版权声明:本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在页面明显位置给出原文链接。 https://blog.csdn.net/mengxiangqihangz/article/details/84309377
ConcurrentLinkedQueue:无界非阻塞线性安全的队列
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
| offer(E e) | 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
| poll() | 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
| peek() | 获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
| remove(Object o) | 从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。 |
无界:相比 LinkedBlockingQueue有边界,默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE,而且有带初始化容器大小的含参数构造器。ConcurrentLinkedQueue没有边界

属性
//记录头节点(不一定指向头,缓更新,非阻塞的,所以没法保证)
private transient volatile Node<E> head;
//记录尾节点(不一定指向尾,缓更新,非阻塞的,所以没法保证)
private transient volatile Node<E> tail;
- 虽然tail不一定是尾节点,但是 节点的next属性 为null的节点,一定是尾节点。
节点
所有链表型集合,都是由一个一个的节点组成,都会自定义节点的数据结构。
节点Node是集合的组成元素,应当优先了解
private static class Node<E> {
volatile E item;//记录当前元素
volatile Node<E> next;//指向下一个节点
Node(E item) {
UNSAFE.putObject(this, itemOffset, item);//为当前节点的 item赋值。
}
boolean casItem(E cmp, E val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, val);//如果this的item等于 cmp,则修改为 val。这是一个原子操作,不存在线程安不安全的说法,一定线程安全。
}
void lazySetNext(Node<E> val) {
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, val);//设置this 的next属性为val,虽然是原子操作,但是当两个线程都获取到当前的this的时候,同时赋值,会导致线程不安全
}
boolean casNext(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);//如果this的next 为 cmp时,则修改为val
}
/**
*
/
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;//通过下面的静态方法,获取Unsafe的实例
private static final long itemOffset;//获得 item属性的位偏移量
private static final long nextOffset;//获得 next属性的位偏移量
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = Node.class;
itemOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("item"));
nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
新增元素 offer、add
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);//新建好一个个节点,并发无影响。
/* 局部变量是基本数据类型,则存储在工作内存中(比如虚拟机栈),
* 局部变量为引用类型,值传递传的是工作内存中存储的地址,实际的引用对象存储在 堆中
所以p的next发生了改变,tail的next也发生了改变。*/
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {//跟while(true)效果差不多(程序只有return true一个出口),但是 t和p的作用域更小。而且不用对比,所以性能更高。
Node<E> q = p.next;
if (q == null) {// 1. q = null表示p为末尾节点
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
return true;
}
} else if (p == q) // 3 . 为什么p会等于q。因为删除节点的时候,会把删除的节点指向自己。
//就是当并发高的时候,积累了十多个节点没添加进去,然后删除节点又比较快,当最后一个节点添加前,之前添加的几个节点已经删除了。但是当前线程的p可能还是之前取的。对于已经删除的p,已经脱离了链表。所以需要将t直接指向tail,从tail处重新开始往下寻找末尾节点。但是当p==t==tail之后,依然p==q,说明tail也已经脱离了链表,则需要从 head处开始找。
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else// 2. 比如单线程添加第二个元素的时候,tail并非根节点。刚进来 q != null,
// 则把 q赋值给p。继续下一次循环 --- 不看第三步。到此就相当于找到末尾节点,添加新节点。
// 当 并发较大的时候,可能10个线程卡在 p.casNext(null, newNode),但每次只能通过一个。
// 剩下的9个线程都要走 2步,如果没有这个三目运算,直接p赋值为q。最后一个通过的节点,
// 要在此循环9次(因为需要一个一个节点往下找,取t的时候到现在增加了几个节点,便要循环几次)。但是有了t != (t = tail)),可以直接找到tail节点,跳过不必要的循环
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
(注意不要去打印this。AbstractQueue 实现了toString方法。toString 调用了 Iterator中的方法,会改变this的属性当前的值)
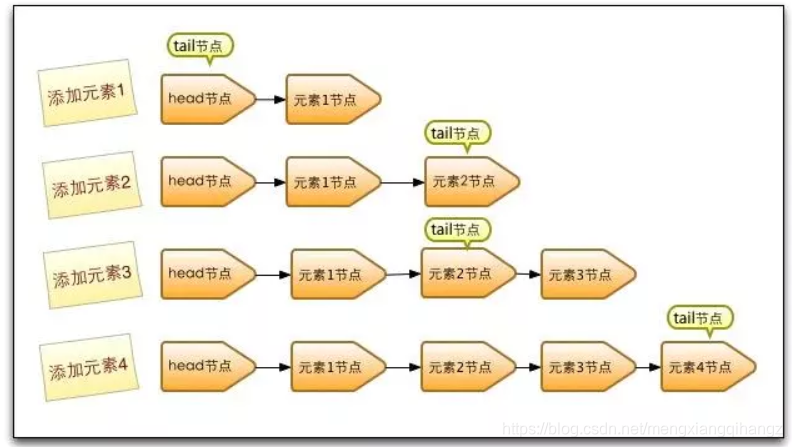
- 单线程
- 未添加元素前,队列中实际有一个 item和 next为null的node
- 添加一个元素,队列中有两个node (null,next) (item,null),此时的head和tail都还是指向第一个元素
- 添加一个元素,(null,next) (item,next) (item,null),此时的 tail才更新到第三个元素。(也就是隔一个更新一次)
附上调试的代码
package com.base.functionClass.collectionT.collection.queue;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.AbstractQueue;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Queue;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements
Queue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 196745693267521676L;
private transient volatile Node<E> head;//记录头节点(不一定指向头,缓更新,非阻塞的,所以没法保证)
private transient volatile Node<E> tail;//记录尾节点(不一定指向尾,缓更新,非阻塞的,所以没法保证)
public ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource() {
Node<E> node0 = new Node<E>(null);
head = tail = node0;
// arrayList.add(node0);
}
public ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Node<E> h = null, t = null;
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
if (h == null)
h = t = newNode;
else {
t.lazySetNext(newNode);
t = newNode;
}
}
if (h == null)
h = t = new Node<E>(null);
head = h;
tail = t;
}
/*
* 获取Unsafe的实例,通过UNSAFE 修改ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource 的两个属性的值。原子操作需要
*/
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long headOffset;//获取head属性的位偏移量
private static final long tailOffset;//获取tail属性的位偏移量
static {
try {
UNSAFE = getUnsafeInstance();
Class k = ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource.class;
headOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("head"));//得到属性 head 在实例中的位偏移量
tailOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("tail"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
// 获取Unsafe实例
public static Unsafe getUnsafeInstance() throws SecurityException,
NoSuchFieldException, IllegalArgumentException,
IllegalAccessException {
Field theUnsafeInstance = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafeInstance.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) theUnsafeInstance.get(Unsafe.class);
}
// 如果this的tail属性(tailOffset位偏移量处)的值等于cmp,则更新为val
private boolean casTail(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, cmp, val);
}
// 如果this的head属性的值为cmp,则更新为val
private boolean casHead(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, cmp, val);
}
/*
* 构成 队列 的 节点
*/
private static class Node<E> {
volatile E item;
volatile Node<E> next;
Node(E item) {
UNSAFE.putObject(this, itemOffset, item);
}
// 修改node的item属性
boolean casItem(E cmp, E val) {// 如果this的 item属性为 cmp,则更新为val
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, val);
}
// 修改node的 next属性
boolean casNext(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
// 修改node的 next属性,虽然为原子操作。但是并未进行对比
void lazySetNext(Node<E> val) {//将this的 next set为 val
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, val);
}
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long itemOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = getUnsafeInstance();
Class k = Node.class;
itemOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("item"));
nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 如果head为h,则把 head更新成p,
* h的next指向自身。 node
*/
final void updateHead(Node<E> h, Node<E> p) {
if (h != p && casHead(h, p))
h.lazySetNext(h);
}
final Node<E> succ(Node<E> p) {//获取下一个节点
Node<E> next = p.next;
return (p == next) ? head : next;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);//新建好一个个节点,并发无影响。
// arrayList.add(newNode);
/* 局部变量是基本数据类型,则存储在工作内存中(比如虚拟机栈),
* 局部变量为引用类型,值传递传的是工作内存中存储的地址,实际的引用对象存储在 堆中
所以p的next发生了改变,tail的next也发生了改变。*/
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {//跟while(true)效果差不多(程序只有return true一个出口),但是 t和p的作用域更小。而且不用对比,所以性能更高。
Node<E> q = p.next;
if (q == null) {// 1. q = null表示p为末尾节点
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
return true;
}
} else if (p == q) // 3 . 为什么p会等于q。因为删除节点的时候,会把删除的节点指向自己。
//就是当并发高的时候,积累了十多个节点没添加进去,然后删除节点又比较快,当最后一个节点添加前,之前添加的几个节点已经删除了。但是当前线程的p可能还是之前取的。对于已经删除的p,已经脱离了链表。所以需要将t直接指向tail,从tail处重新开始往下寻找末尾节点。但是当p==t==tail之后,依然p==q,说明tail也已经脱离了链表,则需要从 head处开始找。
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else// 2. 比如单线程添加第二个元素的时候,tail并非根节点。刚进来 q != null,
// 则把 q赋值给p。继续下一次循环 --- 不看第三步。到此就相当于通过循环找到末尾节点,添加新节点。
// 当 并发较大的时候,可能10个线程卡在 p.casNext(null, newNode),但每次只能通过一个。
// 剩下的9个线程都要走 第2步,如果没有这个三目运算,直接p赋值为q。最后一个通过的节点,
// 要在此循环9次(因为需要一个一个节点往下找,取t的时候到现在增加了几个节点,便要循环几次)。但是有了t != (t = tail)),可以直接找到tail节点,跳过不必要的循环
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
// public List<Node<E>> arrayList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource.Node<E>>());
public E poll() {
restartFromHead: for (;;) {
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {//3 . 走完2之后,下一个元素才item!=null,将p的item更新为null,
// 此时的链表中的节点,依然没有被删除。只是将头节点的item 设置为null。像这样(null,next),(null,next),(item,null)
if (p != h) // 4. 当怕p != h 时,更新 head。
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);//此时的p已经时第二个节点了。此判断表示第二个节点的next不为null,则将head赋值为第三个节点,就是一下跳两个。除非p已经时末尾节点了。
//第一次进入的时候,会掉落第0号节点,第二次进入的时候不掉落节点,第三次进入的时候掉落1,2号节点。节点的掉落也是两个两个进行的(单线程)
// 并且只会将2号节点的next指向自己,1号节点依然指向 2号节点(可以通过断点查看arrayList集合中的节点引用发现其规则。)
return item;
} else if ((q = p.next) == null) {// 1. 第一次进入 head的item==null,所以 将p的next 赋值个q
// 1.1 ==null是因为 q已经到了末尾节点,
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
} else if (p == q)// p已经被其他线程删除了。所以重新将 head赋值给p h
continue restartFromHead;
else// 2. 第一步走完,不满足,再进行比较。 此时的p !=q。所以走else。 将q赋值给p
p = q;
}
}
}
public E peek() {
restartFromHead: for (;;) {
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null || (q = p.next) == null) {//1. item 不为null 则将p的next赋值为q。走else
updateHead(h, p);// 只是为了让head 更靠近
return item;
} else if (p == q)//同上,对于被其他线程删除了的节点,需要重新获取head节点。
continue restartFromHead;
else//2. 也就是一直遍历往下寻找
p = q;
}
}
}
Node<E> first() {//获取第一个item不为null的节点,要是item为null ,p.next也为null。则表示没有节点。注意删除的节点,next是指向自己。
restartFromHead: for (;;) {// head一定是在 头节点之前,一直在追头节点。
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
boolean hasItem = (p.item != null);
if (hasItem || (q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return hasItem ? p : null;
} else if (p == q)
continue restartFromHead;
else
p = q;
}
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first() == null;
}
public int size() {
int count = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p))
if (p.item != null)
// Collection.size() spec says to max out
if (++count == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
break;
return count;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && o.equals(item))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
Node<E> pred = null;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && o.equals(item) && p.casItem(item, null)) {
Node<E> next = succ(p);
if (pred != null && next != null)
pred.casNext(p, next);
return true;
}
pred = p;
}
return false;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
Node<E> beginningOfTheEnd = null, last = null;
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
if (beginningOfTheEnd == null)
beginningOfTheEnd = last = newNode;
else {
last.lazySetNext(newNode);
last = newNode;
}
}
if (beginningOfTheEnd == null)
return false;
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {
Node<E> q = p.next;
if (q == null) {
// p is last node
if (p.casNext(null, beginningOfTheEnd)) {
if (!casTail(t, last)) {
t = tail;
if (last.next == null)
casTail(t, last);
}
return true;
}
} else if (p == q)
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
public Object[] toArray() {
ArrayList<E> al = new ArrayList<E>();
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null)
al.add(item);
}
return al.toArray();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
int k = 0;
Node<E> p;
for (p = first(); p != null && k < a.length; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null)
a[k++] = (T) item;
}
if (p == null) {
if (k < a.length)
a[k] = null;
return a;
}
// If won't fit, use ArrayList version
ArrayList<E> al = new ArrayList<E>();
for (Node<E> q = first(); q != null; q = succ(q)) {
E item = q.item;
if (item != null)
al.add(item);
}
return al.toArray(a);
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence.
* The elements will be returned in order from first (head) to last (tail).
*
* <p>
* The returned iterator is a "weakly consistent" iterator that will never
* throw {@link java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
* ConcurrentModificationException}, and guarantees to traverse elements as
* they existed upon construction of the iterator, and may (but is not
* guaranteed to) reflect any modifications subsequent to construction.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/**
* Next node to return item for.
*/
private Node<E> nextNode;
/**
* nextItem holds on to item fields because once we claim that an
* element exists in hasNext(), we must return it in the following
* next() call even if it was in the process of being removed when
* hasNext() was called.
*/
private E nextItem;
/**
* Node of the last returned item, to support remove.
*/
private Node<E> lastRet;
Itr() {
System.out.println("Itr constructed");
advance();
}
/**
* 流程是 第一次进入 走 1 --> 2
* 第二次进入走 1.1 --> 2.1
* 他的逻辑是 判断nextNode是否为null。若nextNode不为null,则返回nextNode的Item,并将nextNode指向下一个节点。
*/
private E advance() {
lastRet = nextNode;
E x = nextItem;
Node<E> pred, p;
if (nextNode == null) {//初始化p和 pred , 1. (Itr()构造器中会调用一次进行初始化)
p = first();//返回第一个有效的节点
pred = null;
} else {//1.1 pred为nextNode p为nextNode的nextNode
pred = nextNode;
p = succ(nextNode);
}
for (;;) {
if (p == null) {
nextNode = null;
nextItem = null;
return x;
}
E item = p.item;
if (item != null) {// 2. nextNode为第一个节点,nextItem为第一个节点的值。 x为null
nextNode = p;// 2.1 nextNode为第二个节点,item为第二个节点的值,x为第一个节点的值。
nextItem = item;
return x;
} else {
// skip over nulls
Node<E> next = succ(p);
if (pred != null && next != null)
pred.casNext(p, next);
p = next;
}
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextNode != null;
}
public E next() {
if (nextNode == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return advance();
}
public void remove() {
Node<E> l = lastRet;
if (l == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
// rely on a future traversal to relink.
l.item = null;
lastRet = null;
}
}
/**
* Saves the state to a stream (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData All of the elements (each an {@code E}) in the proper order,
* followed by a null
* @param s
* the stream
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden stuff
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
Object item = p.item;
if (item != null)
s.writeObject(item);
}
// Use trailing null as sentinel
s.writeObject(null);
}
/**
* Reconstitutes the instance from a stream (that is, deserializes it).
*
* @param s
* the stream
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in elements until trailing null sentinel found
Node<E> h = null, t = null;
Object item;
while ((item = s.readObject()) != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>((E) item);
if (h == null)
h = t = newNode;
else {
t.lazySetNext(newNode);
t = newNode;
}
}
if (h == null)
h = t = new Node<E>(null);
head = h;
tail = t;
}
/**
* Throws NullPointerException if argument is null.
*
* @param v
* the element
*/
private static void checkNotNull(Object v) {
if (v == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueueTest1 {
static ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource<Integer> q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueueSource();
static AtomicInteger atom = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Demo().start();
new Demo().start();
new Demo().start();
new Demo().start();
new Demo().start();
Iterator<Integer> ite = q.iterator();
while(ite.hasNext()){
int num = ite.next();
}
}
static class Demo extends Thread{
public void run(){
// for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
q.offer(atom.incrementAndGet());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
if(null == q.poll()){
System.out.println("null"+i);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
}
}
}