这还有什么说头吗?饭都不让吃了好吗!!
行。狠。
A. 【NOIP2018普及组】标题统计

这个可能就是想考你一个无限输入的语法和ASCII码的运用吗…
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; int main(){ //freopen("title.in","r",stdin); //freopen("title.out","w",stdout); char Title; int Answer=0; while(~scanf("%c",&Title)){ if(Title>='A'&&Title<='Z'){ Answer++; } else if(Title>='0'&&Title<='9'){ Answer++; } else if(Title>='a'&&Title<='z'){ Answer++; } } printf("%d",Answer); return 0; }
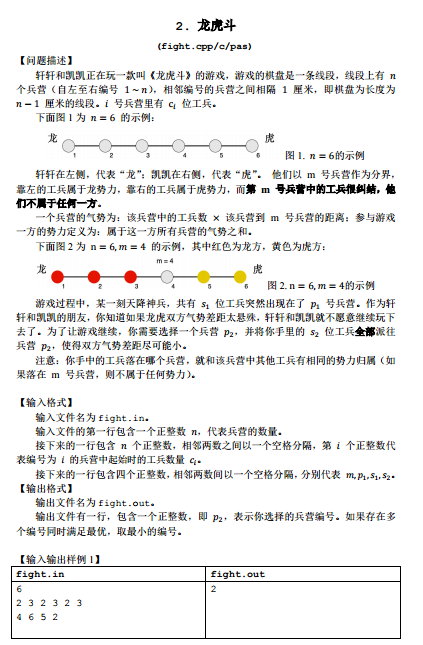
B. 【NOIP2018普及组】龙虎斗

十年OI一场空,不开longlong见祖宗。十年OI一场空,不开longlong见祖宗。十年OI一场空,不开longlong见祖宗。
肥肠简单的差值运算题,计算一下势力值并且计算一下两势力差,然后判断哪边高,把兵给低的那边派过去。具体派哪个地方,暴力枚举即可。最后判断一下,看你枚举了半天有没有刚开始的差值小,如果是初始差值小,输出中立阵营,否则输出你枚举的兵营咯。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> using namespace std; long long Line[500000]; long long n,p1,s1,s2,m,p2; long long Dragon,Tiger,MinLess,Buding,Index,Yuan; //bool TheSame(long long a,long long b){ // if(b>a){ // TheSame(b,a); // } // return a-b<0.00001; //} int main(){ //freopen("fight.in","r",stdin); //freopen("fight.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d",&n); //Minless=9999999; p2=99999999; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&Line[i]); } scanf("%d%d%d%d",&m,&p1,&s1,&s2); Line[p1]+=s1; for(int i=1;i<m;i++){ Dragon+=Line[i]*(m-i); } for(int i=m+1;i<=n;i++){ Tiger+=Line[i]*(i-m); } // if(TheSame(Dragon,Tiger)){ // printf("%d",m); // return 0; // } if(Dragon<Tiger){ // cout<<"阶段1"<<endl; MinLess=abs(Dragon-Tiger); Yuan=MinLess; // cout<<"初始差距为"<<Yuan<<endl; for(int i=1;i<m;i++){ Buding=s2*(m-i); Index=abs(Yuan-Buding); // cout<<"放入节点"<<i<<"所增加的势力为"<<Buding<<endl; // cout<<"此时的龙虎差距为"<<Index<<endl; // cout<<"截止未更新本次前,最小差值为"<<MinLess<<endl; if(Index<MinLess){ MinLess=Index; // cout<<"目标被更换"<<endl; p2=i; } } } else{ // cout<<"阶段2"<<endl; MinLess=abs(Tiger-Dragon); Yuan=MinLess; // cout<<"初始差距为"<<Yuan<<endl; for(int i=m+1;i<=n;i++){ Buding=s2*(i-m); Index=abs(Yuan-Buding); // cout<<"放入节点"<<i<<"所增加的势力为"<<Buding<<endl; // cout<<"此时的龙虎差距为"<<Index<<endl; // cout<<"截止未更新本次前,最小差值为"<<MinLess<<endl; if(Index<MinLess){ MinLess=Index; p2=i; } } } if(MinLess>Yuan){ printf("%d",m); // cout<<"引用自Yuan"; } else{ if(p2==99999999){ printf("%d",m); return 0; } printf("%d",p2); // cout<<"引用自p2"; } return 0; }
但是我没开Long Long呀~(淦)
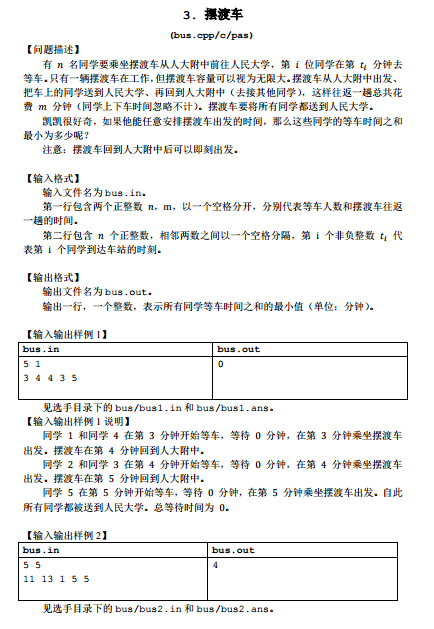
C. 【NOIP2018普及组】摆渡车

D. 【NOIP2018普及组】对称二叉树
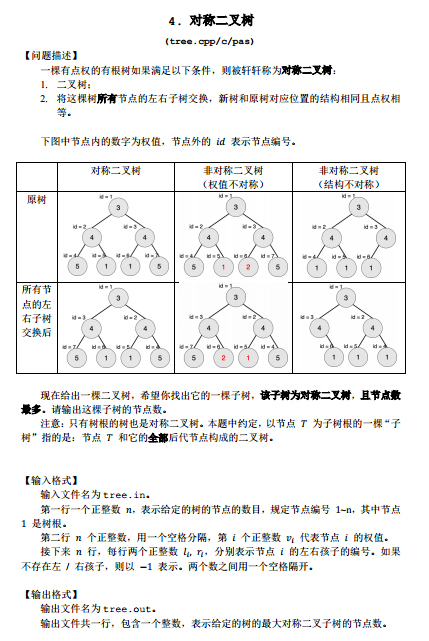


这个题比较尴尬。我误以为必须是那种左右子节点都存在并且权值相等才算对称,然而并不是。并且我的第一想法是去搭建数组并且通过一番递归计算来还原这棵树,然而,这题的端点极限是10^6,如果用数组来模拟,在最差的情况下(线性向下节点),一定会导致爆炸多的空白数据,从而导致根本没有那么大的数组可以构建这棵树。所以虽然建树模拟写得可以,在建树的同时就已经计算了子节点个数,但依旧没什么卵用。拿了个12分。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; struct Node{ int Val; int Id; int pos; int childs; bool SamePossible; }Tree[40000000]; int n,vi,li,ri,ans,maxer; int Vals[40000000]; int child[40000000][3]; void BuildTree(Node now){ if(now.pos>=maxer){ maxer=now.pos; } Tree[now.pos].SamePossible=true; if(now.Id==-1){ Tree[(now.pos)/2].childs--; return; } Tree[now.pos].childs+=2; Tree[now.pos].Val=Vals[now.Id]; Tree[now.pos*2].Id=child[now.Id][1]; Tree[now.pos*2].pos=now.pos*2; Tree[now.pos*2+1].Id=child[now.Id][2]; Tree[now.pos*2+1].pos=now.pos*2+1; BuildTree(Tree[now.pos*2]); BuildTree(Tree[now.pos*2+1]); Tree[now.pos].childs+=Tree[now.pos*2].childs+Tree[now.pos*2+1].childs; } bool IsSame(Node now){ if(now.SamePossible==false){ return false; } if(now.Val==0){ int father=now.pos/2; if(Tree[father*2].Val==Tree[father*2+1].Val){ return true; } return false; } if(IsSame(Tree[now.pos*2])&&IsSame(Tree[now.pos*2+1])){ return true; } else{ Tree[now.pos].SamePossible=false; return false; } } int main(){ //freopen("tree.in","r",stdin); //freopen("tree.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&Vals[i]); } Tree[1].Id=1;Tree[1].Val=Vals[1];Tree[1].pos=1;Tree[1].SamePossible=true; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&li,&ri); child[i][1]=li; child[i][2]=ri; } BuildTree(Tree[1]); for(int i=1;i<=maxer+1;i++){ if(IsSame(Tree[i])){ //cout<<"第"<<i<<"个节点是对称"<<endl; ans=max(ans,Tree[i].childs+1); } else{ //cout<<"第"<<i<<"个节点不是对称"<<endl; Tree[i].SamePossible=false; } } // for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++){ // cout<<"第"<<i<<"个节点的状态"<<endl; // cout<<Tree[i].Id<<" "<<Tree[i].Val<<" "<<Tree[i].childs<<" "<<Tree[i].SamePossible; // cout<<endl; // } printf("%d",ans); }
于是就开始重构,参考了下洛谷的题解,这道题其实不用忙着把树老老实实还原了。看来本来挺简单道题,被想复杂了呢。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long /* 代码来自Luo Gu Koakuma 已经完全理解并可以重构 */ const int maxn = 2000000; using namespace std; ll a[maxn], l[maxn], r[maxn]; ll ans, N; /* a数组存节点数值,l[i]表示编号为i的节点的左孩子的编号, r[i]表示编号为i的节点的右孩子的编号 */ bool f; //全局变量f判断是否为对称二叉子树 inline ll cnt(ll x) //计算以x为根节点的对称二叉子树的节点数 *递归 { ll sum = 0; if(l[x] != -1) sum += cnt(l[x]); if(r[x] != -1) sum += cnt(r[x]); return sum + 1; //别忘了根节点 } void work(ll xx,ll yy) //判断对称二叉子树的函数 *递归 { if(xx == -1 && yy == -1)return ; //如果已经到底了,结束 if(xx == -1 || yy == -1 || a[xx] != a[yy]){ f = 0; return ;} //不对称 work(l[xx], r[yy]); work(r[xx], l[yy]); } int main() { cin >> N;//读入n for (int i = 1 ; i <= N ; ++i) //读入每个节点的值 scanf("%lld", &a[i]); for (int i = 1 ; i <= N ; ++i) //读入每个节点的左右孩子节点编号 scanf("%lld%lld", &l[i], &r[i]); ans = 1; //至少有一个对称(一个节点) for (int i = 1 ; i <= N ; ++i) //枚举对称二叉子树的根节点 if (l[i] != -1 && r[i] != -1 && a[l[i]] == a[r[i]]) //这里可以过滤掉很多不必要的枚举 { f = true; //先默认为是对称二叉子树 work(l[i],r[i]); //开始递归判断 if (f == true) ans = max(ans, cnt(i)); //如果是对称二叉子树就可以计算节点取最大值了 } printf("%lld\n", ans); return 0; }
而关于这一句
work(l[xx],r[yy]); work(r[xx],l[yy]);
其实就是我犯得错误,它是两边对称的…呵,万恶之源。