20175227张雪莹 2018-2019-2 《Java程序设计》
课下选做作业MySort
要求
- 注意:研究sort的其他功能,要能改的动代码,需要答辩
- 模拟实现Linux下Sort -t : -k 2的功能。
- 要有伪代码,产品代码,测试代码(注意测试用例的设计)
- 参考 Sort的实现。提交博客链接。
必须答辩才能得分
import java.util.*;
public class MySort1 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
String [] toSort = {"aaa:10:1:1",
"ccc:30:3:4",
"bbb:50:4:5",
"ddd:20:5:3",
"eee:40:2:20"};
System.out.println("Before sort:");
for (String str: toSort)
System.out.println(str);
Arrays.sort(toSort);
System.out.println("After sort:");
for( String str : toSort)
System.out.println(str);
}
}相关知识
- Linux系统下的Sort功能
- 功能: 将文本文件内容加以排序,sort可针对文本文件的内容,以行为单位来排序。
- 参数:
| 参数 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| -b | 忽略每行前面开始出的空格字符。 |
| -c | 检查文件是否已经按照顺序排序。 |
| -d | 排序时,处理英文字母、数字及空格字符外,忽略其他的字符。 |
| -f | 排序时,将小写字母视为大写字母。 |
| -i | 排序时,除了040至176之间的ASCII字符外,忽略其他的字符。 |
| -m | 将几个排序好的文件进行合并。 |
| -M | 将前面3个字母依照月份的缩写进行排序。 |
| -n | 依照数值的大小排序。 |
| -o <输出文件> | 将排序后的结果存入指定的文件。 |
| -r | 以相反的顺序来排序。 |
| -t <分隔字符> | 指定排序时所用的栏位分隔字符。 |
sort -n -k 2 -t'-' date // -t<分隔字符> 指定排序时所用的栏位分隔字符。 -k 选择以哪个区间进行排序- split方法:一个String类的数组以regex传入的分隔符为标准,对字符串进行分隔,使用时分隔符要放在双括号中。

代码实现
- 伪代码
将字符串数组tosort用“:”分隔,以第二列数值大小为标准从小到大排列:
创建整型数组a,长度与tosort长度相同
调用split函数将tosort数组以:(冒号)为分隔符分成小字符串
将每一个tosort元素的第二例列数值存入数组a中
调用Arrays类的sort函数对a进行排序
输出排序后的结果- 产品代码
/**
* @author 20175227 Xueying Zhang
* @date 2019/5/19 11:44.
*/
import java.util.*;
public class MySort {
public static void main(String [] args) {
String [] toSort = {
"aaa:10:1:1",
"ccc:30:3:4",
"bbb:50:4:5",
"ddd:20:5:3",
"eee:40:2:20"};
System.out.println("Before sort:");//输出排序前字符串数组
for (String str: toSort)
System.out.println(str);
int [] a=new int[toSort.length];
for(int i=0;i<toSort.length;i++){//对toSort每一个元素用split进行划分,并储存进字符串数组list中
String [] list=toSort[i].split(":");
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(list[1]);//将list中第二个元素,即toSort中第二列元素存进a中
}
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println("After sort:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)//对a中每个元素
for (int j = 0; j < toSort.length; j++)//在toSort中每一个元素的第二列中比较
if (a[i] == Integer.parseInt((toSort[j].split(":"))[1]))//如果二者相等
System.out.println(toSort[j]);//就输出该项元素
}
public static int StringTest1(String str){
int a;
String [] list=str.split(":");
a=Integer.parseInt(list[1]);//将list中第二个元素,即toSort中第二列元素存进a中
return a;
}
public static int[] StringTest2(String[] toSort){
int [] a=new int[toSort.length];
for(int i=0;i<toSort.length;i++){//对toSort每一个元素用split进行划分,并储存进字符串数组list中
String [] list=toSort[i].split(":");
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(list[1]);//将list中第二个元素,即toSort中第二列元素存进a中
}
Arrays.sort(a);
return a;
}
}
- 测试代码
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
public class MySortTest extends TestCase {
String [] toSort = {
"aaa:10:1:1",
"ccc:30:3:4",
"bbb:50:4:5",
"ddd:20:5:3",
"eee:40:2:20"};
@Test
public void testl() {
assertEquals(10,MySort.StringTest1("aaa:10:1:1"));
}
public void test2() {
assertEquals(20,MySort.StringTest2(toSort)[1]);
}
}运行示例
- 产品代码运行结果
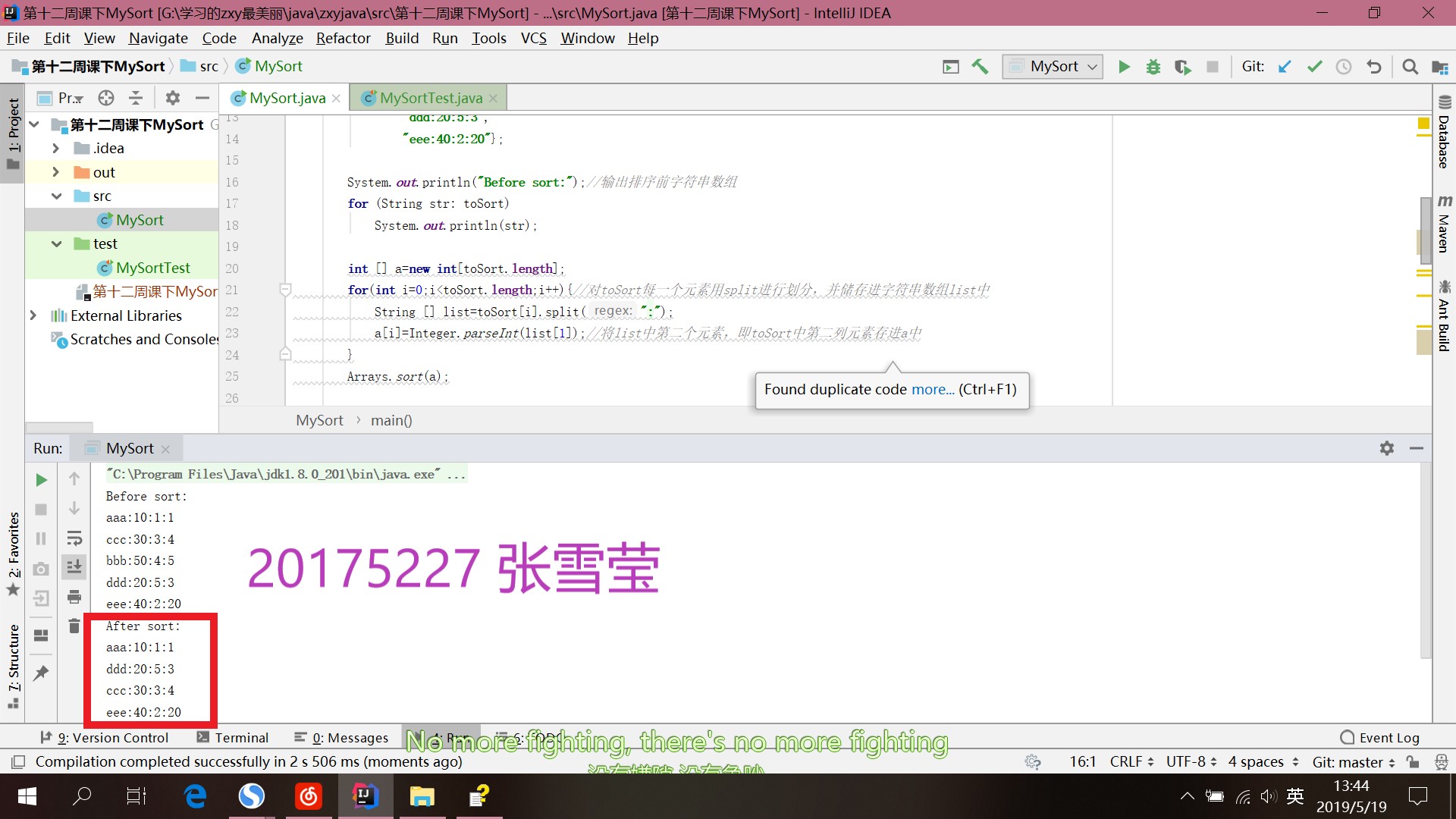
- 测试结果
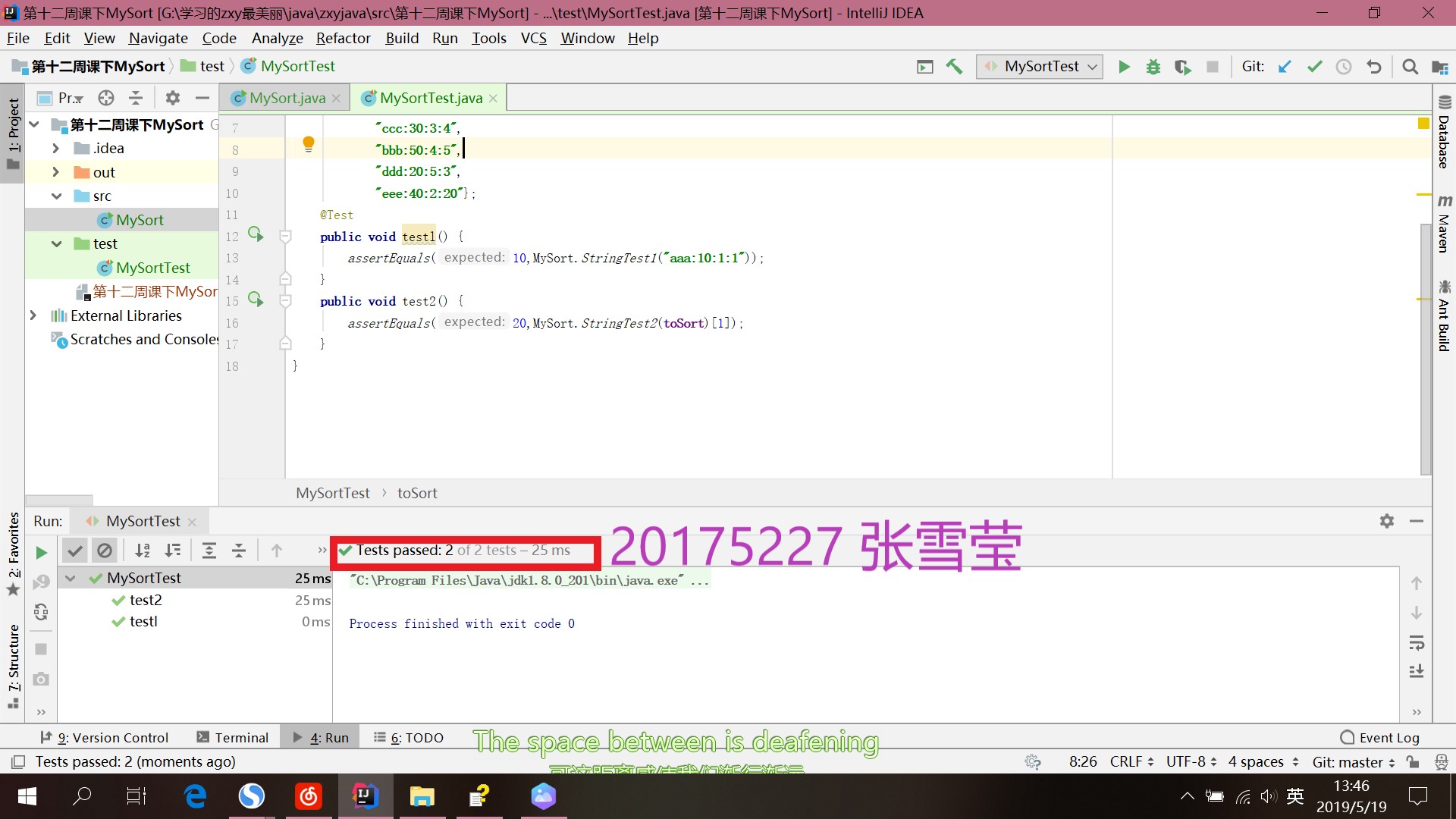
代码托管
参考资料
- https://www.cnblogs.com/fulucky/p/8022718.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/fyss/p/9065173.html