I/O流(Stream)
INPUT:输入流,从文件里读OUPUT:输出流,写内容到文件
IO流分为:字符流和字节流
字符流:处理纯文本文件。
字节流:处理可以所有文件。
测试字节输出流OuPut(写):
@Test
public void test7(){ //字节流
FileOutputStream fos=null;
try {
fos=new FileOutputStream("./fff.txt"); //创建字节流对象
fos.write("abcd".getBytes()); //与字符流相比,字节流写入的内容后面加.getBytes()方法。
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试结果:
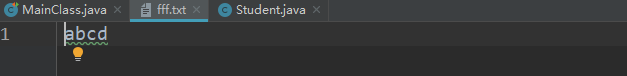
字节输入流InPut(读):
@Test
public void test8(){
//字节流读(INput)
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("./fff.txt");
byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
int len=0;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) { //将读出的内容放入byte型的buffer数组
System.out.println(new String(buffer, 0, len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试结果:
abcd
Process finished with exit code 0
带缓冲区的字节流:
缓冲区的作用:减少调用本地API的次数,从而优化系统的开销,缓冲输入流从被称为缓冲区(buffer)的存储器区域读出数据;
仅当缓冲区是空时,本地输入 API 才被调用。同样,缓冲输出流,将数据写入到缓存区,只有当缓冲区已满才调用本机输出 API。
输出流:
@Test
public void test10(){
BufferedOutputStream bos=null;
try {
bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./sss.txt"));
bos.write("缓冲区字节流".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输入流:
@Test
public void test11(){
BufferedInputStream bis=null;
try {
bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("./sss.txt"));
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while ((len=(bis.read(buffer)))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}