引的二分裂,懒惰初始化的Spliterator
/**
* @since 1.8
* 实例化一个ArrayListSpliterator对象,并返回
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new ArrayListSpliterator<>(this, 0, -1, 0);
}
/**
* Index-based split-by-two, lazily initialized Spliterator
* 并行迭代
* 基于索引的二分裂,懒惰初始化的Spliterator
* */
static final class ArrayListSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
private final ArrayList<E> list;
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Create new spliterator covering the given range */
ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList<E> list, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list; // OK if null unless traversed
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
ArrayList<E> lst;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
hi = fence = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
hi = fence = lst.size;
}
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayListSpliterator<E> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(list, lo, index = mid,
expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)list.elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList<E> lst; Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = lst.modCount;
hi = lst.size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return (long) (getFence() - index);
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}ArrayList总结
1)arrayList可以存放null,本质是Object[]类型的数组。
2)arrayList区别于数组的地方在于能够自动扩展大小,其中关键的方法就是gorw()方法。
3)arrayList由于本质是数组,所以它在数据的查询方面会很快,而在插入删除这些方面,性能下降很多,有移动很多数据才能达到应有的效果,而LinkedList则相反。
4)arrayList实现了RandomAccess,所以在遍历它的时候推荐使用for循环。
5)初始化数组时推荐给初始长度,反复扩容会增加时耗,影响性能效率。