RRT 理论:
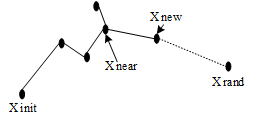
抛X_rand,先得X_near,再得X_new

以上是算法流程图。
close all;
clear all;
% params for function [vertices, edges, path] = rrt(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p)
% MAP
map = load('map.mat');
q_start = [80, 70];
q_goal = [707, 615];
% MAZE
% map = load('maze.mat');
% q_start = [206, 198];
% q_goal = [416, 612];
map = map.map;
k = 10000;
delta_q = 50;
p = 0.3;
% params for function [path_smooth] = smooth(map, path, vertices, delta)
delta = 5;
[vertices, edges, path] = rrt(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p);
path_smooth = smooth(map, path, vertices, delta);
imshow(int32(1 - map), []);
title('RRT (Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees) - Smooth');
% imagesc(1 - map);
% colormap(gray);
hold on;
[edgesRowCount, ~] = size(edges);
for ii = 1 : edgesRowCount
plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(edges(ii, 1), 1), vertices(edges(ii, 2), 1)], ...
[vertices(edges(ii, 1), 2), vertices(edges(ii, 2), 2)], ...
'b', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
plot(q_start(1), q_start(2), 'g*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot(q_goal(1), q_goal(2), 'r*', 'linewidth', 1);
[~, pathCount] = size(path);
for ii = 1 : pathCount - 1
%plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(path(ii), 1), vertices(path(ii + 1), 1)], ...
[vertices(path(ii), 2), vertices(path(ii + 1), 2)], ...
'r', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
[~, pathCount] = size(path_smooth);
for ii = 1 : pathCount - 1
%plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(path_smooth(ii), 1), vertices(path_smooth(ii + 1), 1)], ...
[vertices(path_smooth(ii), 2), vertices(path_smooth(ii + 1), 2)], ...
'black', 'LineWidth', 2);
end
//rrt.m
function [vertices, edges, path] = rrt(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p)
%Algorithm to build a tree to solve map
% that goes from the start position till the goal position and to generate a path that connects
% both vertices
%
% map: matrix that you can obtain loading the mat files.
%
% q_start: coordinates x and y of the start position. You can find the coordinates below the figures
% of the environmentin the previous page.
%
% q_goal: coordinates x and y of the goal position. You can find the coordinates below the figures
% of the environment in the previous page.
%
% k: maximum number of samples that will be considered to generate the tree, if the goal is not
% found before.
%
% delta_q: distance between q_new and q_near.
%
% p: probability (between 0 and 1) of choosing q_goal as q_random.
%
% vertices: list of x and y coordinates of the vertices. The first vertex will correspond to the
% start position and the last one will correspond to the goal position. The variable MUST have 2
% columns for x and y coordinates and n rows (being n the number of vertices found in the tree).
%
% edges: list of edges of the tree. There will be n-1 edges, stored in n-1 rows. Each edge MUST
% contain the index of the vertex (with respect ?vertices? variable) and the index of the vertex
% that is one step to the root (or start position). Once the goal is found, the goal index will be
% stored in the last row, and will contain the goal index and its upper vertex in the direction to
% the start position. By following the vertices, the path to the goal can be extracted directly.
%
% path: list of vertex indices from the start vertex (q_start) to the goal vertex (q_goal). In case
% no solution has been found, the list will be empty. The list MUST be represented as a row vector.
%
% q_start = [80, 70]; q_goal = [707, 615];
tic;
clc;
if nargin < 3
error('First 3 parameter is required: 2D map matrix, start and goal coordinates.');
elseif nargin < 4
k = 10000;
delta_q = 50;
p = 0.3;
elseif nargin < 5
delta_q = 50;
p = 0.3;
elseif nargin < 6
p = 0.3;
end
checkParameters(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p);
% map: <683x803> means: height: 683, width: 803
[mapHeight, mapWidth] = size(map); % columns as the x axis and the rows as the y axis.
q_start = int32(q_start); % q_start = [80, 70] means: q_start(1): y, q_start(2): x
q_goal = int32(q_goal); % q_goal = [707, 615] means: q_goal(1): y, q_goal(2): x
vertices = q_start; % Initialize the vertices variable with q_start
edges = int32.empty(0, 2); % Initialize the edges variable as empty
q_rand = int32.empty(0, 2);
q_near = int32.empty(0, 2);
q_new = int32.empty(0, 2);
for ii = 1 : k % For k samples repeat
if rand() < p % With p probability use q_rand = q_goal
q_rand = q_goal;
else % Otherwise generate q_rand in the dimensions of the map.
q_rand = int32([randi(mapWidth) randi(mapHeight)]); % columns as the x axis and the rows as the y axis.
end
[q_near, qNearIndex] = findQNear(q_rand, vertices); % Find q_near from q_rand in vertices
q_new = findQNew(q_near, q_rand, delta_q); % Generate q_new at delta_q distance from q_near in the direction to q_rand
if q_new(1) < 1 || q_new(2) < 1 || q_new(1) > mapWidth || q_new(2) > mapHeight
continue;
end
if map(q_new(2), q_new(1)) == 0 % If q_new belongs to free space
% If the edge between q_near and q_new belongs to free space
if isEdgeQNearQNewBelongsFreeSpace(map, q_near, q_new)
% Add q_new in vertices
vertices = [vertices; q_new];
% Add [index(q_new) index(q_near)] in edges
[qNewIndex, ~] = size(vertices);
edges = [edges; [int32(qNewIndex), int32(qNearIndex)]];
% If q_new == q_goal or q_goal is on the edge
if isequal(q_new, q_goal) || isQGoalOnQNearQNewEdge(q_near, q_new, q_goal)
if ~isequal(q_new, q_goal) % if goal is not q_new but its on edge
% goal is on the last edge, remove last vertex and add it as goal
vertices = vertices(1 : (end - 1), :);
vertices = [vertices; q_goal];
end
% Fill path and stop break RRT function
path = fillSolutionPath(edges, vertices);
% rrtDraw(map, q_start, q_goal, vertices, edges, path);
toc;
return;
end
end
end
end
path = int32.empty(0, 2);
% rrtDraw(map, q_start, q_goal, vertices, edges, path);
toc;
error('RRT: solution not found :(');
end
function checkParameters(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p)
[mapHeight, mapWidth] = size(map);
if mapWidth < 1 || mapHeight < 1
error('Map size error. Please provide 2D map.');
end
[x, y] = size(q_start);
if x ~= 1 || y ~= 2
error('q_start - start position - should be 1x2 matrix like: [80, 70]');
elseif q_start(1) < 0 || q_start(1) > mapWidth || q_start(2) < 0 || q_start(2) > mapHeight
error('q_start - start position - should be inside the map');
end
[x, y] = size(q_goal);
if x ~= 1 || y ~= 2
error('q_goal - goal position - should be 1x2 matrix like: [707, 615]');
elseif q_goal(1) < 0 || q_goal(1) > mapWidth || q_goal(2) < 0 || q_goal(2) > mapHeight
error('q_goal - goal position - should be inside the map');
end
if k < 1
error('k - iteration count - parameter should be positive');
end
if delta_q < 1
error('delta_q - step size - parameter should be positive');
end
if p < 0 || p > 1
error('p - probability - parameter should be between 0 and 1');
end
end
% Find q_near from q_rand in vertices.
function [q_near, qNearIndex] = findQNear(q_rand, vertices)
[rowCount, ~] = size(vertices);
if rowCount < 1
error('RRT: solution not found :(');
end
euclideanDistances = double.empty(0, 1);
for ii = 1 : rowCount
euclideanDistances(ii, 1) = pdist2(double(q_rand), double(vertices(ii, :)), 'euclidean');
end
minDistanceIndex = find(euclideanDistances == min(euclideanDistances));
q_near = vertices(minDistanceIndex(1), :);
qNearIndex = minDistanceIndex(1);
end
% http://math.stackexchange.com/questions/175896/finding-a-point-along-a-line-a-certain-distance-away-from-another-point
% http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1061276/how-to-normalize-a-vector-in-matlab-efficiently-any-related-built-in-function
% Generate q_new at delta_q distance from q_near in the direction to q_rand
function [q_new] = findQNew(q_near, q_rand, delta_q)
v = double(q_rand - q_near);
u = v / norm(v);
q_new = int32(double(q_near) + delta_q * u);
end
% If the edge between q_near and q_new belongs to free space
function [isBelongsFreeSpace] = isEdgeQNearQNewBelongsFreeSpace(map, q_near, q_new)
% In order to check if an edge belongs to the free space,
% use the incremental (left) or subdivision (right) strategies.
% You can use 10 intermediate points.
intermediatePointCount = 10;
v = double(q_new - q_near);
distance = norm(v);
u = v / distance;
delta_q = distance / intermediatePointCount;
currentCoordinate = double(q_near);
for ii = 1 : intermediatePointCount
currentCoordinate = currentCoordinate + (delta_q * u);
if map(int32(currentCoordinate(2)), int32(currentCoordinate(1))) == 1 % map(q_new(1), q_new(2))
isBelongsFreeSpace = 0;
return;
end
end
isBelongsFreeSpace = 1;
end
% q_near <--> q_goal <--> q_new
function [isQGoalOnEdge] = isQGoalOnQNearQNewEdge(q_near, q_new, q_goal)
v = double(q_new - q_near);
distance = norm(v);
u = v / distance;
distanceQNearQGoal = norm(double(q_goal - q_near));
if distanceQNearQGoal > distance
isQGoalOnEdge = 0;
return;
end
q_goal_hat = double(q_near) + (distanceQNearQGoal * u);
isQGoalOnEdge = isequal(int32(q_goal_hat), q_goal);
end
% Fill path and stop break RRT function
function [path] = fillSolutionPath(edges, vertices)
path = edges(end, 1);
prev = edges(end, 2);
ii = 0;
[edgesCount, ~] = size(edges);
while prev ~= 1
if ii > edgesCount
error('RRT: no path found :(');
end
prevIndex = find(edges(:, 1) == prev);
prev = edges(prevIndex(1), 2);
path = [path, prev];
ii = ii + 1;
end
end
% Plots the RRT result
function rrtDraw(map, q_start, q_goal, vertices, edges, path)
imshow(int32(1 - map), []);
title('RRT (Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees)');
% imagesc(1 - map);
% colormap(gray);
hold on;
[edgesRowCount, ~] = size(edges);
for ii = 1 : edgesRowCount
plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(edges(ii, 1), 1), vertices(edges(ii, 2), 1)], ...
[vertices(edges(ii, 1), 2), vertices(edges(ii, 2), 2)], ...
'b', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
plot(q_start(1), q_start(2), 'g*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot(q_goal(1), q_goal(2), 'r*', 'linewidth', 1);
[~, pathCount] = size(path);
for ii = 1 : pathCount - 1
%plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(path(ii), 1), vertices(path(ii + 1), 1)], ...
[vertices(path(ii), 2), vertices(path(ii + 1), 2)], ...
'r', 'LineWidth', 2);
end
end
//smooth.m
function [path_smooth] = smooth(map, path, vertices, delta)
%SMOOTH Smoothing algorithm for obtaining a shorter and less noisy path.
% We will use the greedy approach: Connect q_goal from q_start,
% if it fails try from a closer position until it connects.
% Once q_goal is connected, start again with its directly connected position.
%
% map: matrix that you can obtain loading the ?.mat? files.
%
% path: list of vertex indices from the start vertex (q_start) to the goal vertex (q_goal).
% The list MUST be represented as a row vector.
%
% vertices: list of x and y coordinates of the vertices.
% The first vertex will correspond to the start position and the last one will correspond t
% the goal position. The variable MUST have 2 columns for x and y coordinates and
% n rows (being n the number of vertices found in the tree).
%
% delta: incremental distance that will be used to check if direct connection between
% the vertices of the path is inside the free space. The edges will be divided obtaining
% several points, each of them separated this delta distance.
%
% path_smooth: reduced list of vertex indices from the start vertex (q_start) to the goal vertex
% (q_goal) after applying the smoothing algorithm. The list MUST be represented as a row vector.
path_smooth = path(1); % initing with goal
currentIndex = 1; % path array iterator
currentSmoothIndex = numel(path); % path reverse array iterator
while currentIndex < numel(path)
while currentIndex < currentSmoothIndex
if isEdgeBelongsFreeSpace(map, vertices(path(currentSmoothIndex), :), vertices(path(currentIndex), :), delta)
path_smooth = [path_smooth, path(currentSmoothIndex)];
currentIndex = currentSmoothIndex;
break;
else
currentSmoothIndex = currentSmoothIndex - 1;
end
end
currentSmoothIndex = numel(path);
end
% rrtSmoothDraw(map, path_smooth, vertices);
end
function [isBelongsFreeSpace] = isEdgeBelongsFreeSpace(map, startPoint, endPoint, delta)
v = double(endPoint - startPoint);
distance = norm(v);
u = v / distance;
intermediatePointCount = distance / delta;
currentCoordinate = double(startPoint);
for ii = 1 : intermediatePointCount
currentCoordinate = currentCoordinate + (delta * u);
if map(int32(currentCoordinate(2)), int32(currentCoordinate(1))) == 1
isBelongsFreeSpace = 0;
return;
end
end
isBelongsFreeSpace = 1;
end
function rrtSmoothDraw(map, path_smooth, vertices)
imshow(int32(1 - map), []);
title('RRT (Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees) - Smooth Path');
% imagesc(1 - map);
% colormap(gray);
hold on;
[~, pathCount] = size(path_smooth);
for ii = 1 : pathCount - 1
%plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(path_smooth(ii), 1), vertices(path_smooth(ii + 1), 1)], ...
[vertices(path_smooth(ii), 2), vertices(path_smooth(ii + 1), 2)], ...
'r', 'LineWidth', 2);
end
end
运行后的结果为:
