原文:https://blog.csdn.net/guoqifa29/article/details/40504189 (注解比较详细,可以辅助阅读源码,感谢原文作者)
启动横屏应用时的整个逻辑:首先会从WindowManagerService那边获取屏幕的方向,然后再设置到ActivityManagerService中来,最后再启动Window的显示逻辑。
这三个步骤分别对应下面这三个函数(横屏最重要的三个调用函数):
(1). WindowManagerService.updateRotationUncheckedLocked()
(2). ActivityManagerService.updateConfigurationLocked(config, r, false, false)
(3). WindowManagerService.setNewConfiguration(mConfiguration)
这三个函数是配套使用的。对于转屏应用,首先是
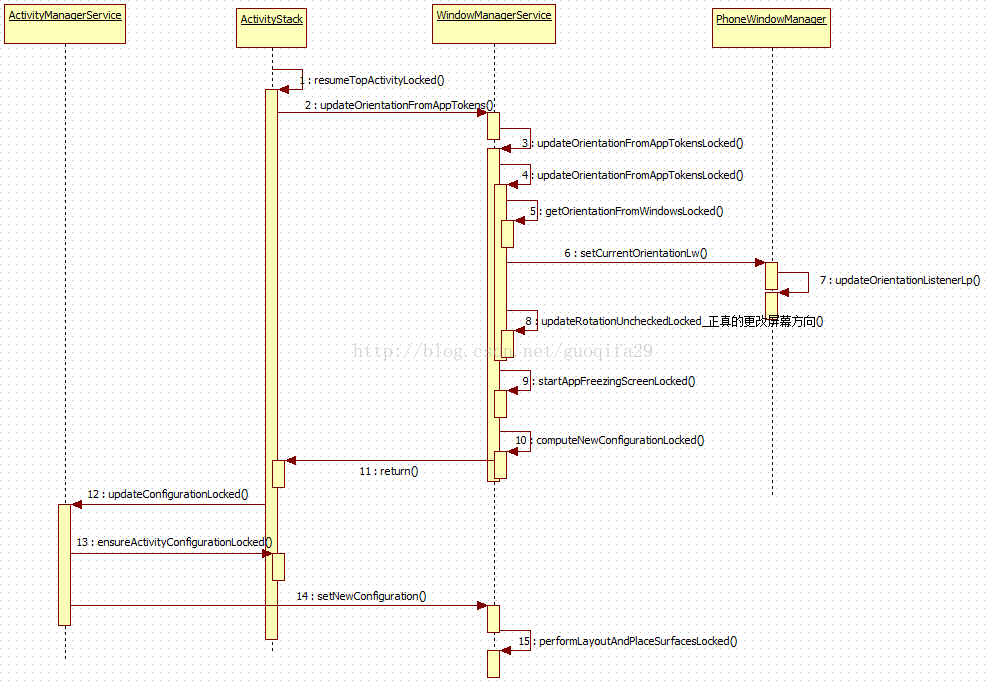
我们找一个具体的转屏场景来分析,启动横屏activity。先给出时序图:
step1、WMS.updateOrientationFromAppTokens()
- public Configuration updateOrientationFromAppTokens(
- Configuration currentConfig, IBinder freezeThisOneIfNeeded) {
- if (!checkCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.MANAGE_APP_TOKENS,
- "updateOrientationFromAppTokens()")) {
- throw new SecurityException("Requires MANAGE_APP_TOKENS permission");
- }
- Configuration config = null;
- long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
- synchronized(mWindowMap) {
- config = updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked(currentConfig,
- freezeThisOneIfNeeded);
- }
- Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
- return config;
- }
step2、updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked()
- private Configuration updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked(
- Configuration currentConfig, IBinder freezeThisOneIfNeeded) {
- Configuration config = null;
- if (updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked(false)) { //①满足这个条件是很苛刻的:从函数名就可以看出来是从可见的应用窗口获取orientation,并且orientation与last orientation不同,同时还必须将new orientation成功update到WMS中,也就是updateRotationUncheckedLocked()也要返回TRUE;
- if (freezeThisOneIfNeeded != null) {
- AppWindowToken atoken = findAppWindowToken(freezeThisOneIfNeeded);
- if (atoken != null) { //②屏幕旋转,并且freezeThisOneIfNeeded不为null,那么调用startAppFreezingScreenLocked()冻结screen;
- startAppFreezingScreenLocked(atoken, ActivityInfo.CONFIG_ORIENTATION);
- }
- }
- config = computeNewConfigurationLocked(); //③调用computeNewConfigurationLocked()计算config;
- } else if (currentConfig != null) { //④什么时候会走这个逻辑呢,具体看step3和step4中return false情况,也就是说没有update new orientation到WMS中。包括,1.可见应用窗口orientation与上一次相同;2.orientation与上一次不同,但是前一次转屏动画还在播放;3.屏幕是灭屏状态;4.PhoneWindowManager策略类综合出的orientation跟上一次相同;;
- // No obvious action we need to take, but if our current
- // state mismatches the activity manager's, update it,
- // disregarding font scale, which should remain set to
- // the value of the previous configuration.
- mTempConfiguration.setToDefaults(); //⑤下面这些逻辑就是即使不从应用窗口更改orientation,还有其他config需要核对差异。
- mTempConfiguration.fontScale = currentConfig.fontScale;
- //Flyme Theme: save the theme flag.
- mTempConfiguration.themeChanged = currentConfig.themeChanged;
- //Flyme Theme: save the theme flag.
- if (computeScreenConfigurationLocked(mTempConfiguration)) {
- if (currentConfig.diff(mTempConfiguration) != 0) {
- mWaitingForConfig = true;
- final DisplayContent displayContent = getDefaultDisplayContentLocked();
- displayContent.layoutNeeded = true;
- int anim[] = new int[2];
- if (displayContent.isDimming()) {
- anim[0] = anim[1] = 0;
- } else {
- mPolicy.selectRotationAnimationLw(anim);
- }
- startFreezingDisplayLocked(false, anim[0], anim[1]);
- config = new Configuration(mTempConfiguration);
- }
- }
- }
- return config;
- }
- /*
- * Determine the new desired orientation of the display, returning
- * a non-null new Configuration if it has changed from the current
- * orientation. IF TRUE IS RETURNED SOMEONE MUST CALL
- * setNewConfiguration() TO TELL THE WINDOW MANAGER IT CAN UNFREEZE THE
- * SCREEN. This will typically be done for you if you call
- * sendNewConfiguration().
- *
- * The orientation is computed from non-application windows first. If none of
- * the non-application windows specify orientation, the orientation is computed from
- * application tokens.
- * @see android.view.IWindowManager#updateOrientationFromAppTokens(
- * android.os.IBinder)
- */
- boolean updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked(boolean inTransaction) {
- long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
- try {
- int req = getOrientationFromWindowsLocked(); //①从非activity窗口中提取orientation;
- if (req == ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_UNSPECIFIED) {
- req = getOrientationFromAppTokensLocked(); //②从activity窗口中提取orientation;
- }
- if (req != mForcedAppOrientation) { //③窗口设置的orientation与当前orientation不同,即更改orientation;
- mForcedAppOrientation = req; //④这个变量值得更改非常重要;
- //send a message to Policy indicating orientation change to take
- //action like disabling/enabling sensors etc.,
- mPolicy.setCurrentOrientationLw(req); //⑤告诉PhoneWindowManager orientation,这样采取关闭或开启sensor;比如打开一个强制横屏的窗口,那么必然要关闭sensor嘛,如何关闭,自然是关闭sensor的listener了!
- if (updateRotationUncheckedLocked(inTransaction)) { //⑥调用updateRotationUncheckedLocked()改变WMS侧屏幕方向,如果确实更新了orientation,那么返回TRUE,如果orientation没有更新,那自然返回false;
- // changed
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- } finally {
- Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
- }
- }
上面的解释的非常清楚这个函数是干嘛的,就是首先从非activity窗口中计算orientation,如果非activity窗口未指定orientation,那么接着从activity窗口中计算orientation。如果计算的orientation跟last不一样,那么首先调用PhoneWindowManager.setCurrentOrientationLw()打开或关闭sensor的listener;接着调用updateRotationUncheckedLocked()做出屏幕转变后WMS侧的处理逻辑。
上面逻辑中第④点中mForcedAppOrientation的赋值非常非常重要,为什么?因为当前启动的应用需要转屏,但是第⑥点中调用updateRotationUncheckedLocked()在很多场景下是无法update orientation的,比如前一个orientation 动画未播完或Rotation被Deferred等,难道就不update orientation了?当然不是,WMS这边在播完orientation动画、resumeRotation、亮屏、等一系列逻辑下会调用updateRotationUnchecked()函数,该函数会完成前面未完成的update orientation工作。看看updateRotationUnchecked()函数:
- public void updateRotationUnchecked(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration, boolean forceRelayout) {
- if(DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG, "updateRotationUnchecked("
- + "alwaysSendConfiguration=" + alwaysSendConfiguration + ")");
- long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
- boolean changed;
- synchronized(mWindowMap) {
- changed = updateRotationUncheckedLocked(false);
- if (!changed || forceRelayout) {
- getDefaultDisplayContentLocked().layoutNeeded = true;
- performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked();
- }
- }
- if (changed || alwaysSendConfiguration) {
- sendNewConfiguration();
- }
- Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
- }
- void sendNewConfiguration() {
- try {
- mActivityManager.updateConfiguration(null);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
- }
step4、updateRotationUncheckedLocked()
更新 new orientation 到WMS中来,如果更新失败,那么返回false,更新成功则返回true。如果更新失败,那么在其他逻辑完成后调用 updateRotationUnchecked()时会重新update orientation到WMS中来,正如step3中所说的mForcedAppOrientation是个关键变量,保存着request orientation。
- // TODO(multidisplay): Rotate any display?
- /**
- * Updates the current rotation.
- *
- * Returns true if the rotation has been changed. In this case YOU
- * MUST CALL sendNewConfiguration() TO UNFREEZE THE SCREEN.
- */
- public boolean updateRotationUncheckedLocked(boolean inTransaction) {
- if (mDeferredRotationPauseCount > 0) { //①如果调用了pauseRotationLocked()来pauses rotation changes,那么mDeferredRotationPauseCount值会加1,此时便不能change rotation;待调用resumeRotationLocked()将mDeferredRotationPauseCount值减为0,便会调用updateRotationUncheckedLocked()再次change rotation;
- // Rotation updates have been paused temporarily. Defer the update until
- // updates have been resumed.
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Deferring rotation, rotation is paused.");
- return false;
- }
- ScreenRotationAnimation screenRotationAnimation =
- mAnimator.getScreenRotationAnimationLocked(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
- if (screenRotationAnimation != null && screenRotationAnimation.isAnimating()) { //②如果此刻正在做屏幕旋转动画,也是不能change rotation的;
- // Rotation updates cannot be performed while the previous rotation change
- // animation is still in progress. Skip this update. We will try updating
- // again after the animation is finished and the display is unfrozen.
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Deferring rotation, animation in progress.");
- return false;
- }
- if (!mDisplayEnabled) { //③灭屏时也是不能change rotation的;
- // No point choosing a rotation if the display is not enabled.
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Deferring rotation, display is not enabled.");
- return false;
- }
- // TODO: Implement forced rotation changes.
- // Set mAltOrientation to indicate that the application is receiving
- // an orientation that has different metrics than it expected.
- // eg. Portrait instead of Landscape.
- int rotation = mPolicy.rotationForOrientationLw(mForcedAppOrientation, mRotation); //④根据mForcedAppOrientation和mRotation、传感器方向等值来综合考虑出orientation。mForcedAppOrientation保存着request orientation,mRotation是当前正在使用的屏幕方向。
- boolean altOrientation = !mPolicy.rotationHasCompatibleMetricsLw(
- mForcedAppOrientation, rotation);
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) {
- Slog.v(TAG, "Application requested orientation "
- + mForcedAppOrientation + ", got rotation " + rotation
- + " which has " + (altOrientation ? "incompatible" : "compatible")
- + " metrics");
- }
- if (mRotation == rotation && mAltOrientation == altOrientation) { //⑤如果综合出来的orientation与last orientation相同,便无需update orientation;
- // No change.
- return false;
- }
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) {
- Slog.v(TAG,
- "Rotation changed to " + rotation + (altOrientation ? " (alt)" : "")
- + " from " + mRotation + (mAltOrientation ? " (alt)" : "")
- + ", forceApp=" + mForcedAppOrientation);
- }
- //⑥以下逻辑是需要update orientation;
- mRotation = rotation;
- mAltOrientation = altOrientation;
- mPolicy.setRotationLw(mRotation); //⑦将mRotation设置到PhoneWindowManager中;
- mWindowsFreezingScreen = true; //⑧准备冻结屏幕;
- mH.removeMessages(H.WINDOW_FREEZE_TIMEOUT);
- mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.WINDOW_FREEZE_TIMEOUT, WINDOW_FREEZE_TIMEOUT_DURATION);
- mWaitingForConfig = true;
- final DisplayContent displayContent = getDefaultDisplayContentLocked();
- displayContent.layoutNeeded = true; //⑨layoutNeeded为true;这样needsLayout()函数就可以返回true;
- final int[] anim = new int[2];
- if (displayContent.isDimming()) {
- anim[0] = anim[1] = 0;
- } else {
- mPolicy.selectRotationAnimationLw(anim); //⑨PhoneWindowManager选择进入和退出转屏动画;
- }
- startFreezingDisplayLocked(inTransaction, anim[0], anim[1]); //⑨调用startFreezingDisplayLocked()冻结屏幕,参数中传入了进入和退出动画,这个函数在下面将详细分析;
- // startFreezingDisplayLocked can reset the ScreenRotationAnimation.
- screenRotationAnimation =
- mAnimator.getScreenRotationAnimationLocked(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY); //⑨获取DisplayContentsAnimator类对象,这个类中包含一个ScreenRotationAnimation类对象;
- // We need to update our screen size information to match the new
- // rotation. Note that this is redundant with the later call to
- // sendNewConfiguration() that must be called after this function
- // returns... however we need to do the screen size part of that
- // before then so we have the correct size to use when initializing
- // the rotation animation for the new rotation.
- computeScreenConfigurationLocked(null); //⑨更新DisplayInfo信息;
- final DisplayInfo displayInfo = displayContent.getDisplayInfo();
- if (!inTransaction) {
- if (SHOW_TRANSACTIONS) {
- Slog.i(TAG, ">>> OPEN TRANSACTION setRotationUnchecked");
- }
- SurfaceControl.openTransaction();
- }
- try {
- // NOTE: We disable the rotation in the emulator because
- // it doesn't support hardware OpenGL emulation yet.
- if (CUSTOM_SCREEN_ROTATION && screenRotationAnimation != null
- && screenRotationAnimation.hasScreenshot()) { //⑨create Rotation Matrix and set Matrix to mSurfaceControl(截图surface)
- if (screenRotationAnimation.setRotationInTransaction(
- rotation, mFxSession,
- MAX_ANIMATION_DURATION, mTransitionAnimationScale,
- displayInfo.logicalWidth, displayInfo.logicalHeight)) {
- scheduleAnimationLocked();
- }
- }
- mDisplayManagerService.performTraversalInTransactionFromWindowManager(); //⑨这个是干啥的??
- } finally {
- if (!inTransaction) {
- SurfaceControl.closeTransaction();
- if (SHOW_LIGHT_TRANSACTIONS) {
- Slog.i(TAG, "<<< CLOSE TRANSACTION setRotationUnchecked");
- }
- }
- }
- final WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
- for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //⑨对于未销毁surface的window,将WindowState.mOrientationChanging设为true;
- WindowState w = windows.get(i);
- if (w.mHasSurface
- // FLYME_BEGIN
- // FUNCTION:optimize the efficiency of rotating screen . added by fujinzhi. transplanted by duzhenhui.
- /*&& !w.prohibitRotation()*/
- // FLYME_END 2014.04.17
- ) {
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Set mOrientationChanging of " + w);
- w.mOrientationChanging = true;
- mInnerFields.mOrientationChangeComplete = false;
- }
- w.mLastFreezeDuration = 0;
- }
- for (int i=mRotationWatchers.size()-1; i>=0; i--) { //⑨将rotation发布到PhoneWindow、KeyguardFaceUnlockView、LegacySensorManager中去;重点是PhoneWindow,这个将在下面详细分析;
- try {
- mRotationWatchers.get(i).watcher.onRotationChanged(rotation);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
- }
- //TODO (multidisplay): Magnification is supported only for the default display.
- if (mDisplayMagnifier != null
- && displayContent.getDisplayId() == Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY) { //⑨如果打开手势放大,那么回调mDisplayMagnifier.onRotationChangedLocked()函数;
- mDisplayMagnifier.onRotationChangedLocked(getDefaultDisplayContentLocked(), rotation);
- }
- return true;
- }
这个函数是WMS侧的屏幕旋转逻辑主要处理函数,WMS侧几乎所有的屏幕旋转操作都在此函数中完成。AMS侧自然是updateConfigurationLocked()函数。
1)、PhoneWindowManager.setRotationLw(int rotation)将rotation传到PhoneWindowManager中去
- @Override
- public void setRotationLw(int rotation) {
- mOrientationListener.setCurrentRotation(rotation);
- }
- /**
- * Sets the current rotation.
- *
- * @param rotation The current rotation.
- */
- public void setCurrentRotation(int rotation) {
- synchronized (mLock) {
- mCurrentRotation = rotation;
- }
- }
2)、startFreezingDisplayLocked(inTransaction, anim[0], anim[1])函数,现在来详细研究下这个函数。
- private void startFreezingDisplayLocked(boolean inTransaction, int exitAnim, int enterAnim) {
- if (mDisplayFrozen) { //①mDisplayFrozen变量为true,表示正在调用startFreezingDisplayLocked()冻结屏幕,并且还未调用stopFreezingDisplayLocked()进行解冻;
- return;
- }
- if (!mDisplayReady || !mPolicy.isScreenOnFully()) { //②系统还未ready或灭屏状态(PhoneWindowManager.mScreenOnFully==false);
- // No need to freeze the screen before the system is ready or if
- // the screen is off.
- return;
- }
- mScreenFrozenLock.acquire(); //③获得一把唤醒锁,防止freeze screen期间系统灭屏并锁屏,锁屏会更改orientation;
- mDisplayFrozen = true;
- mDisplayFreezeTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
- mLastFinishedFreezeSource = null;
- mInputMonitor.freezeInputDispatchingLw(); //④freeze Input Dispatcher,也就是禁止触摸时间上报;
- // Clear the last input window -- that is just used for
- // clean transitions between IMEs, and if we are freezing
- // the screen then the whole world is changing behind the scenes.
- mPolicy.setLastInputMethodWindowLw(null, null);
- if (mAppTransition.isTransitionSet()) { //④如果设置了activity切换动画,那么调用mAppTransition.freeze()设置mAppTransitionState=APP_STATE_READY;
- mAppTransition.freeze();
- }
- if (PROFILE_ORIENTATION) {
- File file = new File("/data/system/frozen");
- Debug.startMethodTracing(file.toString(), 8 * 1024 * 1024);
- }
- if (CUSTOM_SCREEN_ROTATION) {
- mExitAnimId = exitAnim;
- mEnterAnimId = enterAnim;
- final DisplayContent displayContent = getDefaultDisplayContentLocked();
- final int displayId = displayContent.getDisplayId();
- ResSchedulerManager mResSchedulerManager;
- ScreenRotationAnimation screenRotationAnimation =
- mAnimator.getScreenRotationAnimationLocked(displayId);
- if (screenRotationAnimation != null) { //⑤如果上次转屏动画还在播放,那么kill掉;
- screenRotationAnimation.kill();
- }
- mResSchedulerManager = (ResSchedulerManager) mContext
- .getSystemService(Context.RES_SCHEDULER_SERVICE);
- mResSchedulerManager.dispatchSwitchPerfModeCMD(mResSchedulerManager.APP_ROTATE);
- // TODO(multidisplay): rotation on main screen only.
- screenRotationAnimation = new ScreenRotationAnimation(this,mContext, displayContent,
- mFxSession, inTransaction, mPolicy.isDefaultOrientationForced(),mDisableScreenRotationForHdmi);
- mAnimator.setScreenRotationAnimationLocked(displayId, screenRotationAnimation); //⑥设置一个ScreenRotationAnimation对象到DisplayContentsAnimator.mScreenRotationAnimation中;
- }
- }
总结起来这个函数就是静止灭屏、冻结触摸事件、创建ScreenRotationAnimation对象。难道这就是冻结屏幕???
3)、computeScreenConfigurationLocked(),来分析下。
- boolean computeScreenConfigurationLocked(Configuration config) {
- if (!mDisplayReady) {
- return false;
- }
- // TODO(multidisplay): For now, apply Configuration to main screen only.
- final DisplayContent displayContent = getDefaultDisplayContentLocked();
- // Use the effective "visual" dimensions based on current rotation
- final boolean rotated = (mRotation == Surface.ROTATION_90
- || mRotation == Surface.ROTATION_270); //①根据mRotation值,计算出屏幕宽度和高度;mRotation值在是在调用该函数之前已经更新;
- final int realdw = rotated ?
- displayContent.mBaseDisplayHeight : displayContent.mBaseDisplayWidth;
- final int realdh = rotated ?
- displayContent.mBaseDisplayWidth : displayContent.mBaseDisplayHeight;
- int dw = realdw;
- int dh = realdh;
- if (mAltOrientation) {
- if (realdw > realdh) {
- // Turn landscape into portrait.
- int maxw = (int)(realdh/1.3f);
- if (maxw < realdw) {
- dw = maxw;
- }
- } else {
- // Turn portrait into landscape.
- int maxh = (int)(realdw/1.3f);
- if (maxh < realdh) {
- dh = maxh;
- }
- }
- }
- if (config != null) {
- config.orientation = (dw <= dh) ? Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT :
- Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE;
- }
- // Update application display metrics.
- final int appWidth = mPolicy.getNonDecorDisplayWidth(dw, dh, mRotation);
- final int appHeight = mPolicy.getNonDecorDisplayHeight(dw, dh, mRotation);
- final DisplayInfo displayInfo = displayContent.getDisplayInfo();
- synchronized(displayContent.mDisplaySizeLock) {
- displayInfo.rotation = mRotation;
- displayInfo.logicalWidth = dw;
- displayInfo.logicalHeight = dh;
- displayInfo.logicalDensityDpi = displayContent.mBaseDisplayDensity;
- displayInfo.appWidth = appWidth;
- displayInfo.appHeight = appHeight;
- displayInfo.getLogicalMetrics(mRealDisplayMetrics,
- CompatibilityInfo.DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO, null);
- displayInfo.getAppMetrics(mDisplayMetrics);
- mDisplayManagerService.setDisplayInfoOverrideFromWindowManager(
- displayContent.getDisplayId(), displayInfo);
- }
- if (false) {
- Slog.i(TAG, "Set app display size: " + appWidth + " x " + appHeight);
- }
- final DisplayMetrics dm = mDisplayMetrics;
- mCompatibleScreenScale = CompatibilityInfo.computeCompatibleScaling(dm,
- mCompatDisplayMetrics);
- if (config != null) {
- config.screenWidthDp = (int)(mPolicy.getConfigDisplayWidth(dw, dh, mRotation)
- / dm.density);
- config.screenHeightDp = (int)(mPolicy.getConfigDisplayHeight(dw, dh, mRotation)
- / dm.density);
- computeSizeRangesAndScreenLayout(displayInfo, rotated, dw, dh, dm.density, config);
- config.compatScreenWidthDp = (int)(config.screenWidthDp / mCompatibleScreenScale);
- config.compatScreenHeightDp = (int)(config.screenHeightDp / mCompatibleScreenScale);
- config.compatSmallestScreenWidthDp = computeCompatSmallestWidth(rotated, dm, dw, dh);
- config.densityDpi = displayContent.mBaseDisplayDensity;
- // Update the configuration based on available input devices, lid switch,
- // and platform configuration.
- config.touchscreen = Configuration.TOUCHSCREEN_NOTOUCH;
- config.keyboard = Configuration.KEYBOARD_NOKEYS;
- config.navigation = Configuration.NAVIGATION_NONAV;
- int keyboardPresence = 0;
- int navigationPresence = 0;
- final InputDevice[] devices = mInputManager.getInputDevices();
- final int len = devices.length;
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- InputDevice device = devices[i];
- if (!device.isVirtual()) {
- final int sources = device.getSources();
- final int presenceFlag = device.isExternal() ?
- WindowManagerPolicy.PRESENCE_EXTERNAL :
- WindowManagerPolicy.PRESENCE_INTERNAL;
- if (mIsTouchDevice) {
- if ((sources & InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCHSCREEN) ==
- InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCHSCREEN) {
- config.touchscreen = Configuration.TOUCHSCREEN_FINGER;
- }
- } else {
- config.touchscreen = Configuration.TOUCHSCREEN_NOTOUCH;
- }
- if ((sources & InputDevice.SOURCE_TRACKBALL) == InputDevice.SOURCE_TRACKBALL) {
- config.navigation = Configuration.NAVIGATION_TRACKBALL;
- navigationPresence |= presenceFlag;
- } else if ((sources & InputDevice.SOURCE_DPAD) == InputDevice.SOURCE_DPAD
- && config.navigation == Configuration.NAVIGATION_NONAV) {
- config.navigation = Configuration.NAVIGATION_DPAD;
- navigationPresence |= presenceFlag;
- }
- if (device.getKeyboardType() == InputDevice.KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC) {
- config.keyboard = Configuration.KEYBOARD_QWERTY;
- keyboardPresence |= presenceFlag;
- }
- }
- }
- // Determine whether a hard keyboard is available and enabled.
- boolean hardKeyboardAvailable = config.keyboard != Configuration.KEYBOARD_NOKEYS;
- if (hardKeyboardAvailable != mHardKeyboardAvailable) {
- mHardKeyboardAvailable = hardKeyboardAvailable;
- mHardKeyboardEnabled = hardKeyboardAvailable;
- mH.removeMessages(H.REPORT_HARD_KEYBOARD_STATUS_CHANGE);
- mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.REPORT_HARD_KEYBOARD_STATUS_CHANGE);
- }
- if (!mHardKeyboardEnabled) {
- config.keyboard = Configuration.KEYBOARD_NOKEYS;
- }
- // Let the policy update hidden states.
- config.keyboardHidden = Configuration.KEYBOARDHIDDEN_NO;
- config.hardKeyboardHidden = Configuration.HARDKEYBOARDHIDDEN_NO;
- config.navigationHidden = Configuration.NAVIGATIONHIDDEN_NO;
- mPolicy.adjustConfigurationLw(config, keyboardPresence, navigationPresence);
- }
- return true;
- }
step5、AMS.updateConfigurationLocked()
- /**
- * Do either or both things: (1) change the current configuration, and (2)
- * make sure the given activity is running with the (now) current
- * configuration. Returns true if the activity has been left running, or
- * false if <var>starting</var> is being destroyed to match the new
- * configuration.
- * @param persistent TODO
- */
- boolean updateConfigurationLocked(Configuration values,
- ActivityRecord starting, boolean persistent, boolean initLocale) {
- // do nothing if we are headless
- if (mHeadless) return true;
- int changes = 0;
- if (values != null) {
- Configuration newConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
- changes = newConfig.updateFrom(values);
- if (changes != 0) {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
- Slog.i(TAG, "Updating configuration to: " + values);
- }
- EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, changes);
- if (values.locale != null && !initLocale) {
- saveLocaleLocked(values.locale,
- !values.locale.equals(mConfiguration.locale),
- values.userSetLocale);
- }
- mConfigurationSeq++;
- if (mConfigurationSeq <= 0) {
- mConfigurationSeq = 1;
- }
- newConfig.seq = mConfigurationSeq;
- mConfiguration = newConfig; //①将mConfiguration更新到最新config;
- Slog.i(TAG, "Config changes=" + Integer.toHexString(changes) + " " + newConfig);
- final Configuration configCopy = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
- // TODO: If our config changes, should we auto dismiss any currently
- // showing dialogs?
- mShowDialogs = shouldShowDialogs(newConfig);
- AttributeCache ac = AttributeCache.instance();
- if (ac != null) {
- ac.updateConfiguration(configCopy);
- }
- // Make sure all resources in our process are updated
- // right now, so that anyone who is going to retrieve
- // resource values after we return will be sure to get
- // the new ones. This is especially important during
- // boot, where the first config change needs to guarantee
- // all resources have that config before following boot
- // code is executed.
- mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy); //②将config更新到ResourcesManager中去;
- if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
- Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG); //③post一个update消息,该消息处理函数中调用Settings.System.putConfiguration()保存config;
- msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
- mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
- }
- for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) { //④将横屏config通过调用ActivityThread.scheduleConfigurationChanged()传递每个应用进程中去,这个将在下面进行详细分析;
- ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
- try {
- if (app.thread != null) {
- if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending to proc "
- + app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
- app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
- }
- } catch (Exception e) {
- }
- }
- Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED);
- intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY
- | Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REPLACE_PENDING
- | Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
- broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent, null, null, 0, null, null, //⑤发送一个config changed广播;
- null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, false, false, MY_PID,
- Process.SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
- if ((changes&ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE) != 0) {
- intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED);
- intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
- broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent,
- null, null, 0, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
- false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
- }
- }
- }
- boolean kept = true;
- final ActivityStack mainStack = mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
- if (changes != 0 && starting == null) { //⑥如果start 横屏Activity时,参数starting就是正要启动的横屏Activity;如果是旋转屏幕,starting 就为null,此时把top Activity取出来;
- // If the configuration changed, and the caller is not already
- // in the process of starting an activity, then find the top
- // activity to check if its configuration needs to change.
- starting = mainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
- }
- if (starting != null) {
- kept = mainStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(starting, changes); //⑦将config设置到starting中去,下面会详细分析这个函数;
- // And we need to make sure at this point that all other activities
- // are made visible with the correct configuration.
- mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(starting, changes); //⑧调用ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked()
- }
- if (values != null && mWindowManager != null) {
- mWindowManager.setNewConfiguration(mConfiguration); //⑨调用WindowManagerService.setNewConfiguration()启动performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked()
- }
- return kept;
- }
- final void handleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compat) {
- int configDiff = 0;
- synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
- if (mPendingConfiguration != null) {
- if (!mPendingConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config)) {
- config = mPendingConfiguration;
- mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = config.densityDpi;
- updateDefaultDensity();
- }
- mPendingConfiguration = null;
- }
- if (config == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Handle configuration changed: "
- + config);
- mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(config, compat); //①将config更新到应用进程的ResourcesManager中去
- if (mConfiguration == null) {
- mConfiguration = new Configuration();
- }
- if (!mConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config) && compat == null) {
- return;
- }
- configDiff = mConfiguration.diff(config);
- mConfiguration.updateFrom(config);
- config = applyCompatConfiguration(mCurDefaultDisplayDpi);
- }
- ArrayList<ComponentCallbacks2> callbacks = collectComponentCallbacks(false, config);
- // Cleanup hardware accelerated stuff
- WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().trimLocalMemory();
- freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(configDiff);
- if (callbacks != null) {
- final int N = callbacks.size();
- for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
- performConfigurationChanged(callbacks.get(i), config);
- }
- }
- }
再来分析下第⑦点中调用的ActivityStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked()函数。
- /**
- * Make sure the given activity matches the current configuration. Returns
- * false if the activity had to be destroyed. Returns true if the
- * configuration is the same, or the activity will remain running as-is
- * for whatever reason. Ensures the HistoryRecord is updated with the
- * correct configuration and all other bookkeeping is handled.
- */
- final boolean ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(ActivityRecord r,
- int globalChanges) {
- if (mConfigWillChange) {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Skipping config check (will change): " + r);
- return true;
- }
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Ensuring correct configuration: " + r);
- // Short circuit: if the two configurations are the exact same
- // object (the common case), then there is nothing to do.
- Configuration newConfig = mService.mConfiguration;
- if (r.configuration == newConfig && !r.forceNewConfig) {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Configuration unchanged in " + r);
- return true;
- }
- // We don't worry about activities that are finishing.
- if (r.finishing) { //①正在finish的Activity则无需关心;
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Configuration doesn't matter in finishing " + r);
- r.stopFreezingScreenLocked(false);
- return true;
- }
- // Okay we now are going to make this activity have the new config.
- // But then we need to figure out how it needs to deal with that.
- Configuration oldConfig = r.configuration;
- r.configuration = newConfig; //②更新ActivityRecord.configuration值;
- // Determine what has changed. May be nothing, if this is a config
- // that has come back from the app after going idle. In that case
- // we just want to leave the official config object now in the
- // activity and do nothing else.
- final int changes = oldConfig.diff(newConfig);
- if (changes == 0 && !r.forceNewConfig) {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Configuration no differences in " + r);
- return true;
- }
- // If the activity isn't currently running, just leave the new
- // configuration and it will pick that up next time it starts.
- if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Configuration doesn't matter not running " + r);
- r.stopFreezingScreenLocked(false);
- r.forceNewConfig = false;
- return true;
- }
- // Figure out how to handle the changes between the configurations.
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
- Slog.v(TAG, "Checking to restart " + r.info.name + ": changed=0x"
- + Integer.toHexString(changes) + ", handles=0x"
- + Integer.toHexString(r.info.getRealConfigChanged())
- + ", newConfig=" + newConfig);
- }
- if ((changes&(~r.info.getRealConfigChanged())) != 0 || r.forceNewConfig) {
- // Aha,
- r.configChangeFlags |= changes;
- r.startFreezingScreenLocked(r.app, globalChanges);
- r.forceNewConfig = false;
- if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Config is destroying non-running " + r);
- destroyActivityLocked(r, true, false, "config");
- } else if (r.state == ActivityState.PAUSING) {
- // A little annoying: we are waiting for this activity to
- // finish pausing. Let's not do anything now, but just
- // flag that it needs to be restarted when done pausing.
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Config is skipping already pausing " + r);
- r.configDestroy = true;
- return true;
- } else if (r.state == ActivityState.RESUMED) {
- // Try to optimize this case: the configuration is changing
- // and we need to restart the top, resumed activity.
- // Instead of doing the normal handshaking, just say
- // "restart!".
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Config is relaunching resumed " + r);
- relaunchActivityLocked(r, r.configChangeFlags, true);
- r.configChangeFlags = 0;
- } else {
- if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
- "Config is relaunching non-resumed " + r);
- relaunchActivityLocked(r, r.configChangeFlags, false);
- r.configChangeFlags = 0;
- }
- // All done... tell the caller we weren't able to keep this
- // activity around.
- return false;
- }
- // Default case: the activity can handle this new configuration, so
- // hand it over. Note that we don't need to give it the new
- // configuration, since we always send configuration changes to all
- // process when they happen so it can just use whatever configuration
- // it last got.
- if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
- try {
- if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending new config to " + r);
- r.app.thread.scheduleActivityConfigurationChanged(r.appToken); //③调用ActivityThread.scheduleActivityConfigurationChanged();
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- // If process died, whatever.
- }
- }
- r.stopFreezingScreenLocked(false);
- return true;
- }