spring boot是一个简化spring开发的框架,核心在于约定大于配置,去除繁琐的配置。简单的说就是spring boot整合了很多优秀的框架,不用我们去手写一大推的xml文件,它在后台帮我做了这些配置
下面演示如何在IntellJ上面进行spring boot开发
1.new Module
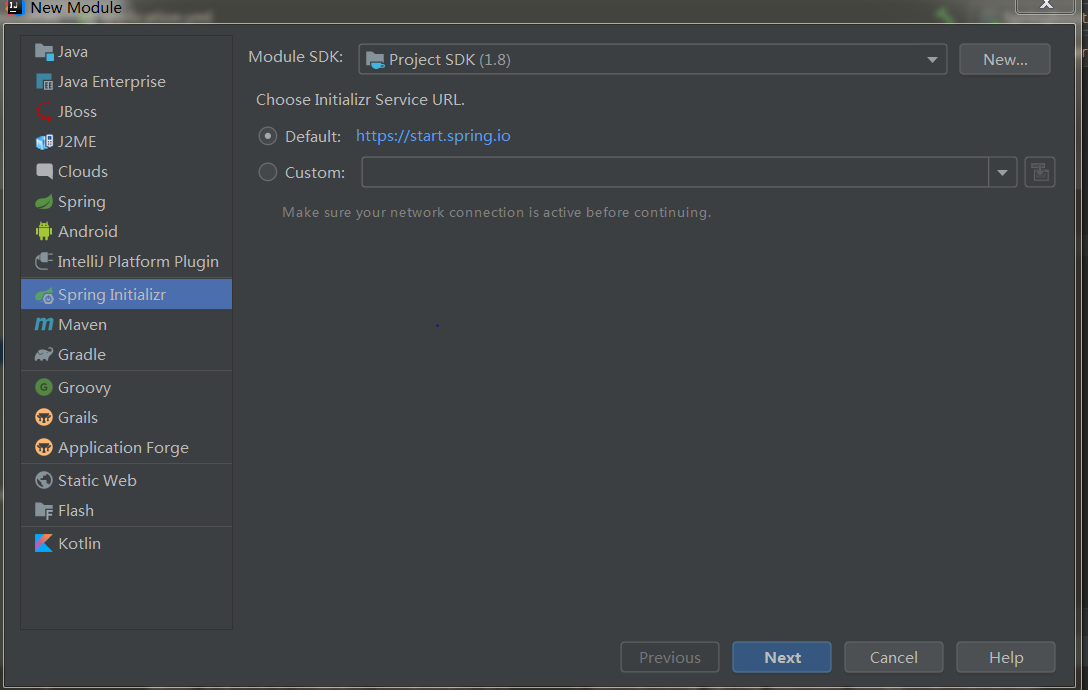
2.配置mvn信息

3.添加应用,这里我们选择web应用
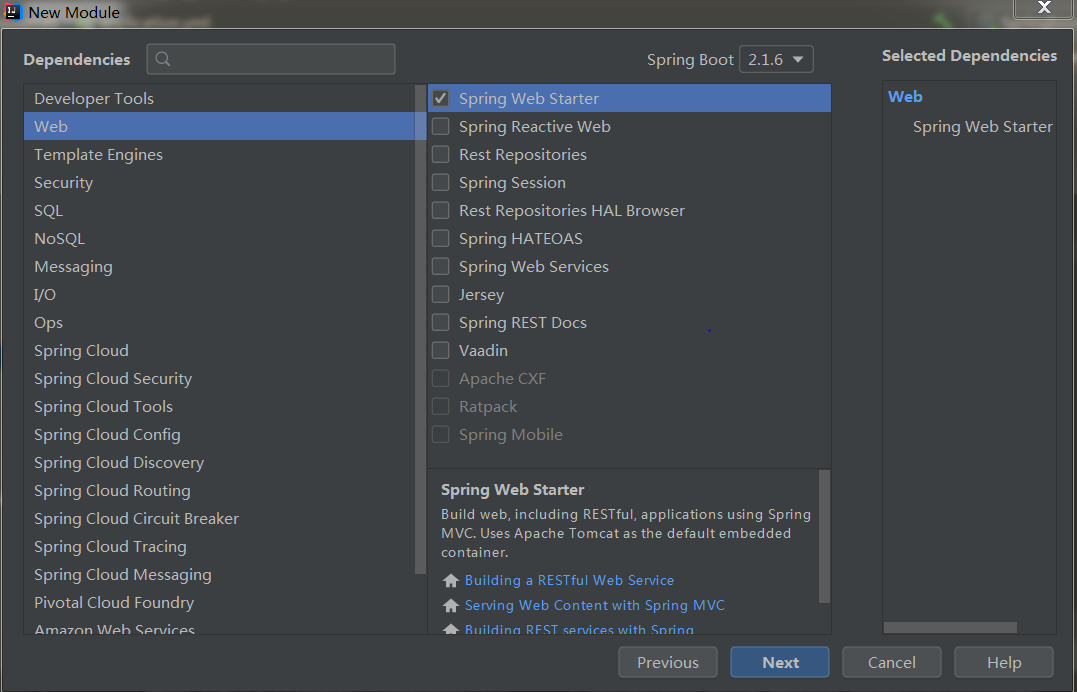
这些操作完成之后,ide会帮我们构建一个基于mvn的spring boot project,查看下pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>springboot</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>springboot</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
1.spring-boot-starter-parent 是一个特殊的starter,它用来提供相关的Maven默认依赖。使用它之后,常用的包依赖可以省去version标签。
2.spring-boot-starter-web 提供mvc功能
package com.example.springboot; import com.examples.model.Animal; import com.examples.model.Dog; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @SpringBootApplication @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.examples") @RequestMapping("springboot") @RestController public class SpringbootApplication { @Autowired private Dog dog; @Autowired private Animal animal; @RequestMapping("/Hello") public String Hello(){ return dog.toString()+"\r\n"+animal.toString(); } @Bean("animal") public Animal getAnimal(){ return new Animal(); } public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args); Dog dog = (Dog)context.getBean("dog"); Animal animal = (Animal)context.getBean("animal"); System.out.println(dog); System.out.println(animal); } } package com.examples.model; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA. * User: chenzhubing * Date: 2019/7/19 */ public class Animal { @Value("${animal.gender}") public Boolean gender; @Override public String toString() { return "Animal{" + "gender=" + gender + '}'; } } package com.examples.model; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA. * User: chenzhubing * Date: 2019/7/19 */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="dog") public class Dog { private String name; public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } private Integer age; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } } //application.yml server: port: 8088 dog: name: 哈士奇 age: 12 animal: gender: false 或者application.properties server.port=8088 dog.name = "wangcai" dog.age = 10 #dog.map.m1 = "hello" #dog.map.m2 = "world"
说明:
@SpringBootApplication = @SpringBootConfiguration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan
@SpringBootConfiguration: extends @Configuration 表明当前类是个spring的配置类,可以在这里面注入bean等。
@ComponentScan: 扫描包下面的@Controller,@Service,@Respority,@Componet等;默认情况下是扫描当前类所在路径,以及所在子路径。
@EnableAutoConfiguration: 启动自动的配置,比如你添加了spring-boot-starter-web,spring boot会自动帮你配置webmvc,tomcat等需要的配置。
@ConfigurationProperties配合 @Component 可以获取配置文件里面的信息,实现属性注入