文章目录
Trie 字典树 前缀树
什么是Trie
基本概念
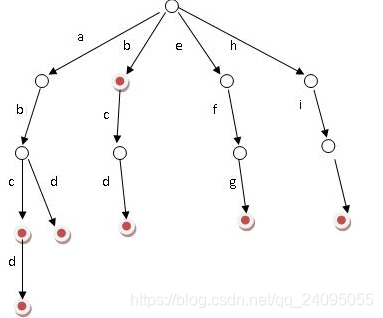
字典树,又称为单词查找树,Trie树,是一种树形结构,它是一种哈希表的变种。
基本性质
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符
- 从根节点到某一节点。路径上经过的字符连接起来,就是该节点对应的字符串
- 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符串都不相同
应用场景
典型应用就是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(不仅限于字符串),经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。
优点
利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度的减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希树高。
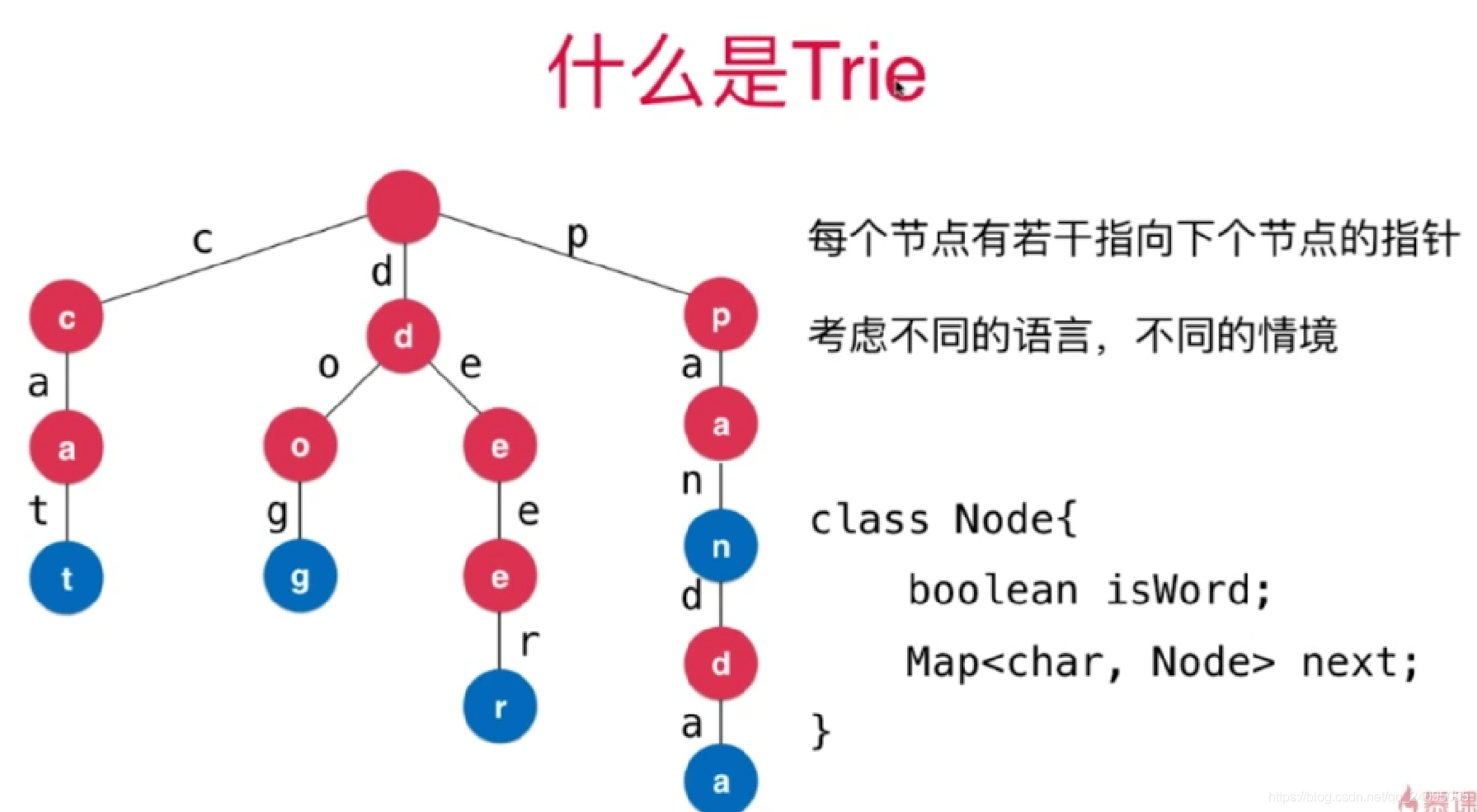
例如下面是一个统计字符串的字典树
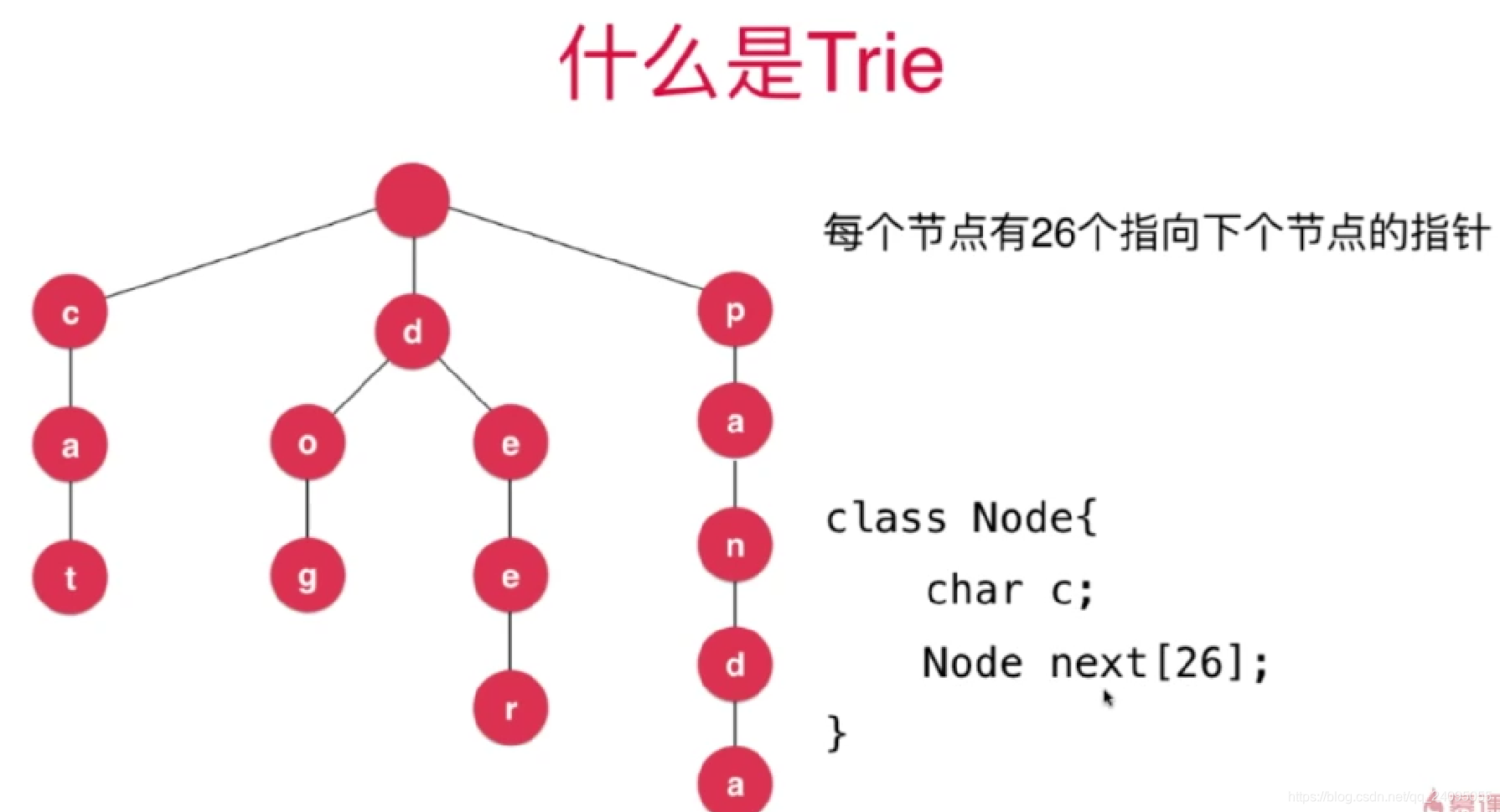
当然这里26是不考虑大小写和其他字符的。
每个节点有若干个指向下个节点的指针
考虑不同的语言,不同的情景,指针数量也不一样
可以用如下的Node结构
class Node{
char c;
Map<char, Node> next;
}
手写一个trie
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Trie {
private class Node{
public boolean isWord;
public TreeMap<Character, Node> next;
public Node(boolean isWord){
this.isWord = isWord;
next = new TreeMap<>();
}
public Node(){
this(false);
}
}
private Node root;
private int size;
public Trie(){
root = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获得Trie中存储的单词数量
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 向Trie中添加一个新的单词word (非递归写法)
public void add(String word){
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0 ; i < word.length() ; i ++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.next.get(c) == null)
cur.next.put(c, new Node());
cur = cur.next.get(c);
}
if (!cur.isWord){
cur.isWord = true;
size ++;
}
}
// 查询单词word是否在Trie中
public boolean contains(String word){
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0 ; i < word.length() ; i ++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.next.get(c) == null)
return false;
cur = cur.next.get(c);
}
return cur.isWord;
}
}
Trie字典树的前缀查询
// 查询是否在Trie中有单词以prefix为前缀
public boolean isPrefix(String prefix){
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0 ; i < prefix.length() ; i ++){
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
if (cur.next.get(c) == null)
return false;
cur = cur.next.get(c);
}
return true;
}
实现Trie(前缀树) LeetCode208
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-trie-prefix-tree/
答案就是我们上面手写的Trie,改掉对应方法名即可。
添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计LeetCode 211
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-and-search-word-data-structure-design/
题目描述:
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
void addWord(word)
bool search(word)
search(word) 可以搜索文字或正则表达式字符串,字符串只包含字母 . 或 a-z 。 . 可以表示任何一个字母。
示例:
addWord(“bad”)
addWord(“dad”)
addWord(“mad”)
search(“pad”) -> false
search(“bad”) -> true
search(".ad") -> true
search(“b…”) -> true
说明:
你可以假设所有单词都是由小写字母 a-z 组成的。
解答代码:
class WordDictionary {
private class Node {
boolean isEnd;
Node[] next;
Node() {
isEnd = false;
next = new Node[26];
}
}
Node root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public WordDictionary() {
root = new Node();
}
/** Adds a word into the data structure. */
public void addWord(String word) {
Node curr = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
index = c - 'a';
if (curr.next[index] == null) {
curr.next[index] = new Node();
}
curr = curr.next[index];
}
curr.isEnd = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter. */
public boolean search(String word) {
return heleper(word, 0, root);
}
/**
*
* @param word 要查找的单词
* @param len 当前已经确定的长度
* @param root 根节点
* @return
*/
private boolean heleper(String word, int len, Node root) {
//递归出口
if (word.length() == len && root.isEnd) return true;
if (word.length() == len) return false;
char c = word.charAt(len);
int index = c - 'a';
//通配符
if (c == '.') {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (root.next[i] != null) {
Node curr = root.next[i];
if (heleper(word, len + 1, curr)) {
return true;
}
}
}
} else {
root = root.next[index];
if (root == null) return false;
return heleper(word, len + 1, root);
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Your WordDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such:
* WordDictionary obj = new WordDictionary();
* obj.addWord(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
*/
键值映射LeetCode677
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/map-sum-pairs/
问题描述
实现一个 MapSum 类里的两个方法,insert 和 sum。
对于方法 insert,你将得到一对(字符串,整数)的键值对。字符串表示键,整数表示值。如果键已经存在,那么原来的键值对将被替代成新的键值对。
对于方法 sum,你将得到一个表示前缀的字符串,你需要返回所有以该前缀开头的键的值的总和。
示例 1:
输入: insert(“apple”, 3), 输出: Null
输入: sum(“ap”), 输出: 3
输入: insert(“app”, 2), 输出: Null
输入: sum(“ap”), 输出: 5
解答:
首先可以使用基础的HashMap解决
import java.util.HashMap;
class MapSum {
HashMap<String, Integer> map;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MapSum() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public void insert(String key, int val) {
map.put(key, val);
}
public int sum(String prefix) {
int sum = 0;
for (String key : map.keySet()){
if (key.length() >= prefix.length() && key.substring(0,prefix.length()).equals(prefix))
sum += map.get(key);
}
return sum;
}
}
/**
* Your MapSum object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MapSum obj = new MapSum();
* obj.insert(key,val);
* int param_2 = obj.sum(prefix);
*/
使用字典树的方式:
import java.util.TreeMap;
class MapSum {
private class Node{
public int value;
public TreeMap<Character, Node> next;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
next = new TreeMap<>();
}
public Node(){
this(0);
}
}
private Node root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MapSum() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word, int val) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0 ; i < word.length() ; i ++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.next.get(c) == null)
cur.next.put(c, new Node());
cur = cur.next.get(c);
}
cur.value = val;
}
public int sum(String prefix) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0 ; i < prefix.length() ; i ++){
char c =prefix.charAt(i);
if (cur.next.get(c) == null)
return 0;
cur = cur.next.get(c);
}
// 找到所有以cur为根节点的子树将他们的value遍历求和 此时cur指向的已经是prefix最后一个字符即前缀找到了
return sum(cur);
}
private int sum(Node node){
// 递归到底的情况 其实不写也没事 不会进入到for中
if (node.next.size() == 0)
return node.value;
int res = node.value;
for (char c : node.next.keySet())
res += sum(node.next.get(c));
return res;
}
}
/**
* Your MapSum object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MapSum obj = new MapSum();
* obj.insert(key,val);
* int param_2 = obj.sum(prefix);
*/
可以看到用时比HashMap小很多。
Trie的缺点:空间问题!
仅以小写字母表为例,一个节点就要包含自身的值和一个大小为26的数组,空间大小要用到27n。