How to train Boosted Trees models in TensorFlow
本教程是使用带有tf.estimator API的决策树训练Gradient Boosting模型的端到端演练。 Boosted Trees模型是回归和分类中最受欢迎和最有效的机器学习方法之一。 这是一种集合技术,它结合了几种(认为10s,100s甚至1000s)树模型的预测。
Boosted Trees模型在许多机器学习实践中很受欢迎,因为它们可以通过最小的超参数调整实现令人印象深刻的性能。
加载titanic数据集
您将使用泰坦尼克数据集,其中(相当病态)的目标是预测乘客的生存,给出性别,年龄,等级等特征。
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
tf.enable_eager_execution()
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
tf.set_random_seed(123)
# Load dataset.
dftrain = pd.read_csv('https://storage.googleapis.com/tfbt/titanic_train.csv')
dfeval = pd.read_csv('https://storage.googleapis.com/tfbt/titanic_eval.csv')
y_train = dftrain.pop('survived')
y_eval = dfeval.pop('survived')
数据集由训练集和评估集组成:
dftrain和y_train是训练集* - 模型用来学习的数据。
模型根据 eval set *,dfeval和y_eval进行测试。
对于培训,您将使用以下功能:
| Feature Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sex | Gender of passenger |
| age | Age of passenger |
| n_siblings_spouses | # siblings and partners aboard |
| parch | # of parents and children aboard |
| fare | Fare passenger paid. |
| class | Passenger's class on ship |
| deck | Which deck passenger was on |
| embark_town | Which town passenger embarked from |
| alone | If passenger was alone |
Explore the data
让我们首先预览一些数据,并在训练集上创建摘要统计。
dftrain.head()
dftrain.describe()
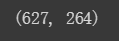
培训和评估集分别有627和264个例子。
dftrain.shape[0], dfeval.shape[0]
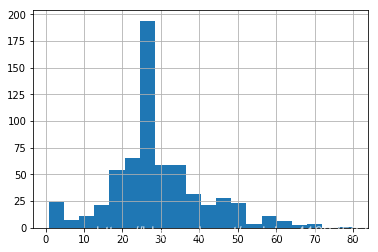
大多数乘客都在20和30年代。
dftrain.age.hist(bins=20)
plt.show()
男乘客大约是女乘客的两倍。
dftrain.sex.value_counts().plot(kind='barh')
plt.show()

大多数乘客都在“第三”类。
(dftrain['class']
.value_counts()
.plot(kind='barh'))
plt.show()

大多数乘客从南安普敦出发。
(dftrain['embark_town']
.value_counts()
.plot(kind='barh'))
plt.show()

Females have a much higher chance of surviving vs. males. This will clearly be a predictive feature for the model.
与男性相比,女性存活的机率要高得多。 这显然是该模型的预测特征。
ax = (pd.concat([dftrain, y_train], axis=1)\
.groupby('sex')
.survived
.mean()
.plot(kind='barh'))
ax.set_xlabel('% survive')
plt.show()

Create feature columns and input functions
Gradient Boosting估算器可以使用数字和分类功能。 功能列适用于所有TensorFlow估算器,其目的是定义用于建模的功能。 此外,它们还提供一些功能工程功能,如单热编码,规范化和bucketization。 在本教程中,CATEGORICAL_COLUMNS中的字段从分类列转换为单热编码列(指标列):
fc = tf.feature_column
CATEGORICAL_COLUMNS = ['sex', 'n_siblings_spouses', 'parch', 'class', 'deck',
'embark_town', 'alone']
NUMERIC_COLUMNS = ['age', 'fare']
def one_hot_cat_column(feature_name, vocab):
return fc.indicator_column(
fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(feature_name,
vocab))
feature_columns = []
for feature_name in CATEGORICAL_COLUMNS:
# Need to one-hot encode categorical features.
vocabulary = dftrain[feature_name].unique()
feature_columns.append(one_hot_cat_column(feature_name, vocabulary))
for feature_name in NUMERIC_COLUMNS:
feature_columns.append(fc.numeric_column(feature_name,
dtype=tf.float32))
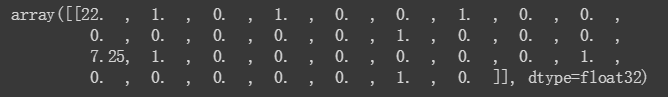
You can view the transformation that a feature column produces. For example, here is the output when using the indicator_column on a single example:
您可以查看要素列生成的转换。 例如,以下是在单个示例中使用indicator_column时的输出:
example = dftrain.head(1)
class_fc = one_hot_cat_column('class', ('First', 'Second', 'Third'))
print('Feature value: "{}"'.format(example['class'].iloc[0]))
print('One-hot encoded: ', fc.input_layer(dict(example), [class_fc]).numpy())
Additionally, you can view all of the feature column transformations together:
此外,您还可以一起查看所有要素列转换:
fc.input_layer(dict(example), feature_columns).numpy()
接下来,您需要创建输入函数。 这些将指定如何将数据读入我们的模型以进行训练和推理。 您将使用tf.dataAPI中的from_tensor_slices方法直接从Pandas读取数据。 这适用于较小的内存数据集。 对于较大的数据集,tf.data API支持各种文件格式(包括csv),以便您可以处理数据集 那些不适合记忆的。
# Use entire batch since this is such a small dataset.
NUM_EXAMPLES = len(y_train)
def make_input_fn(X, y, n_epochs=None, shuffle=True):
def input_fn():
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((dict(X), y))
if shuffle:
dataset = dataset.shuffle(NUM_EXAMPLES)
# For training, cycle thru dataset as many times as need (n_epochs=None).
dataset = dataset.repeat(n_epochs)
# In memory training doesn't use batching.
dataset = dataset.batch(NUM_EXAMPLES)
return dataset
return input_fn
# Training and evaluation input functions.
train_input_fn = make_input_fn(dftrain, y_train)
eval_input_fn = make_input_fn(dfeval, y_eval, shuffle=False, n_epochs=1)
Train and evaluate the model
您将在下面执行以下步骤:
1.初始化模型,指定要素和超参数。
2.使用train_input_fn将训练数据输入模型,并使用train函数训练模型。
3.您将使用此示例中的评估集评估模型性能,即“dfeval”DataFrame。 您将验证预测是否与y_eval数组中的标签匹配。
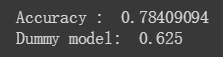
在训练Boosted Trees模型之前,让我们首先训练一个线性分类器(逻辑回归模型)。 最好的做法是从更简单的模型开始建立基准。
linear_est = tf.estimator.LinearClassifier(feature_columns)
# Train model.
linear_est.train(train_input_fn, max_steps=100)
# Evaluation.
results = linear_est.evaluate(eval_input_fn)
print('Accuracy : ', results['accuracy'])
print('Dummy model: ', results['accuracy_baseline'])
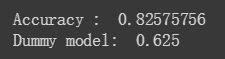
接下来让我们训练一下Boosted Trees模型。 对于增强树,支持回归(BoostedTreesRegressor)和分类(BoostedTreesClassifier),以及使用任何两次可微分的自定义丢失(BoostedTreesEstimator)。 由于目标是预测一个类 - 生存或不生存,你将使用BoostedTreesClassifier。
# Since data fits into memory, use entire dataset per layer. It will be faster.
# Above one batch is defined as the entire dataset.
n_batches = 1
est = tf.estimator.BoostedTreesClassifier(feature_columns,
n_batches_per_layer=n_batches)
# The model will stop training once the specified number of trees is built, not
# based on the number of steps.
est.train(train_input_fn, max_steps=100)
# Eval.
results = est.evaluate(eval_input_fn)
print('Accuracy : ', results['accuracy'])
print('Dummy model: ', results['accuracy_baseline'])
出于性能原因,当您的数据适合内存时,建议使用boosted_trees_classifier_train_in_memory函数。 但是,如果培训时间不是问题,或者您有一个非常大的数据集并且想要进行分布式培训,请使用上面显示的tf.estimator.BoostedTrees API。
使用此方法时,不应批量输入数据,因为该方法对整个数据集进行操作。
def make_inmemory_train_input_fn(X, y):
def input_fn():
return dict(X), y
return input_fn
train_input_fn = make_inmemory_train_input_fn(dftrain, y_train)
eval_input_fn = make_input_fn(dfeval, y_eval, shuffle=False, n_epochs=1)
est = tf.contrib.estimator.boosted_trees_classifier_train_in_memory(
train_input_fn,
feature_columns)
print(est.evaluate(eval_input_fn)['accuracy'])
现在,您可以使用列车模型从评估集中对乘客进行预测。 TensorFlow模型经过优化,可以同时对样本的批处理或集合进行预测。 之前,eval_input_fn是使用整个评估集定义的。
pred_dicts = list(est.predict(eval_input_fn))
probs = pd.Series([pred['probabilities'][1] for pred in pred_dicts])
probs.plot(kind='hist', bins=20, title='predicted probabilities')
plt.show()

最后,您还可以查看结果的接收器操作特性(ROC),这将使我们更好地了解真阳性率和假阳性率之间的权衡。
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_eval, probs)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.title('ROC curve')
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.xlim(0,)
plt.ylim(0,)
plt.show()