重不重写hashcode和equals对于HashSet添加元素的影响就是可否添加重复元素
实验一:不重写hashcode的equals
import java.util.HashSet; public class DemoHashSet { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<>(); Student s1 = new Student("张明",12); Student s2 = new Student("张杰",14); Student s3 = new Student("张杰",14); students.add(s1); students.add(s2); students.add(s3); for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student.getName()+student.getAge()+"岁"); } } } import java.util.Objects; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } /* @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (!(o instanceof Student)) return false; Student student = (Student) o; return getAge() == student.getAge() && Objects.equals(getName(), student.getName()); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(getName(), getAge()); } */ }
结果:
张杰14岁
张明12岁
张杰14岁
Process finished with exit code 0
实验二:重写hashcode和equals
import java.util.HashSet; public class DemoHashSet { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<>(); Student s1 = new Student("张明",12); Student s2 = new Student("张杰",14); Student s3 = new Student("张杰",14); students.add(s1); students.add(s2); students.add(s3); for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student.getName()+student.getAge()+"岁"); } } } import java.util.Objects; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (!(o instanceof Student)) return false; Student student = (Student) o; return getAge() == student.getAge() && Objects.equals(getName(), student.getName()); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(getName(), getAge()); } }
结果:
张明12岁
张杰14岁
没有出现重复元素。
三。原因分析:
HashMap底层
add-》put-》hashmap
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
之前的总结
重写前:2号是==比较地址值不同false,不重写equals比较地址值3号false,结果false,向下执行,添加元素。
重写了hashcode,比较hash值,地址值肯定不同2号false,equal比较的是成员信息3号为true,结果true,执行括号中的,不添加。

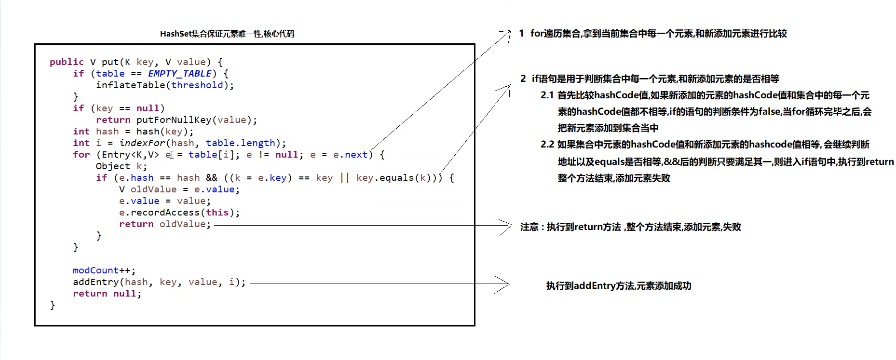
hashmap也是同理
1 import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.HashSet; 3 4 public class DemoHashMap { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 HashMap<String,Integer> students = new HashMap<>(); 7 Student s1 = new Student("张明",12); 8 Student s2 = new Student("张杰",14); 9 Student s3 = new Student("张杰",14); 10 students.put("张明",12); 11 students.put("王明",12); 12 students.put("张明",12); 13 String s = students.toString(); 14 15 System.out.println(s);} 16 }
结果:
{张明=12, 王明=12}