相关必考库的笔记(下)
目录(续):
4. pyinstaller
5. jieba
6. wordcloud
pyinstaller
↶
1.检查是否安装,在cmd中输入pyinstaller
C:\...>pyinstaller
usage: pyinstaller [-h] [-v] [-D] [-F] [--specpath DIR] [-n NAME]
[--add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>]
[--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>] [-p DIR]
[--hidden-import MODULENAME]
[--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH]
[--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS] [--exclude-module EXCLUDES]
[--key KEY] [-d [{all,imports,bootloader,noarchive}]] [-s]
[--noupx] [-c] [-w]
[-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns>]
[--version-file FILE] [-m <FILE or XML>] [-r RESOURCE]
[--uac-admin] [--uac-uiaccess] [--win-private-assemblies]
[--win-no-prefer-redirects]
[--osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER]
[--runtime-tmpdir PATH] [--bootloader-ignore-signals]
[--distpath DIR] [--workpath WORKPATH] [-y]
[--upx-dir UPX_DIR] [-a] [--clean] [--log-level LEVEL]
scriptname [scriptname ...]
pyinstaller: error: the following arguments are required: scriptname
# 出现上述内容基本上算是安装成功
2.pyinstaller的基本使用
待打包的代码(helloWorld.py):
print("Hello World")
input()
(1)基本打包方法
C:\Users\hp>pyinstaller C:\Users\hp\Desktop\helloWorld.py
我的电脑上是这个地址:
C:\Users\hp\dist\helloWorld
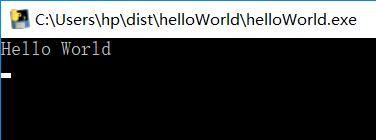
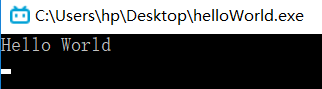
(2)打包为独立exe文件,最后只会产生一个exe文件,没有别的附带文件
C:\Users\hp>pyinstaller -F C:\Users\hp\Desktop\helloWorld.py
(3)带有图标的exe文件
C:\Users\hp>pyinstaller -F -i C:\Users\hp\Desktop\favicon.ico C:\Users\hp\Desktop\helloWorld.py

(3)其它参数指令,参考别的教程或者官方教程
jieba
↶
参考链接:jieba库文档
jieba.cut()
jieba.lcut()
jieba.cut()
↶
方法接受三个输入参数: 需要分词的字符串;cut_all 参数用来控制是否采用全模式;HMM 参数用来控制是否使用 HMM 模型
>>> list(jieba.cut("我喜欢写Python代码", cut_all = True))
['我', '喜欢', '写', 'Python', '代码']
jieba.lcut()
↶
直接返回 list
>>> jieba.lcut("我喜欢写Python代码")
['我', '喜欢', '写', 'Python', '代码']
wordcloud
↶
参考链接:
简单的示例:
from wordcloud import WordCloud
a ="""
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters
Beautiful is better than ugly.
Explicit is better than implicit.
Simple is better than complex.
Complex is better than complicated.
Flat is better than nested.
Sparse is better than dense.
Readability counts.
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
Although practicality beats purity.
Errors should never pass silently.
Unless explicitly silenced.
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
Now is better than never.
Although never is often better than *right* now.
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!"""
wordcloud = WordCloud(background_color="white",
width=500,
height=400,
margin=2).generate(a)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(wordcloud)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
wordcloud.to_file('test.png')

下篇完
点我回顶部 ☚
Fin.