版权声明:转载必须保留原出处,没有书面许可不可用于商用目的, https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43401808/article/details/90768491
本文是英语学习笔记,所有版权归原教材作者所有。

加州四年级《科学》课本,主要分为5个大Section,每个Section由两到三个Chapter构成,每个Chapter含有若干Lesson。
-
Be a Scientist
- What is Science?
-
Life Science
- Chapter 1: Living Things Need Energy
- Lesson 1: Plants and Sunlight
- Lesson 2: Food Chains
- Lesson 3: Food Webs
- Lesson 4: Microorganisms
- Chapter 2: Living Things and Their Environment
- Lesson 1: Ecosystem
- Lesson 2: Living Things Need Each Other
- Lesson 3: Changes in Ecosystems
- Lesson 4: Adaptations
- Chapter 1: Living Things Need Energy
-
Earth Science
- Chapter 3: Rocks and Minerals
- Lesson 1: Minerals: The Building Blocks of Rocks
- Lesson 2: Igneous Rocks
- Lesson 3: Sedimentary Rocks
- Lesson 4: Metamorphic Rocks
- Chapter 4: Slow Changes on Earth
- Lesson 1: Weathering
- Lesson 2: Erosion and Deposition
- Lesson 3: Landforms: Changing Over Time
- Chapter 5: Fast Changes on Earth
- Lesson 1: Landslides
- Lesson 2: Earthquakes
- Lesson 3: Volcanoes
- Chapter 3: Rocks and Minerals
-
Physical Science
- Chapter 6: Electricity
- Lesson 1: Static Electricity
- Lesson 2: Electric Circuits
- Lesson 3: Using Electrical Energy
- Chapter 7: Magnetism
- Lesson 1: Magnets
- Lesson 2: Electromagnets
- Lesson 3: Motors and Generators
- Chapter 6: Electricity
-
Activities
- Life Science
- Earth Science
- Physical Science
看看下面这个术语表,谁再说美国小学课程简单,都是玩到大的,真是自欺欺人。
Glossary
- abiotic factor: A nonliving part of the ecosystem.
Hot temperatures and rainfall are abiotic factors in the desert ecosystem. - abrasion: The peeling or scraping away of an outer layer.

Wind abrasion is a form of physical weathering that wears down rock. - accommodation: An individual organism's response to a change in the ecosystem.
One type of accommodation is a change in the type of food an organism eats. - active volcano: A volcano that is still erupts from time to time.
Mt. Saint Helens is an active volcano. - adaptation: A special trait that helps an organism survive in its environment.
A fish's gills are an example of adaptation. - algae: A plant-like producer in a water environment.

Algae usually float on the surface of ponds and lakes. - alternating current: Electrical current that flows through a circuit, first in one direction, then in the opposite direction.
Most generators that make electrical energy produce an alternating current, or AC.
- amoeba: A type of protist that acts like an animal in some ways.

An amoeba can change its shape to catch food. - analyze data: To use the information that has been gathered to answer a question or solve a problem.
You can analyze data to find how daylight hours change throughout the year. - anthracite: A hard, natural type of coal.
Anthracite burns cleaner and longer than soft coal. <--- anthracite
<--- anthracite  <--- soft coal
<--- soft coal - attract: To pull or draw towards.
An object with positive electrical charge will attract an object with negative electrical charge. - axis: A real or imaginary line through the center of a rotating object.
The geographical North and South poles of Earth are located at the ends of the planet's axis.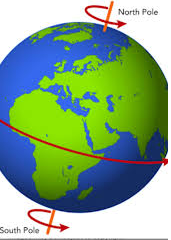
- bacteria: Microorganisms that have cell membranes but no nuclei.


Bacteria can be both helpful and harmful to humans. - barrier island: A long, narrow strip of land formed along the ocean shore by deposition.


- biomass: A measure of the amount of living things in an environment.
Plants make up most of the biomass in many environments. - biotic factor: A living part of the ecosystem.
Fish are biotic factors in the ocean. - blubber: A thick layer of fat found in large mammals.
Whale blubber allows the animal to stay warm in cold waters.

- branch: In a parallel circuit, one of the paths that electric current can follow.

The branches of a parallel circuit devide the current between them. - buildup: Having more of one kind of charge than the other.
Rubbing a balloon will lead to a buildup of electrical charge. - camouflage: An adaptation that allows an animal to blend into its surroundings.

Camouflage allows some animals to hide from predators. - canopy: The part of a forest just below the uppermost branches of the tallest trees.
Most rain-forest animals live in the canopy because of the sunligh and food found there. - canyon: A deep, narrow valley with steep sides.

Canyons are the results of river erosion. - carbon dioxide: A gas in the air.

Plants need carbon dioxide to live. - carbonic acid: A weak acid that forms when carbon dioxide reacts with water.
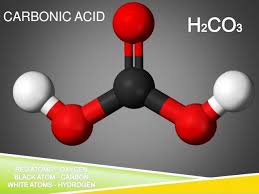
Carbonic acid can wear away limestone and create caves. - carnivore: An animal that eats other animals.
Hawks that eat mice are carnivores. - cell: The smallest unit of life.
Your body is made up of trillions of cells.
- chaparral: An area with dense thickets of small shrubs and trees.
 <--- chaparral
<--- chaparral  <--- thicket
<--- thicket
A chaparral environment is usually very dry and warm. - chemical weathering: The process in which rocks break down due to chemical changes to the minerals.
When oxygen reacts with iron and forms rust, chemical weathering occurs. - chlorophyll: A material in plants that helps them take in sunlight.

Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. - cinder-cone volcano: A volcano shaped like a cone.

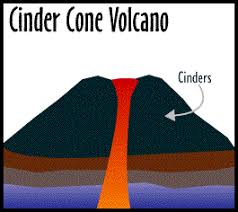
The magma in a cinder-cone volcano is usually quite thick. - circuit: The path along which electric current flows.
A simple circuit has a power source, connectors, and a switch.
- circuit breaker: Something that switches off a circuit when the current gets too high.

A circuit breaker can help prevent electric shock or fire hazard. - classify: To place similar materials together in a group.
The periodic table classifies elements that share the same properties. - cleavage: The way a mineral splits or breaks along flat surfaces.

The cleavage of quartz is uneven. - climate: The typical weather patterns of a region.
Most pond animals need a rainy climate. - closed circuit: A complete, unbroken electrical circuit.
A closed circuit allows electric current to flow. - communicate: To share information.
Recording your data helps you to communicate your observations to others - compass: An instrument that tells direction using Earth's magnetic forces.

A compass needle is a thin magnet that lines up with Earth's magnetic field and points north. - competition: The struggle among living things for the same resources.
There is great competition for mice as food in a woodland food chain. - composite volcano: A volcano made up of layers of lava and ash.

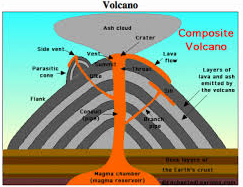
A composite volcano usually forms during periods of alternating quiet and explosive eruptions. - conductor: A material through which heat or electricity flows easily.
Metal such as copper and silver are good conductors. - conglomerate: A substance formed from rocks that have been lumped together.

Conglomerate is usually coarse and chunky. - conserve: To save or protect.
When you conserve resources, you try to use less of them. - consumer: An organism that eats other organisms.
Consumers cannot make their own food. - contour plowing: A farming method that cuts into the soil across a hillside rather than up and down the hillside.

Contour plowing helps farmers reduce erosion. - crater: A cup-like shape in the earth.

On a volcano, a crater often forms around the vent. - creep: A slow movement of plates along a fault.

Plate movement due to creep does not usually lead to earthquakes. - crust: The outermost layer of Earth.

Earth's crust is made up of huge, moving slabs of rocks called plates. - crystal: The geometric shape a mineral forms when its atoms and molecules are in fixed patterns.

Some crystal shapes can be like cubes or hexagons. - decomposer: An organism that breaks down other organisms.
Decomposers return an organism's nutrients to the soil.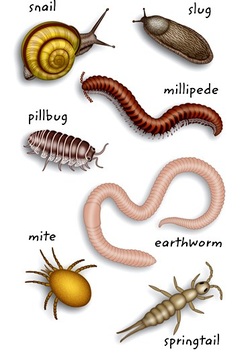
- delta: An area of land caused by deposition at the mouth, or end, of a river.

Most deltas are composed of sediment. - deposition: The dropping off of weathered rock at the end of erosion.
Deposition may leave sand and soil miles away from its original location. - desert: An ecosystem with few plants and little water.

Animals in the desert must be adapted to dry conditions. - diaphragm: The part of a louspeaker that vibrates and produces sound waves.
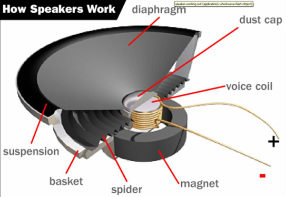
The diaphragm on most loudspeakers is made of either paper or plastic. - direct current: Electrical current that flows through a circuit in just one direction.

Most batteries produce a direct current, or DC. - discharge: A release of electrical energy from one object to another.
Static electricity will discharge from a charged object to a lesser charged object. - dormant volcano: A volcano that is quiet and no longer erupts.

Hawaii's oldest island Kauai is a dormant volcano. - draw conclusion: To arrive at possible answers based on information you have gathered.
After you analyze the data from an experiment, you can draw conclusions about what you observed. - drought: A long period with little or no rain.

A drought can have deadly effects on an ecosystem. - dynamo: Something that generates a great amount of energy.

Dynamos can produce electricity for many homes. - earthquake: A sudden shaking or trembling in Earth's crust.

Earthquakes can be caused by volcanoes or sudden shifts of Earth's plates. - ecosystem: All the living and nonliving things that interact in an environment.
The forest and the ocean are different ecosystems. - electrical charge: A property of matter that tells whether something has a positive or negative charge.
Something with a positive electrical charge will repel an object with the same property. - electrical engineer: A person who plans and constructs electrical systems.
An electrical engineer might figure out how to power all the lights and air conditioning in a shopping mall. - electric current: A flow of electrical charges.
Electric current moves in one direction like a river. - electrician: A person who works with electrical power.
An electrician might install wiring throughout a house. - electromagnet: A magnet formed when electric current flows through wire coiled around an iron rod.
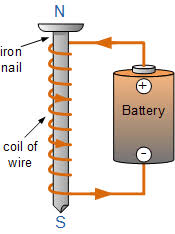
When the current stops in an electromagnet, the iron bar is no longer magnetic. - element: A basic building block of all matter.
Oxygen, carbon, and iron are all elements. - emergent: A tree that rises above the forest around it.
The tops of the tallest trees form the emergent layer of the rain forest. - endangered: close to extinction.
When very few of a kind of animal exist, it becomes an endangered species. - energy pyramid: A diagram that shows the amount of energy at each level of the food web in an ecosystem.

Humans are usually at the top of the energy pyramid; insects are near the bottom. - environment: All the living and nonliving things that surround an organism.
Plants need an environment in which they can get sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and other nutrients. - erosion: The transportation of weathered rock from one place to anohter.
Erosion can be caused by rainfall, waves, and wind. - eruption: A violent outburst or outpouring.

The eruption of a volcano forces melted rock, gases, and rock out of the vent. - euglena: A type of protist that behaves like both a plant and an animal.
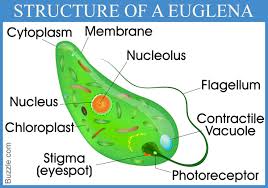

Euglena is also classified as a kind of algae. - exfoliation: A kind of physical weathering in which layers of rock peel off.

Rocks that are partly buried may show signs of exfoliation on the exposed surfaces. - experiment: An organized test designed to support or disprove a hypothesis.
Most expriments are designed and carried out very carefully. - extinct: All dead; no more left alive on Earth.
Animals that cannot adapt to changes in their ecosystem may become extinct. - extrusive: A kind of igneous rock formed when magma cools and hardens above Earth's surface.

Extrusive igneous rock may form in a matter of hours. - fault: A break or crack in Earth's crust where two plates come together.

Earthquakes are common along faults. - filament: A thin wire.
The filament in an incandescent light heats up and glows as it resists electric current.
- flood: The flow of water over the banks of a body of water and across land.

Large amounts of rainfall can cause floods along rivers. - food chain: The path that energy takes from one organism to another in the form of food.

A food chain shows how energy goes from the Sun to a plant to an insect to a bird. - food web: The food chains that link together in an environment.
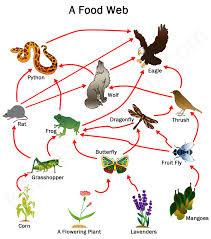
A food web shows that some animals are part of more than one food chain. - forester: Someone who takes care of a forest or wilderness area.
A forester might interact with hikers, campers, and hunters. - forest floor: The ground level of a forest ecosystem.
Not many plants grow on the forest floor because of the lack of sunlight that reaches it. - fossil: The remains of a living thing from many years ago.

Most fossils are found in sedimentary rock. - fungus (pl. fungi): A plant-like organism that breaks down dead or dying plants.

Fungi are one kind of decomposers in a woodland environment. - fuse: A device that melts if too much electric current is flowing through a circuit.
When a fuse metls, it must be replaced to restore power to the circuit. - gem: A mineral valued for its beauty.

Diamonds, rubies, and emeralds are gems. - generate: To create or produce.
Magnets can be used to generate electricity. - generator: A device that creates alternating current when an electric coil spins between the poles of a magnet.

An electric generator changes motion into electrical energy. - genetics: The study of how organisms pass along tratis over periods of time.
Genetics helps to explain why the necks of giraffes are so long. - geologist: A scientist who studies rocks to learn about Earth's history.
Geologists use the properties of rocks to classify them. - glacier: A large mass of moving ice.

Glaciers cut into landforms and create valleys over time. - gneiss: A type of metamorphic rock.

Gneiss is formed when granite is heated under great pressure. - gravity: The pulling force between two objects.
The gravity between your body and Earth prevents you from floating into space. - hardness: A property of minerals that tells how well it resists scratching.
Diamond has the highest degree of hardness. - herbivore: An animal that eats mainly plants.
Deer, rabbits, and cows are all herbivores. - horizon: A layer of soil that is distinct from the layers above and below it.
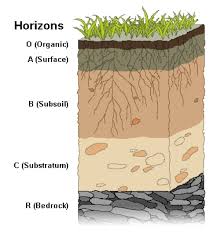
Each horizon has its own properties. - hot spot: A place where magma has partially melted through Earth's crust.

Plates moving over hot spots may give rise to volcanoes. - humus: Decayed plant or animal material in soil.

Each layer of soil has different amount of rock and humus. - hybrid: Having two or more different things mixed together.
A hybrid car uses both gasoline and electricity as power sources. - Hypothesis: A suggested statement or explanation that can be tested to answer a question.
An experiment can help you to test a hypothesis. - igneous rock: A type of rock formed when melted rock cools and hardens
Igneous rock, such as granite, can be found near a volcano. - insulator: Something that slows or stops the flow of energy, such as heat, electricity, or sound.
Wood, rubber, and glass are good insulators. - intrusive: A kind of igneous rock formed when magma cools and hardens below Earth's surface.

Intrusive igneous rock may take thousands of years to form. - kelp: A type of seaweed.

Kelp is usually large and brown in color. - kidney: A bean-shaped organ that filters water and waste materials out of the blood.
In some animals, the kidneys can help store water for later use. - landform: A natural feature on Earth's surface.

Plains, mountains, and valleys are all landforms. - landslide: The rapid, downhill movement of large amounts of rock, soil, and other material.

An earthquake might cause landslides in mountainous areas. - lapis lazuli: A type of metamorphic rock formed from limestone.

Lapis lazuli is a deep blue color and used to make jewelry. - lava: Magma that reaches Earth's surface.

Lava often flows when a volcano erupts. - lava rock: Another name for pumice, an extrusive igneous rock.

Lava rock is very light in weight with many tiny holes. - leaf: The part of a plant that collects light from the Sun.
The leaves of most plants are green. - levitation: The act of lifting something or being lifted off the ground.
Maglev trains use magnets for levitation above the ground.

- lightening: A large spark caused by the discharge of static electricity in a thunderhead.

Lightening can jump from one cloud to another or from a cloud to the ground. - loudspeaker: A device that changes electrical energy into sound.
Headphones are small loudspeakers with tiny electromagnets that make them work. - luster: The way light reflects off a mineral's surface.

Luster is one of several properties of minerals. - magma: Hot, molten rock below Earth's crust.

Magma flows like liquid even though it is rock. - magnet: An object that can attract iron and produce a magnetic field.

When you bring two magnets together, they will either attract or repel each other. - magnet field: The region of positive and negative attractive forces surrounding a magnet.
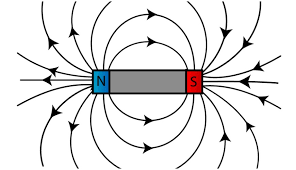
Earth has a magnetic field similar to a bar magnet. - malaria: A disease that causes high fever.
Malaria is caused by microorganisms in the blood. - measure: To find the size, volume, area, mass, weight, or temperature of an object.
When you measure something, you gather data or information about it. - mechnical energy: Motion, or the energy in moving objects.
A motor can produce mechanical energy in power tools, toys, and cars. - metallic: Shiny and reflective.

Some minerals have a metallic luster. - metamorphic rock: Rock whose form has been changed by heat or pressure.
Under pressure, limestone becomes the metamorphic rock marble. <--- limestone
<--- limestone  <--- marble
<--- marble - microbiologist: A person who studies microorganisms.
A microbiologist might study the small organisms that cause disease. - microorganism: An organism that is too small to see without a microscope.
Protists and bacteria are microorganisms. - microphone: A device that converts sound into electrical signals.

Magnets in a microphone turn your voice into signals that can be sent to other locations. - microscope: A tool that makes small objects appear larger.
You can see bacteria using a microscope. - mimicry: When one organism imitates the traits of another.

Some insects use mimicry to look like other insects and fool predators. - mineral: A natural, nonliving substance.
Some mineral are the building blocks of rocks. - Mohs hardness scale: A table that shows the hardness of minerals.
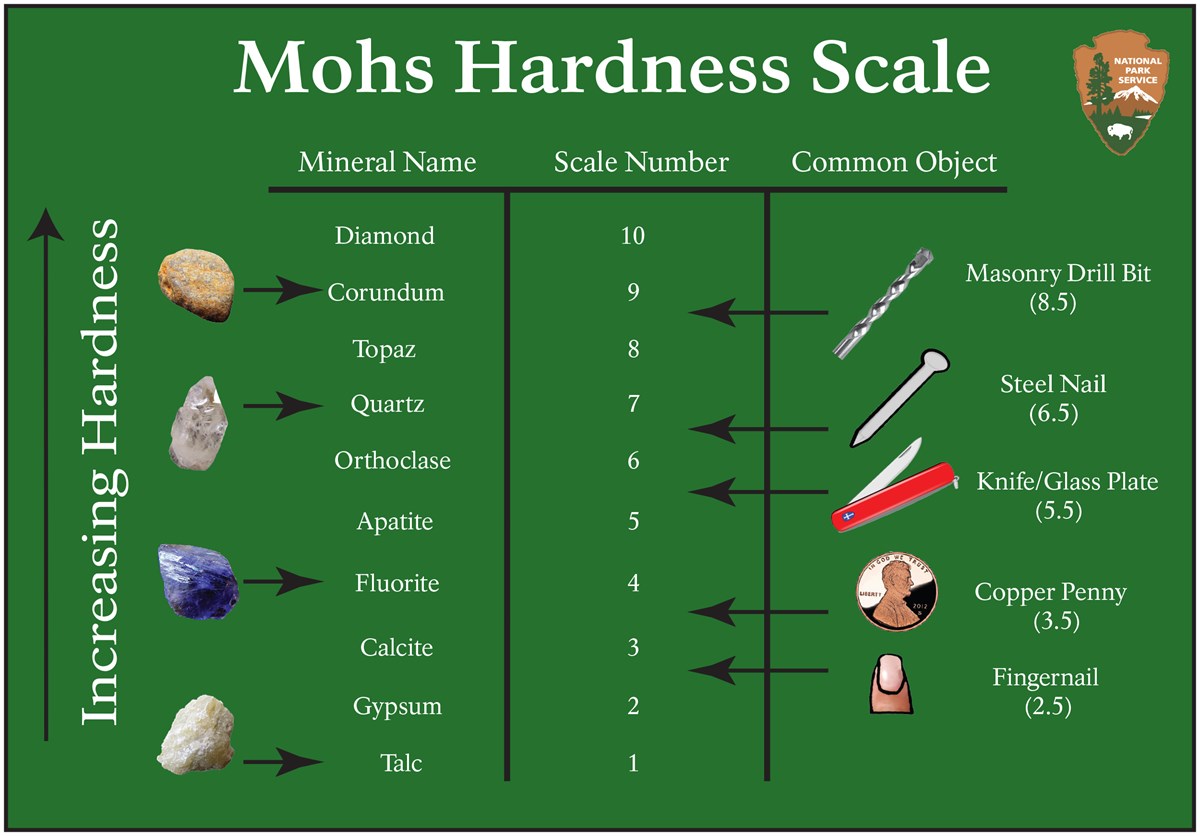
On the Mohs hardness scale, talc has a value of 1 and diamond has a value of 10. - mold: A type of fungi.

Many food grow mold over time if left alone. - motor: A device that changes electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Electric motors are used in everyday device such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and electric trains. - mudslide: Land that becomes too full of water and slides down a slope.

Mudslides may occur after a period of heavy rain. - nectar: A sweet liquid found inside flowers.

The nectar attracts animals that help flowers pollinate. - neutral: Having no overall electrical charge.
In neutral object, the positive and negative electrical charges canel each other out. - normal fault: The crack or line between two plates that are pulling apart.
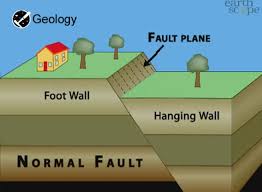

Rocks above a normal fault move down. - observe: To use one or more of your senses to identify or learn about an object or event.
You conduct an experiment to observe what happens in a controlled situation. - omnivore: An animal that eats both plants and animals.
Most humans are omnivores. - open circuit: An electrical circuit with breaks or openings.
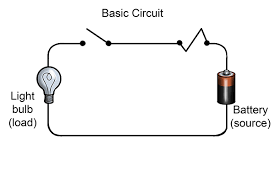
Electric current cannot flow in an open circuit. - ore: A mineral or rock containing a useful property or substance.
Hematite is an ore that contains iron.
- organism: A living thing.
All organisms carry out five basic life functions. - oxygen: A gas that most plants and animals need to live.
The air that we breathe contains oxygen. - parallel circuit: A circuit in which the electrical current follows more than one path.
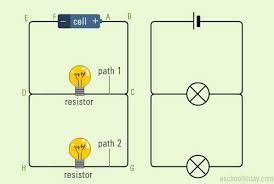
Each branch of a parallel circuit has its own electric current. - photographer: A person who takes pictures with a camera.
Nature photographers work in many outdoor places like jungles and oceans. - photosynthesis: The process by which plants turn sunlight into food.
Most photosynthesis takes place in the summer. - physical weathering: The processes that change the size and shape of rocks without changing them chemically.
Extreme high and low temperatures can lead to physical weathering. - pistil: The parts of a plant that produce the female sex cells.
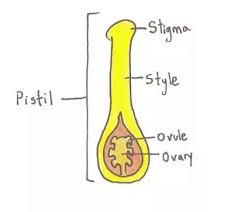


The ovary is part of the plant's pistil. - plain: A large, flat stretch of land.

The Great Plains are located in the middle of the United States. - plate: An extremely large, moving slab of rock that forms Earth's crust.
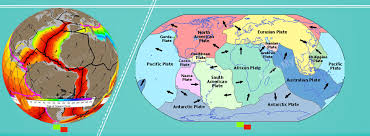
The movement of plates can cause earthquakes. - pole: The part of a magnet where the magnetic force is strongest.

When two magnets are brought together, the north pole will attract the south pole. - pollen: The powder-like grains in a flower that contain male sex cells.

During pollination, pollen is transferred from stamen to pistil. - pollination: The process in which the male and female cells of plants come together.

After pollination a seed develops that lets the plant reproduce. - population: All the members of a single type of living thing in an environment.
When one population changes, it affects other populations in the same food web. - predator: An animal that hunts another animal for food.
Sharks are the ocean's fiercest predators. - predict: To state likely results of an event or experiment.
You might be able to predict the weather by looking at clouds in the sky. - pressure: The squeezing force that pushes things together.

Pressure deep in the Earth can form new kinds of rock from old kinds. - prey: An animal that is hunted by another animal for food.
Mice are prey to hawks. - primary consumer: The first consumer in the food chain.
Herbivores, such as deer or rabbits, are often the primary consumers in their food chains. - producer: An organism that makes its own food.
Green plants are producers that make their own food from water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight. - protist: A microorganism that lives in water.

Many harmful protists are found in ponds and lakes. - repel: To push away.
An object with positive electrical charge will repel another object with positive electrical charge. - reproduce: To make new living things like the original.
Not all organisms reproduce the same way. - resistance: The ability of a substance to stop or slow down electric current.
Resistance allows electrical energy to be changed into other forms of energy, such as heat or light. - reverse fault: The crack or line between two plates that are pushing together.


Rocks above a reverse fault move upward. - rift volcano: A volcano that forms where Earth's plates move apart.
Most rift volcanoes form along the ocean floor. - rock cycle: The series of processes that show how rocks change from one into another.
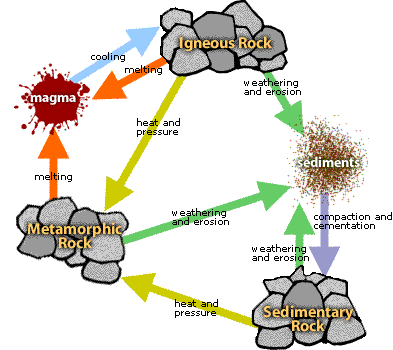
Over time, all rocks melt and harden in the rock cycle. - rock-forming minerals: The types of nonliving substances common to rocks.
Quartz and feldspar are two common rock-forming minerals.
- root: The part of a plant that gets water and food from the soil.
Some roots reach far underground. - sand dune: Hill-like deposit of sand left behind by wind erosion.

Winds off the ocean create sand dunes along the shore. - sediment: Small pieces of material normally carried and deposited by water or wind.
Some sediments are tiny particles of rocks and minerals or bits of bone and shell. - sedimentary rock: A type of rock that forms when sediments are pressed together in layers.

 <--- limestone
<--- limestone
Limestone is an example of sedimentary rock. - seed disperal: The process of spreading seeds that allow plants to reproduce.
Animals play an important role in seed dispersal. - series circuit: A circuit in which all the electrical charges flow along the same path.

If any part of a series circuit is broken, no electric current will flow. - shaft: A pole or rod that spins or moves.
A motor shaft might turn a gear or a wheel.
- shield volcano: A volcano with sides taht are wide and flat.


The Hawaiian Islands are examples of shield volcanoes. - short circuit: A path of electric current with almost no resistance.
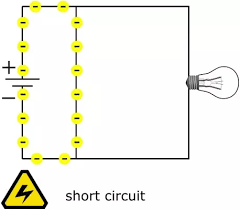
A short circuit can create dangerous levels of heat in the rest of the circuit. - solar energy: Energy that comes from the Sun.
Most plants rely on solar energy to grow. - stamen: The part of the plant that holds the male cells for reproduction.
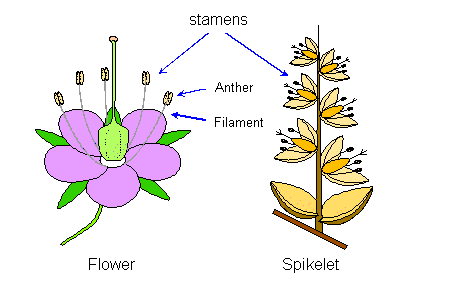
The stamen is part of the plant's anther. - static electricity: A buildup of electrical charge on an object.
Objects rubbing against one another in a clothes dryer create static electricity. - stem: The part of a plant that holds it upright.
A plant's stem also carries food and water. - stomata (pl. stoma): Holes on the bottoms of leaves through which air and water pass.
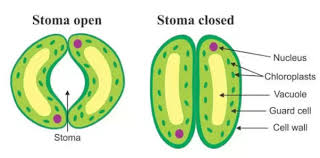
Carbon dioxide enters a plant through its stomata. - Streak: A property of minerals that tells the color of powder left behind when the mineral is scratched along a white tile.

Not all minerals leave a streak that is the same color as the mineral itself. - strike-slip fault: The crack or line between two plates that are sliding past each other in different directions.


California's San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault. - strip farming: Planting alternating rows of grasses and food crops in an area.

Strip farming slows down soil erosion. - submersible: Something that can work underwater.
Scientists use vehicles called submersibles to study the bottom of the ocean. - survey technician: A person who creates maps and locates boundaries of land.
A survey technician might use a special instrument to calculate large distances. - switch: A device that can make, break, or change the flow of electric current in a circuit.
Most switches turn the electric current on or off. - transformer: Something that changes the voltage of electric current.


Some transformers increase voltage as electric current leaves a power plant, then others decrease the voltage before it enters a home. - tsunami: A gaint ocean wave.

A tsunami is usually caused by an earthquake in the ocean. - turbine: A type of engine that provides the mechanical energy for a generator.
A simple turbine looks like an electric fan that moves when steam, water, or air pushes against the blades. - understory: The area in a forest between the canopy and the ground.
Leopards, frogs, and many insects live in the understory. - valley: An area of low land between hills or mountains.
Rivers can cut away at landforms and create valleys. - vent: The central opening in a volcano.

During eruption, lava and rocks are forced out of the volcano's vent. - volcano: A mountain that builds up around an opening in Earth's crust.

When trapped energy is released from a volcano, there may be an explosive eruption. - voltage: The strength of a power source.
A power source with more voltage can produce more electric current. - volt: A unit of measurement of the strength of a power source.
Most wall outlets have 120 volts. - warning: In weather, a term used to report that something is occurring or will occur soon.
A flood warning means that water is rising over the banks of rivers or lakes. - watch: In weather, a term used to report taht a weather event is possible.
A flood watch means that conditions are good for a flood in the near future. - watt: A unit of measure that tells how much electrical power is used.
Light bulbs that use more watts generally provide more light. - weathering: The natural processes that break down rocks without transporting them.
Freezing, wind, and pressure can lead to weathering. - wind abrasion: A kind of physical weathering in which blowing sand wears away the rock.
A sandstorm can cause a high level of wind abrasion.