版权声明:转载必须保留原出处,没有书面许可不可用于商用目的, https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43401808/article/details/90695728
本文是英语学习笔记,所有版权归原教材作者所有。

加州三年级《科学》课本,主要分为5个大Section,每个Section由两到三个Chapter构成,每个Chapter含有若干Lesson。
-
Be a Scientist
- What is Science?
-
Life Science
- Chapter 1: Adaptations in Land Environments
- Lesson 1: Living Things and Their Needs
- Lesson 2: Life in the Desert
- Lesson 3: Life in the Granssland
- Lesson 4: Life in the Forest
- Lesson 5: Life in the Arctic Tundra
- Chapter 2: Adaptations in Water Environments
- Lesson 1: The Water Planet
- Lesson 2: Life in an Ocean
- Lesson 3: Life in the Wetlands
- Chapter 3: Environment Change
- Lesson 1: Living Things Change Their Environment
- Lesson 2: Changes Affect Living Things
- Lesson 3: Living Things of the Past
- Chapter 1: Adaptations in Land Environments
-
Earth Science
- Chapter 4: Our Earth, Sun, and Moon
- Lesson 1: Day and Night
- Lesson 2: The Seasons
- Lesson 3: The Moon
- Chpater 5: Our Solar System
- Lesson 1: The Sun and Its Planets
- Lesson 2: Telescopes: Discovering the Solar System
- Lesson 3: The Stars
- Chapter 4: Our Earth, Sun, and Moon
-
Physical Science
- Chapter 6: Matter
- Lesson 1: Solids, Liquids, and Gases
- Lesson 2: Building Blocks of Matter
- Lesson 3: Changing Matter
- Chapter 7: Energy
- Lesson 1: Energy All Around
- Lesson 2: Using Energy
- Lesson 3: Energy on the Move
- Chapter 8: Light
- Lesson 1: How Light Moves
- Lesson 2: Seeing Light and Color
- Lesson 3: Shadows
- Chapter 6: Matter
-
Activities
- Life Science
- Earth Science
- Physical Science
看看下面这个术语表,谁再说美国小学课程简单,都是玩到大的,真是自欺欺人。
Glossary
- absorb: To take in.
Some materials absorb more lights than others. - adaptation: A special trait that helps a living thing survive in its environment.
A fish's gills are an example of adaptation. - air bladder: a balloonlike structure in plants and animals for holding gases.
Kelp has air bladders that help it float. - algae: Tiny one-celled organisms that use water, air, and sunlight to make food.
Algae are plantlike living things often found in shallow water. - amphibian: An animal that spends part of its life in water and part on land.
Frogs and salamanders are amphibians. - analyze data: To use information that has been gathered to answer a question or solve a problem.
You can analyaze data to find how daylight hours change throughout the year. - arctic tundra: A cold biome above the Arctic Circle.
Winters on the arctic tundra are long and dark.
(pictures from Google)


- asteroid: A large piece of rock or metal in space.
Many asteroid orbit the Sun. - astronaut: A person who travels into space.
Astronauts traveled to the Moon to study it up close. - astrophysicist: Someone who studies how objects in the universe interact.
An astrophysicist can explain how the planets move around the Sun. - atom: The smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element.
Atoms are too small to see on your own. - axis: A real or imaginary line through the center of a spinning object.
The geographic north and south poles are the ends of Earth's axis. - binary starts: Two stars that act as a pair.
If one of the binary stars weakens, the other one might absorb it. - biomass: Plant materials and animal waste.
Biomass can be used as fuel to create energy. - biome: An area of land or water that has certain kinds of living and nonliving things.
A desert biome is very different from an ocean biome. - blubber: A thick layer of fat found in large mammals.
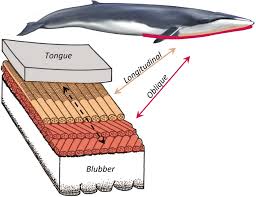
Whale blubber allows the animal to stay warm in cold waters. - bog: A freshwater wetland filled with moss and rich soil.

The ground in bogs is sually wet and spongelike. - brackish environment: The living thing and nonlivining things that exist in a place with a mixture of fresh and salt water.

Many marine animals lay their eggs in a brackish environment. - buttress: Something that supports or strengthens.
Some trees have special root structures called buttresses that spread out from the trunk and support the tree. - calorie: A measure of the energy stored in a substance, such as food.
Rich foods, such as ice cream and fried dough, have many more calories than others. - camouflage: An adaptation that allows an animal to blend into its surroundings.
Camouflages might help an inset look like a leaf. - canopy: The part of a forest just below the uppermost branches of the tallest trees.

Most rain-forest animals live in the canopy because of the sunlight and food found there. - carbon: One of the basic elements.
All living matter on Earth contains carbon. - chemical change: A change that causes a new kind of matter to form with different properties.
When food burns, the chemical change makes it taste different. - chemical energy: Energy that is stored in a substance.
Your body uses chemical energy stored in sugar and other foods. - classify: To place similar materials together in a group.
The periodic table classifies elements that share the same properties. - climate: The average weather patterns of a region.
Most people prefer a warm climate. - comet: A chunk of ice mixed with rocks and dust moving through space.
A comet may have a glowing tail. - communicate: To share information.
Writing helps you to communicate your ideas to others. - community: All the different populations in an ecosystem.
A rural community may include people, cows, and grasses. - compare: To see what is the same and what is different between two or more things.
You can begin to classify thngs after you compare them. - competition: The struggle among living things.
There is a great competition for water in desert. - compression wave: A wave that moves in a back and forth motion.

Sound waves are examples of compression waves. - condense: What happens when matter changes state from gas to liquid.
When water vapor in the air condenses, it can form dewdrops. - coniferous: A kind of temerate forest that stays green all year.
Pines, firs, and spruces grow in coniferous forests.


- constellation: A group of stars that forms a pattern or picture.
The Big Dipper is a major constellation. - coral: Colorful rocklike formations created by certain marine animals.

Coral reefs are some of the most beautiful parts of the ocean. - cornea: The clear, outer covering of the eye.

A contact lens rests on the cornea and assists with vision. - crescent moon: The phase of the moon in which the lighted side has almost disappeared.
A crescent moon is either just begging to wax or almost done waning. <- Waxing
<- Waxing  <- Waning
<- Waning - deciduous: A kind of forest biome with many trees that lose their leaves each winter.
Maples, birches, and oaks can be found in deciduous forests.


- depth: The distance away from the surface.
Water temperature in the ocean grows colder with depth. - desert: A hot, dry place with very little rain.

The Mojave (=Mohave) Desert is a hot desert. 莫哈韦沙漠(美国加利福尼亚西南) - dew: Water vapor that has condensed into liquid on a cool object.


Small drops of dew often appear overnight as the moist air cools. - dinosaur: An extinct kind of large reptile.
The word dinosaur comes from Greek words meaning "fearfully great lizard." - draw conclusions: To arrive at possible answers based on information you have gathered.
After you analyze the data from an experiment, you can draw conclusions about what you observed. - ecosystem: All the living and nonliving things that interact in an environment.
The desert and the forest are different ecosystems. - electrical energy: Energy produced by the movement of small particles called electrons.
A light bulb uses eletrical energy to create light. - electron microscope: A tool that allows you to see very small objects.
Atoms can only be seen using an electron microscope. - element: A basic building block of matter.
Oxygen, carbon, and iron are all elements. - emergent layer: The highest level in a forest biome.

The tops of the tallest trees from the emergent layer of the rain forest. - energy: The ability to do work.
Matter needs energy to move, grow, or change its state. - environment: All the living and nonliving things that surround a living thing.
Plants need an environment in which they can get sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and other nutrients. - equator: The imaginary line that divides Earth into the north and south hemisphere.
Sunlight strikes Earth most directly at the equator. - evaporate: What happens when matter slowly changes state from liquid to gas.
Water can evaporate into a gas in direct sunlight. - expand: To spread out.
Pumping air into a balloon causes the material to expand. - experiment: A test designed to support or disprove a hypothesis.
Most experiments are designed and carried out very carefully. - extinct: All dead, no more left alive on Earth.
The mammoths became extinct after a change in climate (that) killed them all.
Note: there is no 'that' in the original text. I personally think it is a wrong grammar without relative pronoun 'that.' - force: A push or pull.
You use force when you make an object move. - forest: A biome that has many trees.
Different types of forests exist in different parts of the word. - forest floor: The ground level of a forest biome.


Very litle sunlight reaches the forest floor. - fossil: The hardened remains of a living thing.
Most fossils are buried deep in the ground. - fossile fuel: A source of energy that comes from the breakdown of animal and plant remains.
Gasline is a fossil fuel. - freeze: what happens when matter changes state from liquid to solid.
When water freezes, it becomes ice. - freshwater environment: The living and nonliving that exist in a place where the water is not salty.
Most ponds and most reviers are freshwater environments. - friction: The force created when surfaces rub against each other.
Friction from rubbing your hands makes them warm. - fuel: A source of stored energy.
Cars use fuel called gasoline to make their engines run. - galaxy: A very large group of starts.
Our galaxy is called the milky way. - gamma waves: An invisible form of light with high energy.
Gamma waves are used in nuclear power plants. - gas: Matter in a state that has no definite shape or volume.
The air we breathe is made up of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. - geothermal: Using heat from inside the Earth.
Steam from a hot spring that turns a turbine is an example of geothermal engery. - gibbous: More than half but not yet full.
A gibbous moon can be waxing toward full or waning toward half.

- gills: Body parts in fish and other animals that allows them to breathe in water.
Gills collect oxygen from the water. - grassland: A biome that is covered with grass.
Grasslands provide a great deal of food for many animals. - habitat: The place where a living thing makes its home.
Whales live in an ocean habitat. - heat energy: Energy that causes the temperature of something to rise.
The Sun is the main source of heat energy on Earth. - hibernate: To sleep through the winter.
Bears hibernate in caves from late fall until spring. - horizon: The distance line where the land seems to meet the sky.
The Sun rises over the eastern horizon. - humus: Leftover decomposed plant or animal material in soil.

Each layer of soil has different amounts of rock and humus. - hydropower: Using water to create energy.
Many dams turn a river's current into hydropower. - hypothesis: A suggested statement or explanation that can be tested to answer a question.
An experiment can help you to test a hypothesis. - image: A picture produced by the reflection of light.
A mirror shows you an image of yourself. - infur: To come up with an idea based on facts or observations.
The data from an experiment can help you infer what happened. - infrared waves: A form of light energy that we feel as heat.
Devices that detect infrared waves can be used to "see" in the drak. - inner planets: The four planets closes to the Sun.

Mercury, Venue, Earth, and Mars are the inner planets. - iris: in the eye, the colored circle around the pupil.
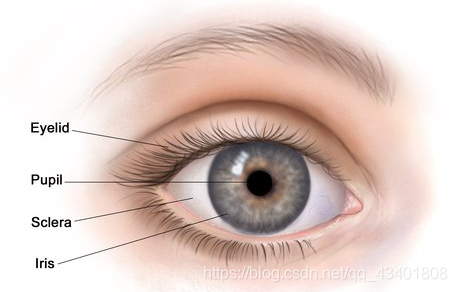
The iris changes the size of the pupil in different light conditions. - kelp: A type of algae that groups together.

Kelp has large, brown leaflike structures. - kinetic energy: Energy in the form of movement or motion.
A falling leaf has kinetic energy. - laser: A tool that uses a very thin beam of light.
Doctors can use lasers to perform surgery. - lens: A piece of clear material that affects the path of light rays.
The lens in your eye focuses incoming light.
- light: A form of energy made up of transverse waves.
Color is light energy we can see. - liquid: Matter in a state that has a definite volume but not a definite shape.
Water in its liquid state takes the shape of its container. - lunar cycle: The full sequence of the Moon's phases.

The lunar cycle takes about four weeks. - lunar eclipse: A period of time when the Moon moves into Earth's shadow.
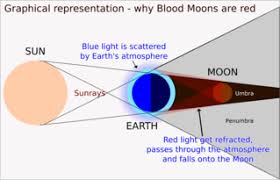

The Moon may appear to be dark red during a total lunar eclipse. - mangrove: A kind of tropical tree often found in swamps.

Mangrove roots provide shelter for fish and shrimp. - marine environment: Another name for a saltwater environment.
Whales and dolphins live in a marine evnironment. - marsh: A type of wetland featuring soft plants such as grasses. There are no trees in marshes.

- mass: A measure of the amount of matter in an object.
Mass is often measured in grams. - matter: Anything that takes up space.
The Earth is made up of all kinds of matter. - measure: To find the size, volume, area, mass, weight, or temperature of an object, or to find how long an event occurs.
When you measure something, you gather data or information about it. - mechanical energy: The energy in moving objects.
The rushing water in a river has mechanical energy. - melt: What happens when matter changes state from solid to liquid.
When ice melts, it becomes liquid water. - meteor: A small piece of ice, rock, or metal that has broken off a comet or asteroid.

Most shootig stars are also meteors. - meteorite: A meteor that hits the Earth.
Some meteorites create huge holes where they hit the ground. - microscope: A tool that allows us to make small objects seem larger.

You can see some plant cells using a microscope. - microwave: A form of light energy.
The energy in microwaves can be used to cook food. - migrate: To move from one place to another.
Some birds migrate to new homes each fall and spring. - mimicry: When one thing imitates the traits of another.

Some insects use mimicry to look like other insects and fool predators. - mixture: Different kinds of matter blended together.
Soda is a mixture of sugar, water, and other ingredients. - model: Something that represents another object or event.

A spinning ball can serve as a model to show the rotation of a planet. - nocturnal: Active during the night.
Nocturnal animals usually sleep during the day and hunt for food at night. - observe: To use one or more of your senses to identify or learn about an object or event.
You conduct an experiment to observe what happens in a particular situtation. - ocean: A large body of salt water.

The Atlantic and the Pacific are both oceans. - opaque: Unable to let light pass through.
A piece of heavy construction paper is opaque. <--- construction paper
<--- construction paper - orbit: The path an object takes as it travels around another object.
Earth's orbit around the Sun takes about 365 days. - ornithologist: A scientist who studies birds.
An ornithologist will often record the flight paths of birds. - outer planets: The four planets farthest from the Sun.

Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are the outer planets. - oxygen: A common gas found in air and water that many animals need to survive.
When you breathe, you body is taking in oxygen. - periodic table: A chart that lists all of the known elements and their properties.
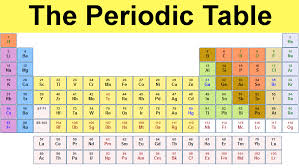
The periodic table helps us to group and classify elements. - permafrost: A layer of soil that is always forzen.

Most permafrost can be found in arctic and antarctic regions. - phase: A temporary state of being.
The Moon has many phases based on its appearance, including full, half, and gibbous. - physical change: A change in which matter looks different but is still the same matter.
Breaking an ice cube into pieces is a physical change because it is all still water. - planet: A large sphere in space that orbits a star.
Out planet moves around the Sun. - pollution: What happens when harmful materials get into the air, water, or land.
Litter is a kind of pollution.
- population: All the members of a single type of living thing in an ecosystem.
Population might go down if an area's resources are used up. - potential energy: Energy that is stored up inside of matter.
You release the potential energy in a lifted object when you drop it. - prairie: A temperate grassland.

Prairies have soil that is rich in humus. - predator: An animal that hunts another animal for food.
Sharks are the ocean's fiercest predators. - predict: To state likely results of an event or experiment.
You might be able to predict the weather by looking at clouds in the sky. - prey: An animal that is hunted by another animal for food.
Mice are prey to hawks. - prism: A special lens that can break light into many parts and colors.

Some telescopes use prisms to alter the light coming in. - property: A trait of something that can be observed or measurement.
The properties of matter include size, color, and state. - pupil: The central opening into the eye.
The pupil grows larger in dark condition to let in more light. - radio waves: An invisible form of light energy.
Radio waves are used to transmit signals for phones, radios, and televisions. - record data: To make note of an observation in a permanent way, as in writing.
When you record data on a chart, you organize your observations. - recycle: To turn an old thing into something new.
Paper can be recycled in many ways, including the creation of more paper. - reduce: To use less of something.
When you reduce the amount of napkins you use during a meal, you conserve paper-making resources.<--- napkin
- reflection: Light bouncing off an object.
Your reflection in a mirror is light bouncing back at you.
- renewable energy: Energy that can be replaced once it is used.
Wind power is a source of renewable energy. - reuse: To use something again.
When you refill a water bottle on a hiking trip, you are reusing the bottle. - revolve: To move around another object in a circular way.
The Earth revolves in a regular path around the Sun. - rotate: To turn.
Earth rotates from the west to the east. Each complete rotation takes 24 hours. - saltwater environment: The living and nonliving things that exist in a place where the water is salty. (cf. marine environment)
Oceans and seas are saltwater environments. - savanna: A tropical grassland. (cf. prairie)

Africa's Serengeti Plain is a savanna. - scientific method: The procedure for finding out how something works by controlled experiments.
You can test a hypothesis by using the scientific method. - sequioa: A kind of huge tree that grows in California.

Sequioas are sometimes called redwoods. - shadow: The darkened area that results when light energy is blocked.
If you face away from the Sun, your shadow will appear in front of you. - shelter: A place or object that protects an animal and keeps it safe.
During a rainstorm, you might seek shelter under a tree. - soil: A mixture of tiny rock particles, minerals, and decayed plant and animal matter.

Every biome has a certain kind of soil. - solar energy: Energy that comes from the Sun.
On Earth, we see solar energy as light and feel it as heat. - solar system: The Sun and the objects in orbit around it.
Our solar system is in the Milky Way galaxy. - solid: Matter in a state that has a definite shape and volume.
You can measure a solid using both meters and liters.

- sound energy: Waves of energy created when an object vibrates.
When you hit a drum hard, your ear responds to the sound energy. - sphere: A body that has the shape of a ball or globe.
Most planets are spheres. - star: A hot, glowing ball of gases in space.
The nearest star to the Earth is the Sun. - state: One of three categories of matter that has certain properties.
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. - structure: A thing that is developed or built for a particular use.
Fish have structures called gills to help them breathe in the ocean. - sundial: A device that shows time using the shadow cast by the Sun.

The shadows cast on a sundial are shorter around noon. - surgeon: A kind of doctor who works inside the body to treat problems.
Many eye surgeons today use lasers to fix vision problems. - swamp: A wetland with many trees or shrubs.
Cypress and willow trees grow well in swamps.<--- cypress
- telescope: A tool to make distant object appear closer and larger.
The Hubble telescope helps us to see planets and starts more clearly.
- temperate: Having few or no extremes.
A temperate environment has a mild climate and four seasons. - temperate forest: A forest biome with four distinct seasons.
Temperate forests are found in North America, Europe, and Asia. - tentacle: a long, thin, armlike structure.
Jellyfish use their tentacles to capture food.
- translucent: A material that absorbs some light energy but lets some through.
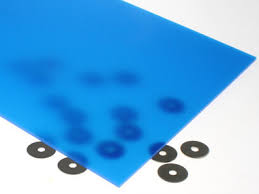
Colored glass is a translucent material. - transparent: A material that does not absorb or reflect much light energy.

A clear glass windows is transparent. - transverse waves: A wave that moves in an up and down motion.
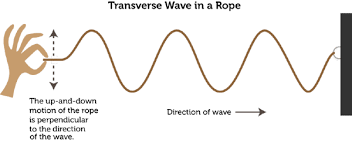
Light is made up of transverse waves. - tropical: Coming from a region near the equator with warm temperatures all year long.

Tropical fish live in a warm marine environment. - tropical rain forest: A hot, wet forest biome found near the equator.

There are more kind of living things in tropical rain forests than any other land biome. - turbine: A machine that turns and produces energy.
A simple turbine looks like an electric fan that moves when steam, water or air pushes against the blades. - ultraviolet waves: An invision form of light that can cause a reaction in the skin.
Tans and sunburns are caused by ultraviolet waves from the Sun. - understory: The area in a forest between the canopy and the ground.

Leopards, frogs, and many insects live in the understory of the rain forest. - variable: something that can be changed or controlled.
In a plant-growing experiment, the amounts of light and water you provide are variables. - vibrate: To move back and forth quickly.
A guitar string vibrates when you pull and release it. - visible light: The range of light energy that humans can see.
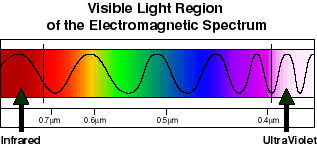
Visible light includes all of the colors you see. - volume: The amount of space that an object takes up.
Volume is often measured in liters or cubic meters. - waning: In the process of getting smaller.
A waning Moon may go from full to half. - water vapor: The gas state of water.
You cannot see water vapor in the air. - wave: A disturbance that moves through matter or space.
If you jostle water in a glass, you create small waves. - waxing: In the process of getting larger.
A waxing Moon may go from half to full. - wetland: Environments where water covers the soil for most of the year.
Bogs, swamps, and marshes are all wetland environments. - whitle drawf: A small, hot, white start.

A white drawf may be about the size of our Sun but has much more matter packed into it. - wind power: A renewable kind of energy that uses the power of the wind.
Windmills are actually turbines that can gather wind power and create electricity. - X-ray waves: An invisible form of light energy that can pass through objects.
X-ray waves are used to take pictures of bones inside the body.