二级索引之— —Global Indexing
转载自朋友的博客 技术分享,https://my.oschina.net/u/3511143/blog/1808831 侵权必究,转载请说明
1.1 说明
在HBase中,只有一个单一的按照字典序排序的rowKey索引,当使用rowKey来进行数据查询的时候速度较快,但是如果不使用rowKey来查询的话就会使用filter来对全表进行扫描,很大程度上降低了检索性能。而Phoenix提供了二级索引技术来应对这种使用rowKey之外的条件进行检索的场景。
Phoenix支持两种类型的索引技术:Global Indexing和Local Indexing,这两种索引技术分别适用于不同的业务场景(主要是偏重于读还是偏重于写)。下面分别对这两种索引技术简单使用一下,具体性能方面没有进行测试。
以上文字摘自官方文档
http://phoenix.apache.org/secondary_indexing.html
本篇主要介绍Global Indexing相关技术。
1.2 Global Indexing
Global indexing targets read heavy,low write uses cases. With global indexes, all the performance penalties for indexes occur at write time. We intercept the data table updates on write (DELETE, UPSERT VALUES and UPSERT SELECT), build the index update and then sent any necessary updates to all interested index tables. At read time, Phoenix will select the index table to use that will produce the fastest query time and directly scan it just like any other HBase table. By default, unless hinted, an index will not be used for a query that references a column that isn’t part of the index.
Global indexing适用于多读少写的业务场景。使用Global indexing的话在写数据的时候会消耗大量开销,因为所有对数据表的更新操作(DELETE, UPSERT VALUES and UPSERT SELECT),会引起索引表的更新,而索引表是分布在不同的数据节点上的,跨节点的数据传输带来了较大的性能消耗。在读数据的时候Phoenix会选择索引表来降低查询消耗的时间。在默认情况下如果想查询的字段不是索引字段的话索引表不会被使用,也就是说不会带来查询速度的提升。
1.2.1 配置hbase-site.xml
使用Global Indexing的话需要配置hbase-site.xml,在HBase集群的每个regionserver节点的hbase-site.xml中加入如下配置并重启HBase集群。
-
<property>
-
<name>hbase.regionserver.wal.codec </name>
-
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.wal.IndexedWALEditCodec </value>
-
</property>
1.2.2 创建表
进入phoenix的CLI的界面创建company表。
> create table company(id varchar primary key, name varchar, address varchar);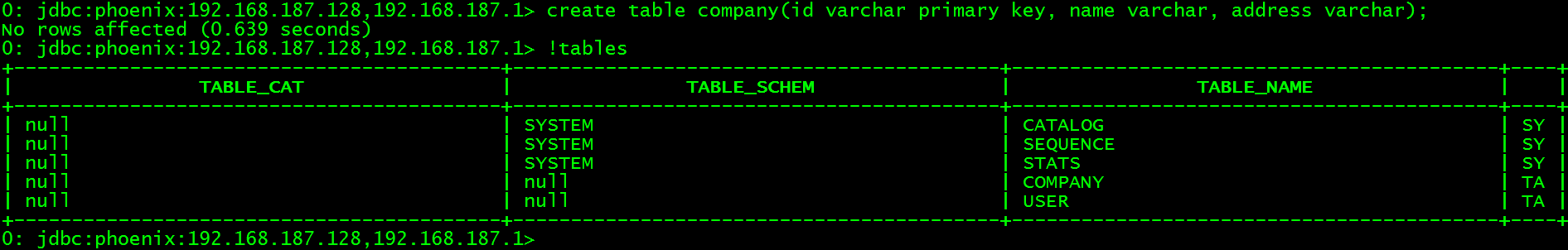
查看company表索引
> !indexes company
1.2.3 创建索引
对company表的name字段创建索引,索引名为my_index。
> create index my_index on company(name);查看当前所有表会发现多一张MY_INDEX索引表,查询该表数据。
-
> !tables
-
> select * from my_index;
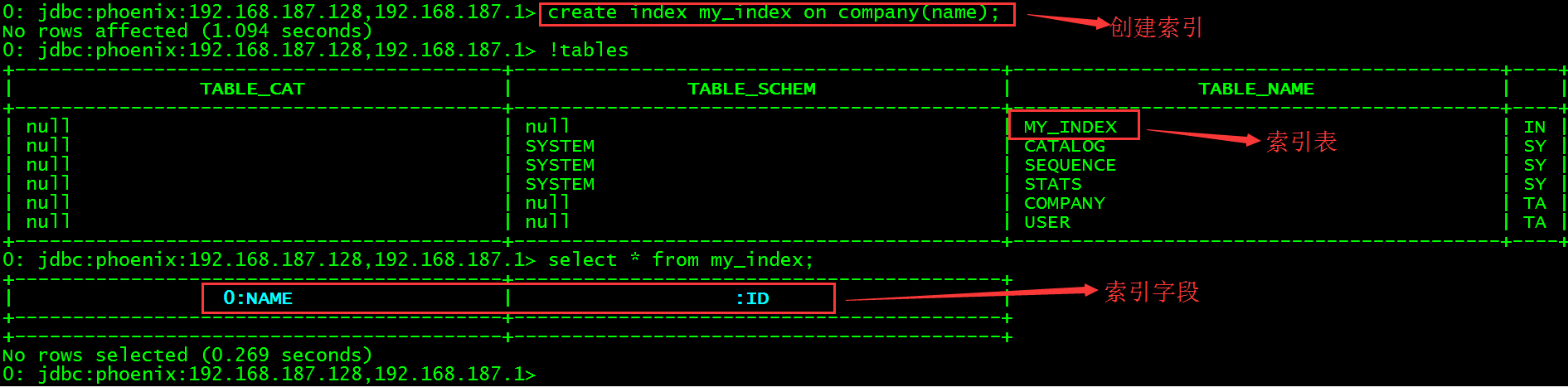
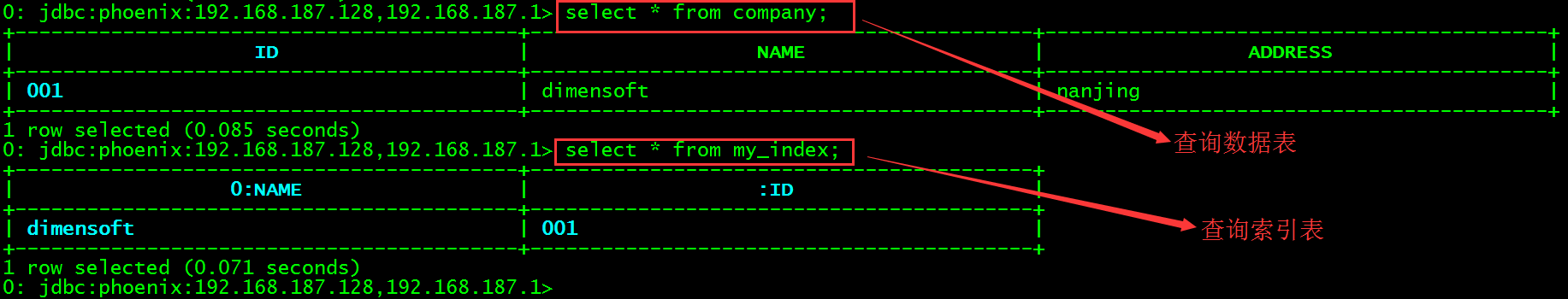
该表中会有2个字段,其中:ID是自动创建的,其实就是HBase中的主键RowKey,0:NAME是我们刚刚手动创建的。
1.2.4 插入数据
在company表中添加测试数据。
> upsert into company(id, name, address) values('001', 'dimensoft', 'nanjing');1.2.5 查询数据
查询company表数据
> select name,address from company where name='dimensoft';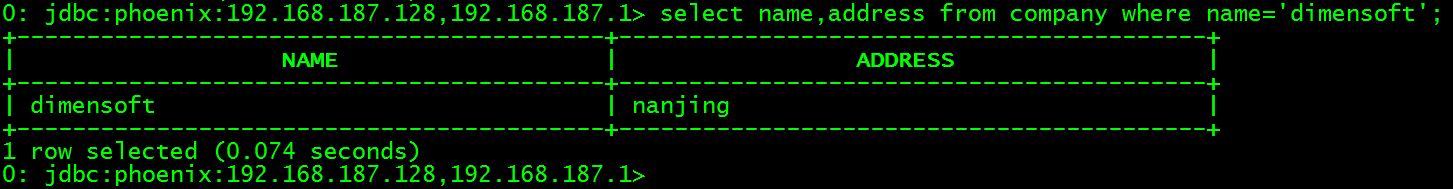
查询索引表my_index
> select * from my_index;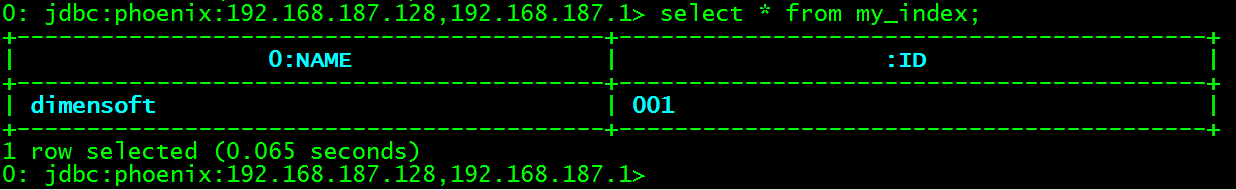
从HBase的CLI界面查看索引表MY_INDEX
> scan 'MY_INDEX'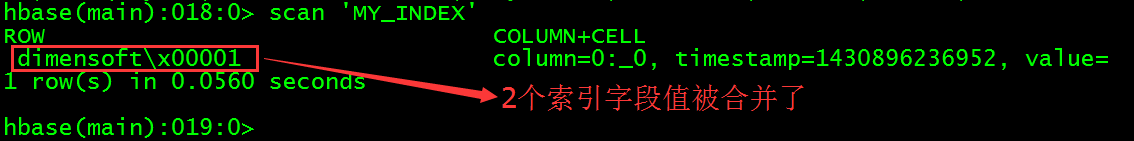
2个索引字段NAME和ID的值被合并为索引表MY_INDEX的rowKey,\x000是十六进制表示,转换为字符串是空格。
1.2.6 查询索引中的半索引问题
高能预警:
> select name,address from company where name='dimensoft';这样的查询语句是不会用到索引表的
Global mutable index will not be used unless all of the columns referenced in the query are contained in the index.
name字段虽然是索引字段但是address字段并不是索引字段!也就是说需要查询出来的字段必须都是索引字段如:
> select name from company where name='dimensoft';如果希望使用索引表进行查询的话可以使用以下三种方式来解决这个半索引问题:
强制使用索引表
在进行查询的时候通过sql语句强制使用索引查询。
> SELECT /*+ INDEX(company my_index) */ name,address FROM company WHERE name = 'dimensoft';This will cause each data row to be retrieved when the index is traversed to find the missing address column value. This hint should only be used if you know that the index has good selective (i.e. a small number of table rows have a value of ‘dimensoft’ in this example), as otherwise you’ll get better performance by the default behavior of doing a full table scan.
这样的查询语句会导致二次检索数据表,第一次检索是去索引表中查找符合name为dimensoft的数据,这时候发现address字段并不在索引字段中,会去company表中第二次扫描,因此只有当用户明确知道符合检索条件的数据较少的时候才适合使用,否则会造成全表扫描,对性能影响较大。
创建covered index
创建索引的时候指定一个covered字段,先删除my_index索引
> drop index my_index on company;
创建covered index
> create index my_index on company(name) include(address);This will cause the address column value to be copied into the index and kept in synch as it changes. This will obviously increase the size of the index.
使用这种方式创建的所有会导致address字段的值被拷贝到索引中,缺点就是会导致索引表大小有一定的增加。
查询索引表my_index数据。
> select * from my_index;

这里的数据是自动同步过来的,可以发现address字段的值也被存储了。
从HBase的CLI中查看MY_INDEX表数据会发现比不使用include的时候多了一行数值,并且里面包含了address字段的值。
> scan 'MY_INDEX'
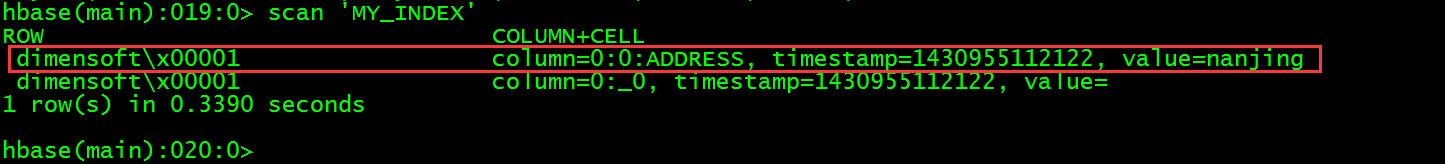
这个时候就再使用下面的查询语句就会使用到索引来进行查询了。
> select name,address from company where name='dimensoft';使用Local Indexing创建索引
与Global Indexing不同,当使用Local Indexing的时候即使查询的所有字段都不在索引字段中时也会用到索引进行查询(这是由Local Indexing自动完成的)。这部分内容会放到后一篇文章详细介绍。
2 Local Indexing
2.1 说明
在HBase中,只有一个单一的按照字典序排序的rowKey索引,当使用rowKey来进行数据查询的时候速度较快,但是如果不使用rowKey来查询的话就会使用filter来对全表进行扫描,很大程度上降低了检索性能。而Phoenix提供了二级索引技术来应对这种使用rowKey之外的条件进行检索的场景。
Phoenix支持两种类型的索引技术:Global Indexing和Local Indexing,这两种索引技术分别适用于不同的业务场景(主要是偏重于读还是偏重于写)。下面分别对这两种索引技术简单使用一下,具体性能方面没有进行测试。
以上文字摘自官方文档
http://phoenix.apache.org/secondary_indexing.html
本篇主要介绍Local Indexing相关技术。
2.2 Local Indexing
Local indexing targets write heavy, space constrained use cases. Just like with global indexes, Phoenix will automatically select whether or not to use a local index at query-time. With local indexes, index data and table data co-reside on same server preventing any network overhead during writes. Local indexes can be used even when the query isn’t fully covered (i.e. Phoenix automatically retrieve the columns not in the index through point gets against the data table). Unlike global indexes, all local indexes of a table are stored in a single, separate shared table.At read time when the local index is used, every region must be examined for the data as the exact region location of index data cannot be predetermined.Thus some overhead occurs at read-time.
Local indexing适用于写操作频繁的场景。与Global indexing一样,Phoenix会自动判定在进行查询的时候是否使用索引。使用Local indexing时,索引数据和数据表的数据是存放在相同的服务器中的避免了在写操作的时候往不同服务器的索引表中写索引带来的额外开销。使用Local indexing的时候即使查询的字段不是索引字段索引表也会被使用,这会带来查询速度的提升,这点跟Global indexing不同。一个数据表的所有索引数据都存储在一个单一的独立的可共享的表中。在读取数据的时候,标红的那句话不会翻译大意就是在读数据的时候因为存储数据的region的位置无法预测导致性能有一定损耗。
2.2.1 配置hbase-site.xml
使用Local Indexing的话需要配置hbase-site.xml,在HBase集群的master节点的hbase-site.xml中添加如下配置并重启HBase集群。
Local indexing also requires special configurations in the master to ensure data table and local index regions co-location.
配置这个参数的目的是确保数据表与索引表协同定位。
-
<property>
-
<name>hbase.master.loadbalancer.class </name>
-
<value>org.apache.phoenix.hbase.index.balancer.IndexLoadBalancer </value>
-
</property>
-
<property>
-
<name>hbase.coprocessor.master.classes </name>
-
<value>org.apache.phoenix.hbase.index.master.IndexMasterObserver </value>
-
</property>
高能预警:如果使用的是Phoenix 4.3+的版本的话还需要在HBase集群的每个regionserver节点的hbase-site.xml中添加如下配置并重启HBase集群。
To support local index regions merge on data regions merge you will need to add the following parameter to hbase-site.xml in all the region servers and restart. (It’s applicable for Phoenix 4.3+ versions)
这个配置是为了支持在数据region合并之上进行索引region合并(这句话感觉翻译的不太准确)。
-
<property>
-
<name>hbase.coprocessor.regionserver.classes </name>
-
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.LocalIndexMerger </value>
-
</property>
2.2.2 创建表
进入phoenix的CLI的界面创建company表。
> create table company(id varchar primary key, name varchar, address varchar);
查看company表索引
> !indexes company
2.2.3 创建索引
对company表的name字段创建索引,索引名为my_index。
> create local index my_index on company(name);查看当前所有表会发现多一张MY_INDEX索引表,查询该表数据。
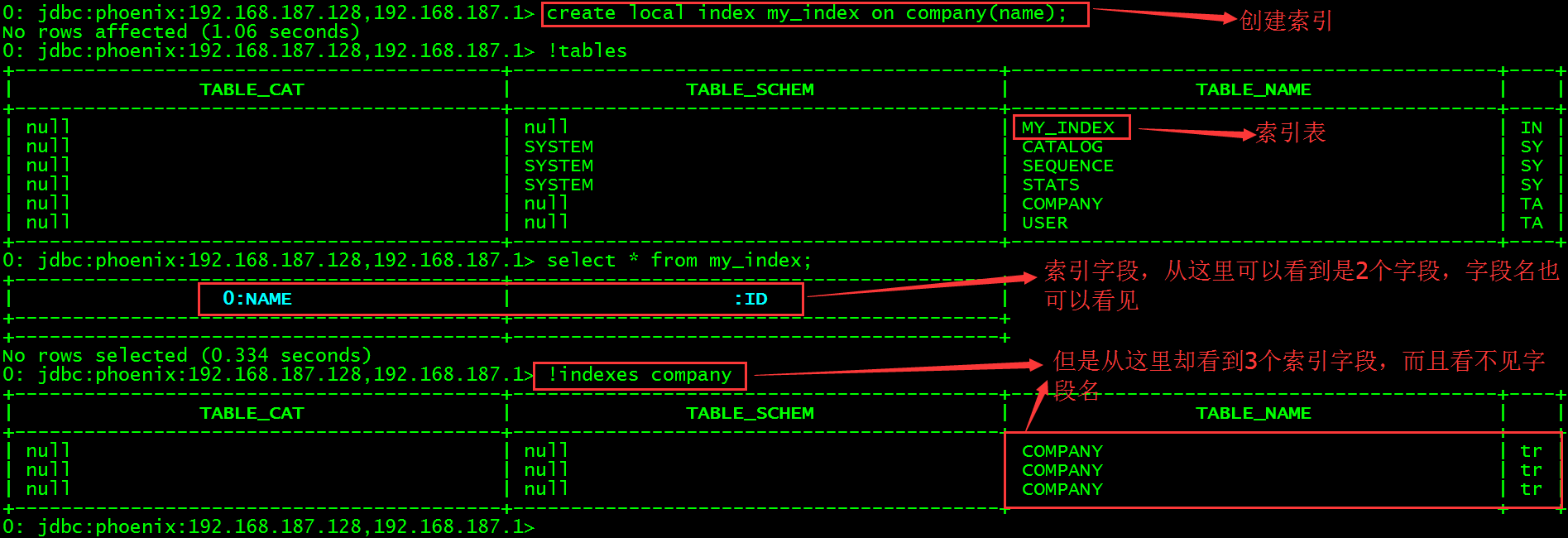
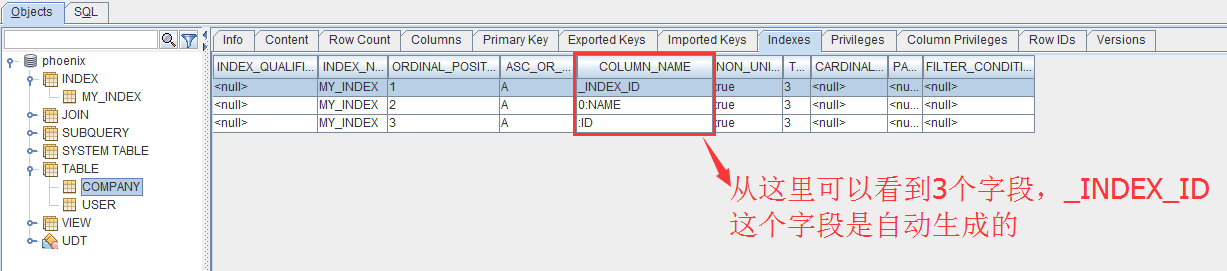
通过squirrel来查看company的索引字段。
从HBase的CLI界面查看当前所有表。
> list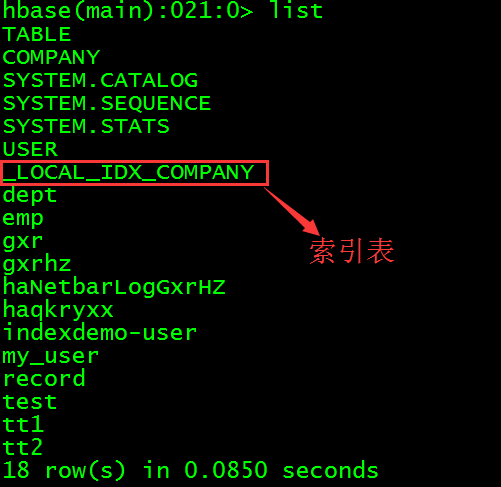
高能预警:这里的索引表并不叫MY_INDEX,而是叫_LOCAL_IDX_COMPANY,但是在Phoenix的CLI中进行数据查询的时候仍然是使用MY_INDEX进行查询,应该是做了映射。
2.2.4 插入数据
在company表中添加测试数据。
> upsert into company(id, name, address) values('001', 'dimensoft', 'nanjing');2.2.5 查询数据
查看company表数据以及索引表my_index数据。
-
> select * from company;
-
> select * from my_index;
从HBase的CLI界面查看索引表_LOCAL_IDX_COMPANY。
> scan '_LOCAL_IDX_COMPANY'
3个索引字段_INDEX_ID、NAME和ID的值被合并为索引表的rowKey,其中_INDEX_ID并没有值(\x000是十六进制表示,转换为字符串是空格)。
3 Append-only Data
3.1 说明
觉得还是有必要把这种类型的索引说明一下,phoenix将其二级索引技术划分为global and local indexing 2种,但是如果继续往下细分的话又分为mutable global indexing、mutable local indexing、immutable global indexing、immutable local indexing一共四种。
默认创建的二级索引为mutable的(mutable global ing或者mutable local indexing)。在上两篇文章中都对这两种索引技术大致都做出了说明。immutable类型的索引主要针对的是数据一次入库之后永不改变的场景(only written once and never updated)。
3.2 Append-only Data
For a table in which the data is only written once and never updated in-place, certain optimizations may be made to reduce the write-time overhead for incremental maintenance. This is common with time-series data such as log or event data, where once a row is written, it will never be updated. To take advantage of these optimizations, declare your table as immutable by adding the IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true property to your DDL statement
CREATE TABLE my_table (k VARCHAR PRIMARY KEY, v VARCHAR) IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true;All indexes on a table declared with IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true are considered immutable (note that by default, tables are considered mutable). For global immutable indexes, the index is maintained entirely on the client-side with the index table being generated as change to the data table occur. Local immutable indexes, on the other hand, are maintained on the server-side. Note that no safeguards are in-place to enforce that a table declared as immutable doesn’t actually mutate data (as that would negate the performance gain achieved). If that was to occur, the index would no longer be in sync with the table.
在一些数据一次写入永不更新的场景中,核心的优化就是减少了在写数据时性能的开销。例如日志数据与事件类型的数据都是一次写入永不更新。通过在场景数据表的时候声明IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true来显示的说明该表的所有索引都是immutable的(默认的是mutable类型)。Global immutable indexes由客户端维护,而Local immutable indexes由服务端维护。即使创建表的时候使用了immutable声明,数据表中的数据也是可以进行更新的。如果进行了这个的操作会引起数据表的数据与索引表的数据不同步。
3.2.1 创建表
在创建数据表的时候声明IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true来显示的说明该表的所有索引都是immutable的。
> create table company_immutable(id varchar primary key, name varchar, address varchar) IMMUTABLE_ROWS=true; 3.2.2 创建索引
对company_immutable表的name字段创建索引。
> create index name_test on company_immutable(name); 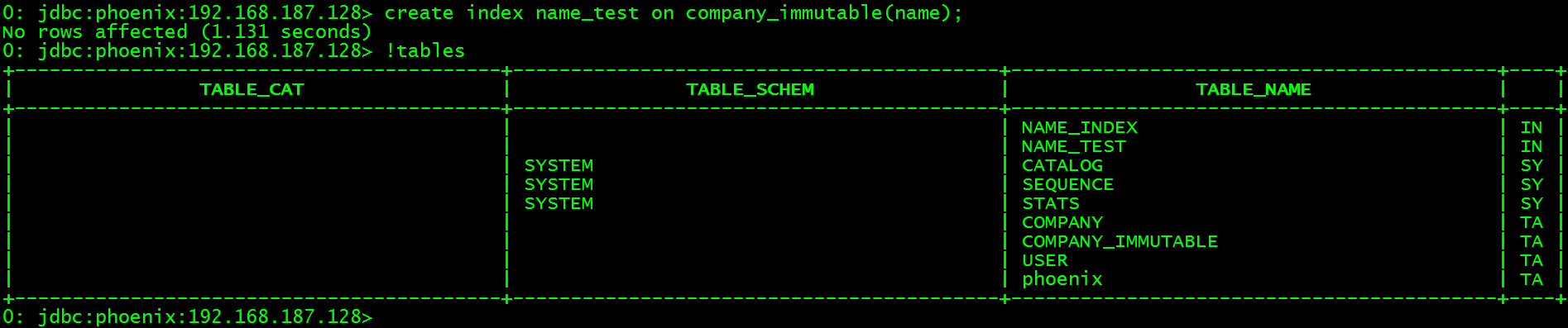
3.2.3 插入数据
插入测试数据。
> upsert into company_immutable(id, name, address) values('001', 'dimensoft', 'nanjing');3.2.4 查询数据
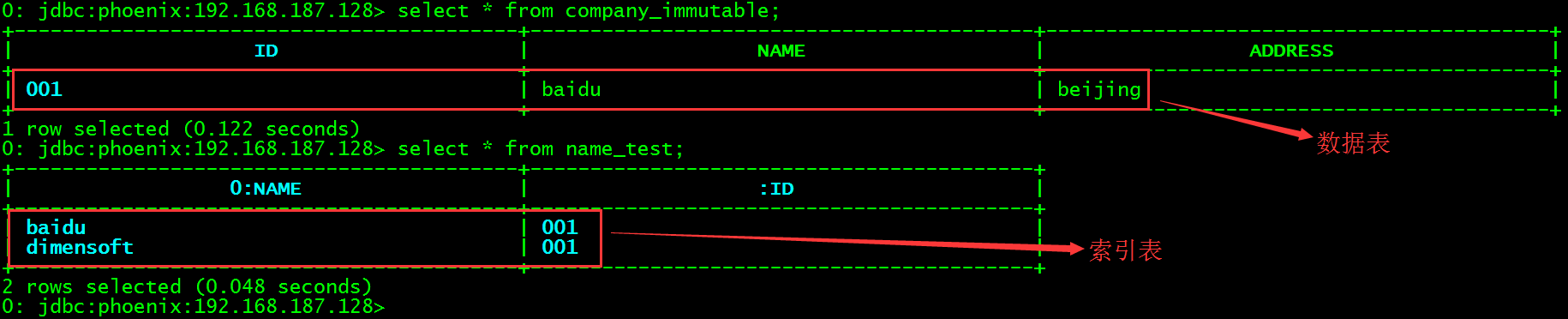
查询数据表与索引表数据。
-
> select * from company_immutable;
-
> select * from name_test;
3.2.5 更新数据
更新id为001的数据(这里是为了测试才进行数据更新操作的,否则的话最好不要对声明了immutable的表进行数据更新)。
upsert into company_immutable(id, name, address) values('001', 'baidu', 'beijing');重新查询数据表与索引表。
-
> select * from company_immutable;
-
> select * from name_test;
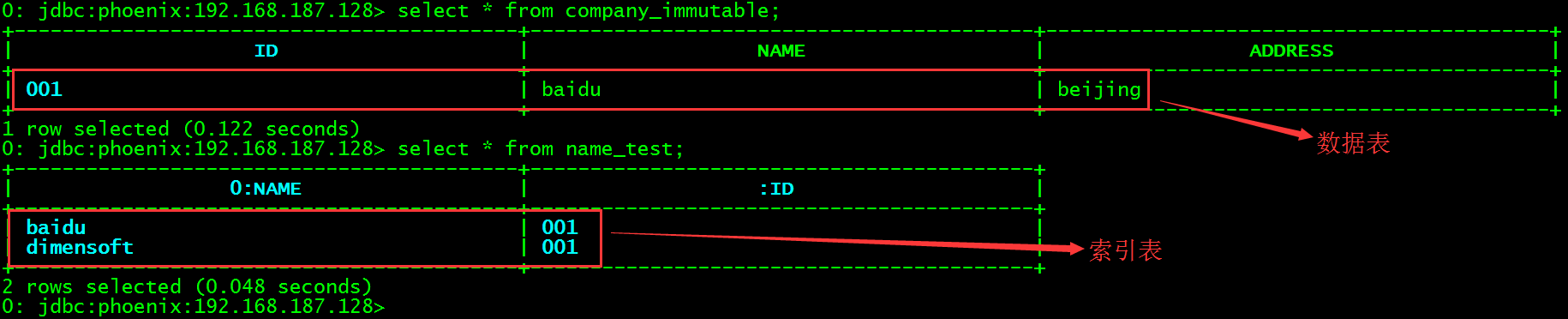
可以看到索引表中的数据并没有被修改,而是被追加了!这就是immutable类型的索引。
4 二级索引性能优化篇
4.1 说明
在使用phoenix二级索引的时候可以进行一些参数的修改来优化性能,这个没有经过实际使用,但是在这里也记录一下以供有需要的人参考,内容来自官方文档。
http://phoenix.apache.org/secondary_indexing.html
4.2 优化
All the following parameters must be set in hbase-site.xml - they are true for the entire cluster and all index tables, as well as across all regions on the same server (so, for instance, a single server would not write to too many different index tables at once).
- index.builder.threads.max
- Number of threads to used to build the index update from the primary table update
- Increasing this value overcomes the bottleneck of reading the current row state from the underlying HRegion. Tuning this value too high will just bottleneck at the HRegion as it will not be able to handle too many concurrent scan requests as well as general thread-swapping concerns.
- Default: 10
- index.builder.threads.keepalivetime
- Amount of time in seconds after we expire threads in the builder thread pool.
- Unused threads are immediately released after this amount of time and not core threads are retained (though this last is a small concern as tables are expected to sustain a fairly constant write load), but simultaneously allows us to drop threads if we are not seeing the expected load.
- Default: 60
- index.writer.threads.max
- Number of threads to use when writing to the target index tables.
- The first level of parallelization, on a per-table basis - it should roughly correspond to the number of index tables
- Default: 10
- index.writer.threads.keepalivetime
- Amount of time in seconds after we expire threads in the writer thread pool.
- Unused threads are immediately released after this amount of time and not core threads are retained (though this last is a small concern as tables are expected to sustain a fairly constant write load), but simultaneously allows us to drop threads if we are not seeing the expected load.
- Default: 60
- hbase.htable.threads.max
- Number of threads each index HTable can use for writes.
- Increasing this allows more concurrent index updates (for instance across batches), leading to high overall throughput.
- Default: 2,147,483,647
- hbase.htable.threads.keepalivetime
- Amount of time in seconds after we expire threads in the HTable’s thread pool.
- Using the “direct handoff” approach, new threads will only be created if it is necessary and will grow unbounded. This could be bad but HTables only create as many Runnables as there are region servers; therefore, it also scales when new region servers are added.
- Default: 60
- index.tablefactory.cache.size
- Number of index HTables we should keep in cache.
- Increasing this number ensures that we do not need to recreate an HTable for each attempt to write to an index table. Conversely, you could see memory pressure if this value is set too high.
- Default: 10
- org.apache.phoenix.regionserver.index.priority.min
- Value to specify to bottom (inclusive) of the range in which index priority may lie.
- Default: 1000
- org.apache.phoenix.regionserver.index.priority.max
- Value to specify to top (exclusive) of the range in which index priority may lie.
- Higher priorites within the index min/max range do not means updates are processed sooner.
- Default: 1050
- org.apache.phoenix.regionserver.index.handler.count
- Number of threads to use when serving index write requests for global index maintenance.
- Though the actual number of threads is dictated by the Max(number of call queues, handler count), where the number of call queues is determined by standard HBase configuration. To further tune the queues, you can adjust the standard rpc queue length parameters (currently, there are no special knobs for the index queues), specifically ipc.server.max.callqueue.length and ipc.server.callqueue.handler.factor. See the HBase Reference Guide for more details.
- Default: 30