这次的人工智能实验是产生式系统——动物分类。
规则库:
R1:动物有毛发→ 哺乳类
R2:动物有奶 → 哺乳类
R3:动物有羽毛 → 鸟类
R4:动物会飞 ∧会下蛋 → 鸟类
R5:哺乳类∧动物吃肉→ 食肉动物
R6:动物有犬齿 ∧有爪 ∧眼盯前方→食肉动物
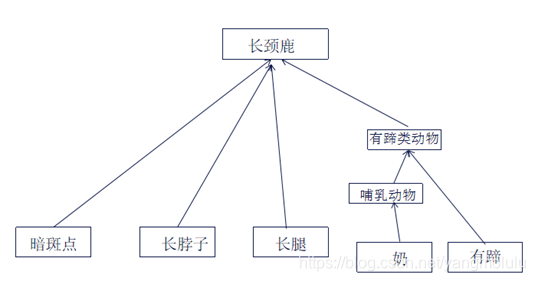
R7:哺乳类 ∧有蹄 →蹄类
R8:哺乳类 ∧反刍 → 蹄类
R9:哺乳类 ∧ 食肉动物∧ 黄褐色 ∧ 有斑点→ 金钱豹
R10:哺乳类∧ 食肉动物 ∧ 黄褐色 ∧ 有黑色条纹→虎
R11:蹄类 ∧ 长脖 ∧ 长腿 ∧ 有斑点→ 长颈鹿
R12:蹄类 ∧ 有黑色条纹→ 斑马
R13:鸟类 ∧长脖 ∧ 长腿 ∧ 不会飞∧黑白二色 →鸵鸟
R14:鸟类 ∧会游泳 ∧黑白二色 ∧ 不会飞 →企鹅
R15:鸟类 ∧善飞 →信天翁
通过这个规则库,根据用户输入的已知条件,来判断所描述的动物。
产生式系统的问题求解过程即为对解空间的搜索过程,也就是推理过程。按照搜索的方向可把产生式系统分为正向推理、逆向推理和双向推理。
正向推理:从一组表示事实的谓词或命题出发,使用一组产生式规则,用以证明该谓词公式或命题是否成立。
逆向推理:从表示目标的谓词或命题出发,使用一组产生式规则证明事实谓词或命题成立,即首先提出一批假设目标,然后逐一验证这些假设。
双向推理:双向推理的推理策略是同时从目标向事实推理和从事实向目标推理,并在推理过程中的某个步骤,实现事实与目标的匹配。
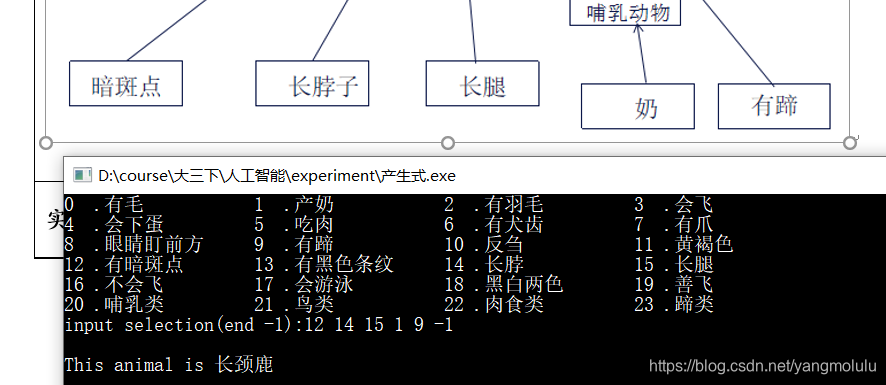
已知 有斑点、长脖子、长腿、有奶、有蹄子
正向推理:R11–>R2–>R7
反向推理:假设R1到R7的某个结论成立,逐个与现有事实匹配
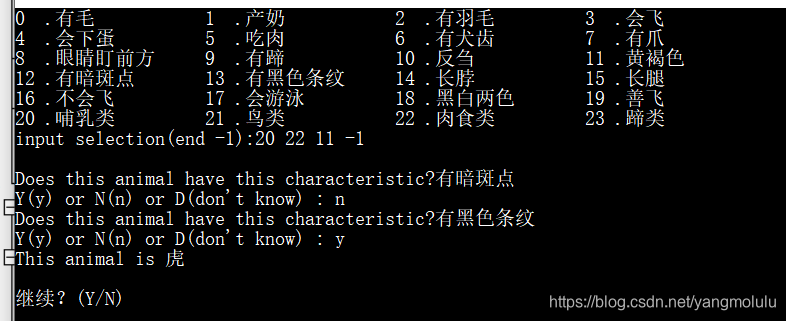
正反向混合推理(双向推理):正向推理,有斑点–>豹子或长颈鹿;根据其他事实反向推理
这里我们采用双向推理。
思路:将所有名词编号,然后用编号来组织成一条条件,遍历这些条件,根据用户给出的名词,进行比较,同时计算每个条件的符合程度,推理出的名词加入到已知的名词队列中,重新遍历条件,更新符合度,如果没有100%符合的条件,则寻找符合度最高的条件,进行逆向推理,询问可能的且没有在已知名词队列中的名词,进行判断,加入名词队列,重新遍历,更新符合度,直至找到属于结果类的名词,即是结果。
例
代码说明:
int change_speices(); // 对推理树中的可以直接推理的叶子节点进行推理,如有毛 --》哺乳类 将哺乳类加入名词队列中,将有毛去掉
就是对推理树中的可以推理的叶子节点进行推理,得到其父母节点,并将这些使用过的叶子节点去掉。
typedef struct{ // 存放可能的动物
int animal; // name
float confidence; //置信度 = 满足的特性数 / 所含特征数;
int site; // 在rule中的位置
int num; // 满足的特征数
}Result;
vector<Result> result;
result存放可能的结果,按照置信度从大到小进行排序。
完整实现代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<memory.h>
using namespace std;
string animal[]={"企鹅","海燕","鸵鸟","斑马","长颈鹿","虎","金钱豹"};
string feature[]={"有毛","产奶","有羽毛","会飞","会下蛋","吃肉","有犬齿","有爪","眼睛盯前方","有蹄","反刍","黄褐色","有暗斑点",
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
"有黑色条纹","长脖","长腿","不会飞","会游泳","黑白两色","善飞","哺乳类","鸟类","肉食类","蹄类",
// 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
"企鹅","信天翁","鸵鸟","斑马","长颈鹿","虎","金钱豹"};
// 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
typedef struct { //存放规则的结构体
int relation[6]; //关系
int name; //推理结果
}Rule;
typedef struct{ // 存放可能的动物
int animal; // name
float confidence; //置信度 = 满足的特性数 / 所含特征数;
int site; // 在rule中的位置
int num; // 满足的特征数
int size; // 此animal的所含总特征数
}Result;
vector<Result> result;
// 规则库 -1 代表规则结束
Rule rule[15]={{{0,-1},20},{{1,-1},20},{{2,-1},21},{{3,4,-1},21},{{5,-1},22},
{{6,7,8,-1},22},{{20,9,-1},23},{{20,10,-1},23},{{20,22,11,12,-1},30},
{{20,22,11,13,-1},29},{{23,14,15,12,-1},28},{{23,13,-1},27},
{{21,14,15,16,18,-1},26},{{21,19,-1},25},{{21,17,18,16,-1},24}};
int flag[23]={0};//标记各个特征是否选择
int IsAnimal(int a);
int change_speices(); // 将可以推理出 动物类的规则推理出来
int fnum(); // 获取flag标记的数目
int z_inference(); //正向推理
int category(); // 输出动物类别
int cal_confi(); // 计算置信度
int r_inference(); //反向推理
void input(); //输入
void menu(); //选择菜单
bool Compare(const Result& a,const Result& b){
return a.confidence > b.confidence;
}
void Rsort(vector<Result>& r){
sort(r.begin(),r.end(),Compare);
return ;
}
//选择特征菜单
void menu(){
for(int i = 0; i < 24;i++){
if(i % 4 == 0 && i != 0)
cout<<endl;
cout<<setiosflags(ios::left)<<setw(3)<<i<<".";
cout<<setiosflags(ios::left)<<setw(15)<<feature[i];
}
memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag));
}
//特征输入值 选择数字
void input(){
for(int i = 0; i < 24; i++)
flag[i] = 0;
int ti = 0;
cout<<"\ninput selection(end -1):";
while(ti!=-1){
cin>>ti;
if(ti >= 0 && ti <= 23)
flag[ti] = 1;
else if(ti != -1){
cout<<"Input error! Please enter a number between 0~23!"<<endl; //notanimal=25
cin.clear(); //清除流错误错误标记
cin.sync(); //清空输入缓冲区
cout<<"Please continue to enter: ";
}
}
}
//是某动物 而不是某种物种
int IsAnimal(int a){
if(a>=24&&a<=30)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// 判断是否某一物种类
int IsAnimal_speices(int a){
if(a >= 20 && a <= 23)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// 返回flag数组中标记的总数
int fnum(){
int fum=0;
for(int i = 0;i < 24;i++)
if(flag[i] == 1)
fum++;
return fum;
}
//输出打印物种类别
int category(){
bool k;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 20;i < 24; i++){
k = false;
if(flag[i] == 1){
k = true;
count++;
if(count == 1)
cout<<"Can't reason about specific animals! Category is ";
cout<<setiosflags(ios::left)<<setw(10)<<feature[i];
}
}
cout<<endl;
if(!k)
cout<<"Sorry! No such animal in the system"<<endl;
return 1;
}
// change_speices --》 flag 发生变化 推理是否有 物种种类 并将用到的事实 清空
//如 有毛 --》哺乳动物 就将flag中哺乳动物的项置一 并将有毛这一特征flag清0
int change_speices(){
int i ,j,k,ti;
bool t;
int temp[23]={0}; //临时
int f[23] = {0}; // 标记使用过的flag[] & < 20 20 哺乳类
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){ // rule 前8个 规则
t = true;
j = 0;
ti = rule[i].relation[j];
while(ti != -1){
if(flag[ti] == 1) temp[ti] = 1;
else {
memset(temp,0,sizeof(temp));
t = false;
break;
}
j++;
ti = rule[i].relation[j];
}
if(t){
for(int k = 0; k <= 20; k++)
if(temp[k] == 1)
f[k] = 1;
flag[rule[i].name] = 1;
}
memset(temp,0,sizeof(temp));
}
// 推理过的事实 则删除 保留结果
for(i = 0; i <= 20; i++)
if(f[i] == 1)
flag[i] = 0;
return 1;
}
// 重新计算置信度
int cal_confi(){
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
for(int j = 8; j < 15; j++){
if(result[i].animal == rule[j].name){
result[i].confidence = 1.0 * result[i].num / result[i].size;
break;
}
}
}
}
//推理 双向推理 -- 正向推理不下去 事实不够 采用逆向推理
int z_inference(){
int ti,num;
int i,j;
int fum = fnum();
cout<<endl;
for(i = 8;i < 15;i++){ //检查规则库
Result temp;
j = 0; num = 0;
ti = rule[i].relation[j];
while(ti != -1){
if(flag[ti] == 1) num++;
j++;
ti = rule[i].relation[j];
}
// 此时 j 保存则rule[i]所含有的特征数
if(num != 0 && fum <= j){ // 给定特征数小于等于的情况 (即flag数组中标记位数目大于此动物的特征数则不放入result)
if(IsAnimal(rule[i].name)){ // 是具体的动物
temp.animal = rule[i].name;
int size = j; // rule[i]所含有的特征数
temp.size = size;
temp.confidence = 1.0 * num / size;
temp.site = i;
temp.num = num;
result.push_back(temp);
}
}
}
if(!result.empty())
Rsort(result); //对置信度从高到低排序
/*
//打印排序后的vector
for(vector<Result>::iterator it = result.begin();it != result.end();++it){
cout<<setiosflags(ios::left)<<setw(10)<<feature[(*it).animal]<<" ";
cout<<(*it).confidence<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
*/
// 判断 -- 未询问 --正向推理 后
if(result.empty()) { // 给定特征数无法用任何一规则推理 可能没有这种动物 可能是一种动物类别 (系统中无此动物,则输出类别)
category();
}else if(result.front().confidence == 1.0){ // 可能给的特征刚好推理出 可能特征还没用完
cout<<"This animal is "<<feature[result.front().animal]<<endl;
result.clear(); // 清空
return 1;
}else // 特征描述不全 逆向推理 询问特征
r_inference();
}
//特征不足推理 进入反向推理
int r_inference(){
vector<Result>::iterator it = result.begin();
int enquire[23]; // 用来标记询问过的特征数组 0 N 1 Y 2 D(0 代表没有此特征 1 代表有 2 代表不请楚、不知道)
memset(enquire,-1,sizeof(enquire));
for(int i = 0; i< result.size();){// 从置信度最高开始询问
bool in_i = true; // i ++ 的标记
int nu = result[i].size;
for(int j = 0; j < nu; j++){ // 询问 未说明 特征
if(flag[rule[result[i].site].relation[j]] == 0){
int en = rule[result[i].site].relation[j];
char c;
if(enquire[en] == -1){ // 此特征未被询问过 则输出询问语句 否则直接判断处理
cout<<"Does this animal have this characteristic?"<<feature[rule[result[i].site].relation[j]]<<endl;
cout<<"Y(y) or N(n) or D(don't know) : ";
cin>>c;
while(c != 'Y' && c != 'y' && c != 'N' && c != 'n' && c != 'D' && c != 'd'){
cout<<"Please enter Y(y) or N(n) or D(d)!"<<endl;
cin>>c;
};
}
if(enquire[en] == 1 || c == 'Y' || c == 'y'){ //有此特征 改变置信度
result[i].num++;
enquire[en] = 1;
}else if(enquire[en] == 0 || c == 'N' || c == 'n'){ // 没有此特征 直接去掉
enquire[en] = 0;
result.erase(it+i); // erase删除后 i不自增 就能删除最后的元素(迭代器就是指向删除之前元素后的第一个元素)
in_i = false; // 如果 擦除了元素 则 i不自增
if(result.empty()) // result 为空 输出类别 退出
category();
break;
}else if(enquire[en] == 2 ||c == 'D' || c == 'd'){enquire[en] = 2;} // 不确定、不知道 置信度不改变
}
}
if(in_i)
++i;
}
if(!result.empty()){
// 改变置信度
cal_confi();
if(result.size() > 1) //重新排序
Rsort(result);
//判断 -- 询问后 -- 双向推理后
if(result.front().confidence == 1.0){
cout<<"This animal is "<<feature[result.front().animal]<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"Possible animals (confidence from big to small) :";
for(vector<Result>::iterator it = result.begin();it != result.end();++it)
cout<<setiosflags(ios::left)<<setw(10)<<feature[(*it).animal]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
result.clear(); // 清空
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
char q;
while(q != 'N' && q != 'n'){
menu();
input();
change_speices();
z_inference();
cout<<"\n继续?(Y/N)"<<endl;
cin>>q;
system("cls");
}
return 0;
}
运行截图: