一、简介
ConcurrentSkipListSet是线程安全的有序的集合,适用于高并发的场景。
ConcurrentSkipListSet和TreeSet,它们虽然都是有序的集合。但是,第一,它们的线程安全机制不同,TreeSet是非线程安全的,而ConcurrentSkipListSet是线程安全的。第二,ConcurrentSkipListSet是通过ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的,而TreeSet是通过TreeMap实现的。
1.1、原理和数据结构
说明:
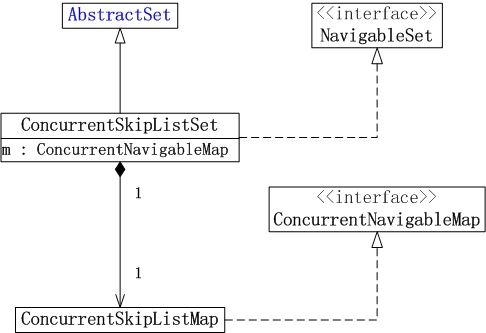
(01) ConcurrentSkipListSet继承于AbstractSet。因此,它本质上是一个集合。
(02) ConcurrentSkipListSet实现了NavigableSet接口。因此,ConcurrentSkipListSet是一个有序的集合。
(03) ConcurrentSkipListSet是通过ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的。它包含一个ConcurrentNavigableMap对象m,而m对象实际上是ConcurrentNavigableMap的实现类ConcurrentSkipListMap的实例。ConcurrentSkipListMap中的元素是key-value键值对;而ConcurrentSkipListSet是集合,它只用到了ConcurrentSkipListMap中的key!
1.2、示例
/* * ConcurrentSkipListSet是“线程安全”的集合,而TreeSet是非线程安全的。 * * 下面是“多个线程同时操作并且遍历集合set”的示例 * (01) 当set是ConcurrentSkipListSet对象时,程序能正常运行。 * (02) 当set是TreeSet对象时,程序会产生ConcurrentModificationException异常。 * */ public class ConcurrentSkipListSetDemo1 { // TODO: set是TreeSet对象时,程序会出错。 //private static Set<String> set = new TreeSet<String>(); private static Set<String> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<String>(); public static void main(String[] args) { // 同时启动两个线程对set进行操作! new MyThread("a").start(); new MyThread("b").start(); } private static void printAll() { String value = null; Iterator iter = set.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { value = (String) iter.next(); System.out.print(value + ", "); } System.out.println(); } private static class MyThread extends Thread { MyThread(String name) { super(name); } @Override public void run() { int i = 0; while (i++ < 10) { // “线程名” + "序号" String val = Thread.currentThread().getName() + (i % 6); set.add(val); // 通过“Iterator”遍历set。 printAll(); } } } }
1.3、使用场景
二、源码分析
打