1. 什么是Vue.js
- 目前最火的两大框架之一,另一个框架为React,不同的是React可以开发App,Vue.就是需要借助于Weex。
- 是前端三大主流框架之一,还有一个框架为Angular.js。
- Vue.js是一套用于构建用户界面的框架,只关注视图层
- 能够让用户不再操作DOM元素,解放用户双手,有恒多的事件去关注业务逻辑。
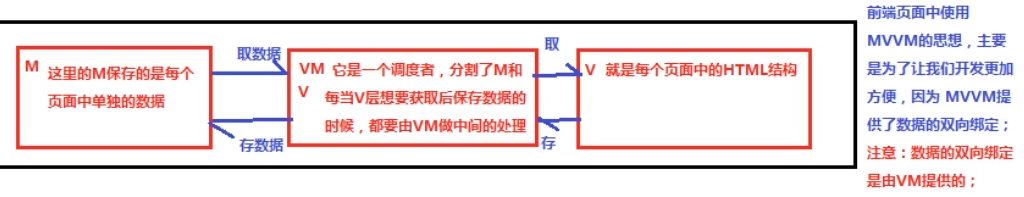
2. MVC和MVVM的区别
MVC:
 MVVM:
MVVM:

3. Vue的学习
1. 第一个hello world
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Vue的基本代码</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Vue实例所控制的这个元素区域,就是我们的V -->
<div id="app">
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</div>
<script>
//创建一个Vue的实例
//new出来的这个vm对象,就是我们MVVM中的VM调度者
new Vue({
el:'#app',
//这里的data就是MVVM中的M ,专门用来保存每个页面的数据
data:{
msg:'欢迎学习Vue'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. vue基本属性方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>v-clock的学习</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
[v-cloak]{
display:none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- v-cloak 能够解决插值表达式闪烁的问题 -->
<p v-cloak>{{msg}}</p>
<!-- 默认v-text是没有闪烁问题的 -->
<!-- v-text会覆盖元素中原本的内容,但是 插值表达式 只会替换自己的这个占位符,不会将内容清空 -->
<h5 v-text="msg"></h5>
<div v-html="msg2">90789098</div>
<!-- v-bind中可以写合法的js表达式 缩写 : -->
<!-- v-on:事件绑定机制 缩写 @ -->
<input type="button" value="这是一个按钮" :title="mytitle + '132132'"
@click="show"/>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
msg:'123',
msg2:'<h1>我是一个H1标题</h1>',
mytitle:'这是一个title'
},
//这个methods属性中定义了当前Vue实例所有可用的方法
methods:{
show:function(){
alert("hello")
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
3. 一个简单的跑马灯实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 1.绑定一个点击事件
2.在按钮的事件处理函数中,写相关的逻辑代码:
拿到msg字符串,然后使用substring来进行字符串的截取操作,将第一个字符串截取出来放到最后一个位置
3.为了实现点击按钮自动截取,要把2步骤中的代码放到一个定时器中去 -->
<div id="app">
<button @click="lang">开始滚动</button>
<button @click="stop">低调</button>
<h4>{{msg}}</h4>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
msg:'猥琐发育,别浪。。。',
intervalId:null
},
methods:{
lang(){
if(this.intervalId!=null){
return;
}
// 如果想要获取data上的数据或者是想要调用methods中的方法,
// 必须使用this.数据属性名 或 this.方法名来进行访问
//开启一个定时器,每0.4秒执行一次操作
//=>用来解决this的指向问题,这样函数内部和外部使用的this保持一致
this.intervalId = setInterval(() => {
var start=this.msg.substring(0,1)
var end=this.msg.substring(1)
//vm实例会监听自己身上data数据的改变,只要数据已发生变化,就会自动把最新的数据从data上同步到页面中去
//程序员只需要关心数据,不需要渲染页面
this.msg=end+start
},400)
},
//停止定时器
stop(){
clearInterval(this.intervalId)
//每当清除了定时期之后需要重新赋值为null
this.intervalId=null
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. v-on的事件修饰符

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
.inner{
height:150px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.outer{
padding: 40px;
background-color: crimson;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Vue实例所控制的这个元素区域,就是我们的V -->
<div id="app" >
<!-- <div class="inner" @click="div1Handler">
//使用.stop阻止冒泡
<button @click.stop="btnHandler">戳他</button>
</div> -->
<!-- 使用.prevent阻止默认行为 -->
<!-- <a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="linkclick">百度一下</a> -->
<!-- 使用.capture实现捕获触发事件的机制 -->
<!-- <div class="inner" @click.capture="div1Handler">
<button @click="btnHandler">戳他</button>
</div> -->
<!-- 使用.self实现只有点击当前元素的时候才会触发事件机制 -->
<!-- <div class="inner" @click.self="div1Handler">
<button @click="btnHandler">戳他</button>
</div> -->
<!-- 使用.once指触发一次事件 -->
<!-- <a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent.once="linkclick">百度一下</a> -->
<!-- 演示 .stop 和 .self 的区别 -->
<!-- <div class="outer" @click="div2Handler">
<div class="inner" @click="div1Handler">
<button @click.stop="btnHandler">戳他</button>
</div>
</div> -->
<!-- .self 只会阻止自己身上的冒泡,并不会阻止其他的冒泡行为 -->
<div class="outer" @click="div2Handler">
<div class="inner" @click.self="div1Handler">
<button @click="btnHandler">戳他</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
//创建一个Vue的实例
//new出来的这个vm对象,就是我们MVVM中的VM调度者
new Vue({
el:'#app',
//这里的data就是MVVM中的M ,专门用来保存每个页面的数据
data:{
msg:'欢迎学习Vue'
},
methods:{
div1Handler(){
console.log('这是出发了inner div的点击事件')
},
btnHandler(){
console.log('这是触发了按钮的点击事件')
},
linkclick(){
console.log('这是触发了跳转的点击事件');
},
div2Handler(){
console.log('c触发outer的点击事件')
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
5. v-model双向绑定
我们这里使用v-model双向绑定来写一个计算器类:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="n1" />
<select v-model="opt">
<option value="+">+</option>
<option value="-">-</option>
<option value="*">*</option>
<option value="/">/</option>
</select>
<input type="text" v-model="n2"/>
<input type="button" value="=" @click="calc"/>
<input type="text" v-model="result" />
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
n1:0,
n2:0,
result:0,
opt:'*'
},
methods:{
calc(){ //计算器算数的方法
// switch (this.opt){
// case '+':
// this.result=parseInt(this.n1)+parseInt(this.n2)
// break;
// case '-':
// this.result=parseInt(this.n1)-parseInt(this.n2)
// break;
// case '*':
// this.result=parseInt(this.n1)*parseInt(this.n2)
// break;
// case '/':
// if(this.n2!=0){
// this.result=parseInt(this.n1)/parseInt(this.n2)
// break;
// }else{
// console.log("除数不能够为0")
// }
// }
//注意:这个方式很投机取巧,正式开发中少用
var codeStr='parseInt(this.n1)'+this.opt+'parseInt(this.n2)'
this.result=eval(codeStr)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
6. 使用class样式

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
.red{
color: red;
}
.thin{
font_weight:200;
}
.italic{
font-style: italic;
}
.active{
letter-spacing: 0.5em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 使用数组来添加样式 -->
<!-- 数组中还有三元表达式 -->
<!-- <h1 :class="['red','italic',flag ? 'active':'']">干巴得啊小伙伴们</h1> -->
<!-- 使用对象来代替三元表达式,提高可读性 -->
<!-- <h1 :class="['red','italic',{'active':flag}]">干巴得啊小伙伴们</h1> -->
<!-- 直接使用对象-->
<h1 :class=classObj>干巴得啊小伙伴们</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
flag:false,
classObj:{red:true,thin:true,italic:true,active:false}
},
methods:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
7.使用内联样式

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Vue入门</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 对象就是无序键值对的集合 -->
<h1 :style="[styleObj,styleObj2]">喵喵喵</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
styleObj:{color:'red','font-weight':200},
styleObj2:{'font-style':'italic'}
},
methods:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
8. v-for循环四种元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- <p v-for="(item,index) in list" key="index">索引值:{{index}}----数组的值:{{item}}</p> -->
<!-- 循环对象数组 -->
<!-- <p v-for="(user,index) in list">{{user.id}} --- 名字:{{user.name}}</p> -->
<!-- 循环对象 -->
<!-- <p v-for="(val,key,i) in user">值是:{{val}}---键是:{{key}}---索引:{{i}}</p> -->
<!-- 迭代数字,item从1开始 -->
<p v-for="item in 10">这是第{{item}}次循环</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
// list:[
// {id:1,name:'kaishui'},
// {id:3,name:'hong'},
// {id:0,name:'yoyo'},
// {id:8,name:'qing'}
// ]
// user:{
// id:1,
// name:'lalala',
// gender:'nan'
// }
},
methods:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
9. v-key的使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Vue入门</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>
<label>Id:
<input type="text" v-model="id"/>
</label>
<label>Name:
<input type="text" v-model="name" />
</label>
<button @click="add">添加</button>
</div>
<!-- 注意:v-for循环的时候,key属性只能够使用number或string-->
<!-- key在使用的时候必须使用v-bind属性绑定形式,指定key的值 -->
<!-- 在组件中使用v-for循环的时候,或者在一些特殊情况中如果v-for有问题,必须在使用v-for的同时指定唯一的字符串、数字类型key值 -->
<p v-for="item in list" :key="item.id">
<input type="checkbox" />
{{item.id}}----{{item.name}}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
list:[
{id:1,name:'李斯'},
{id:2,name:'嬴政'},
{id:3,name:'赵高'},
{id:4,name:'韩非'},
{id:5,name:'荀子'}
]
},
methods:{
add(){ //添加方法
this.list.unshift({id:this.id,name:this.name})
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
10.v-if 和 v-show 的区别
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<button @click="flag=!flag" >toggle</button>
<!-- v-if 每次都会重新删除或者创建元素 -->
<!-- 有较高的切换性能消耗 -->
<h3 v-if=flag>这是用v-if控制的元素</h3>
<!-- v-show 每次不会进行DOM的删除和创建操作,只是切换了元素的display:none样式 -->
<!-- 有较高的初始渲染消耗 -->
<h3 v-show=flag>这是用v-show控制的元素</h3>
<!-- 如果元素涉及到频繁的切换,最好不用使用v-if -->
<!-- 如果元素可能永远也不会被显示出来被用户看到,则推荐使用v-if -->
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
flag:true
},
methods:{
// toggle(){
// this.flag=!this.flag
// }
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>