现在新服务模板的ORM框架基本上都是使用mybatis3.4.6、mybatis-plus2.2.0
最近在项目中偶然发现CouponRecord实体类中增加了这样一行代码如下,可能之前没有测试吧,当调用需要查询此表使用的默认com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.BaseMapper提供的方法的相关接口后直接报NPE。当然出现NPE很好解决,直接判断下是否为null就OK了。
@Data @Builder @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @TableName("t_record") public class TRecord{ ... @TableField(value = "product_quantity") private BigDecimal productQuantity; public BigDecimal getProductQuantity() { // 提交上的代码 return this.productQuantity.setScale(2, RoundingMode.HALF_DOWN); // 解决方式如下 //return this.productQuantity == null ? null : this.productQuantity.setScale(2, RoundingMode.HALF_DOWN); } ... }
BaseMapper接口提供的方法如下:
public interface BaseMapper<T> { Integer insert(T entity); Integer insertAllColumn(T entity); Integer deleteById(Serializable id); Integer deleteByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap); Integer delete(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); Integer deleteBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList); Integer updateById(@Param("et") T entity); Integer updateAllColumnById(@Param("et") T entity); Integer update(@Param("et") T entity, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); T selectById(Serializable id); List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList); List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap); T selectOne(@Param("ew") T entity); Integer selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); List<T> selectPage(RowBounds rowBounds, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); List<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage(RowBounds rowBounds, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper); }
其实不看源码大概也知道,肯定某个地方对这些方法直接解析为sql并将其存入到缓存中,便于需要的时候直接取。但是也想趁这次机会将mybatis、mybatis-plus以及mybatis-spring他们之间是如何处理的大概过下并且记录下。以前也好像过了下,但是很快就忘记了,好记性不如烂笔头说的没错。
如何使用
任何框架,首先要会用,不然就是扯淡。因为框架都是在实际的应用中逐渐抽象出来的。主要代码如下:
@Service public class TRecordService extends ServiceImpl<TRecordDao, TRecord> { public int count() { TRecord conditionTRecord = TRecord.builder().status(Status.USED).isDelete(YesNo.NO.getValue()).build(); return selectCount(new EntityWrapper<>(conditionTRecord).le("create_time", endTime).isNotNull("order_no")); } } public interface TRecordDao extends BaseMapper<TRecord> { }
spring的相关配置如下:
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 自动扫描entity目录, 省掉Configuration.xml里的手工配置 --> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:mapper/**/*.xml"/> <property name="plugins"> <array> <!-- 分页插件配置 --> <bean id="paginationInterceptor" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.plugins.PaginationInterceptor"> <property name="dialectType" value="mysql"/> </bean> <bean id="limitInterceptor" class="com.test.common.mybatis.LimitInterceptor"/> </array> </property> </bean> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="com.test.merchant.activity.**.dao"/> <property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/> </bean> <context:component-scan base-package="com.wlqq.gs.merchant.common.**,com.test.merchant.activity.**"> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan>
深入分析是查看源码解析
在深入看之前先看看为什么在TRecordService类中直接调用selectCount方法可以查询?看看ServiceImpl中的部分代码如下:
public class ServiceImpl<M extends BaseMapper<T>, T> implements IService<T> { @Autowired protected M baseMapper; ... @Override public int selectCount(Wrapper<T> wrapper) { return SqlHelper.retCount(baseMapper.selectCount(wrapper)); } ... }
通过这段代码,可以看出,spring在实例化CouponRecordService后,会将baseMapper注入到这里,那么这里我们可以推测出baseMapper应该是XX的代理类(自动生成)。这个XX是j继承BaseMapper,从上面代码可以看到应该是CouponRecordDao。看到这个dao在想到spring的配置扫描,好像有点感觉了哈。不扯了。下面将会以解析生成sql为主线,最后到生成代理为止的源码分析,其他分支就不细说了。看看是如何解析,代码是如何实现的。
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean
主要是创建SqlSessionFactory,具体可以查看这个类的MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean#buildSqlSessionFactory,这里不做详细的源码阅读,有兴趣的可以看下。我们主要是研究ServiceImpl中的Wrapper生成的sql以及baseMapper的代理类的生成。
MapperScannerConfigurer
这个类主要是扫描我们配置的basePackage包下的类并将这些bean初始化。接下来就大概过下整个流程.
-
ClassPathMapperScanner扫描包下的类
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware { ... @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // 验证是否配置了basePackage notNull(this.basePackage, "Property 'basePackage' is required"); } @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // left intentionally blank } @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { // 是否有占位符,处理之 if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) { processPropertyPlaceHolders(); } // 扫描 ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry); scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig); scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass); scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface); scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory); scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate); scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName); scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName); scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator); scanner.registerFilters(); scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS)); } ... }
-
ClassPathMapperScanner#scanClassPathMapperScanner继承ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,在子类中未实现scaner,所以调用父类的scan方法。为了便于阅读这里将源码中的日志删除了。
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner extends ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider { ... public int scan(String... basePackages) { // 获取之前容器中bean的数量 int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount(); // 真正干事的---扫描, 调用子类ClassPathMapperScanner#doScan(basePackages)方法 doScan(basePackages); // Register annotation config processors, if necessary. if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) { AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry); } // 返回bean的数量 return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart); } // 真正干事的扫描实现 protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified"); // BeanDefinitionHolder 的集合 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(); for (String basePackage : basePackages) { // 通过查找候选bean定义 Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage); // 遍历进行部分逻辑处理 for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) { ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate); // 设置作用域 candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); // 生成beanName String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry); if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { // 增加默认值,autowireCandidate postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName); } if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate); } // 注册BeanDefinition到容器中。 if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); } } } return beanDefinitions; } ... } public class ClassPathMapperScanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner { public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { // 调用父类的ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScaner(basePackages)方法,扫描生产BeanDefinitionHolder集合 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages); if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) { logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration."); } else { // MapperBean 需要一些额外的处理,查看这个方法 processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions); } return beanDefinitions; } //对每个Mapper的BeanDefinition定义处理, private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) { GenericBeanDefinition definition; for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) { definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition(); // the mapper interface is the original class of the bean // but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName()); // 这一步非常重要,把我们的Bean设置为MapperFactoryBean,回头看下MapperFactoryBean的结构 definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass()); definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig); boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false; // 在bean中增加sqlSessionFactory if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } // 在bean中增加sqlSessionTemplate if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) { if (explicitFactoryUsed) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } // 设置自动注入模式 if (!explicitFactoryUsed) { definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE); } } } }
-
接下来看看MapperBeanFactory的继承关系并分析

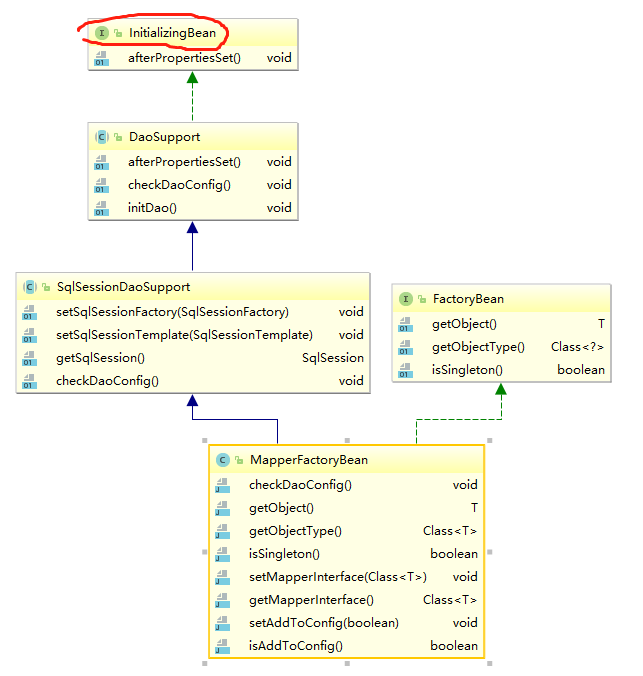
从图中,看出MapperFactoryBean是实现了InitializingBean。DaoSupport对afterPropertiesSet()实现了。我们都知道Spring在初始化会自动调用afterPropertiesSet()方法。那么接下来看看这个方法干了什么事。
public abstract class DaoSupport implements InitializingBean { protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); @Override public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException { // Let abstract subclasses check their configuration. checkDaoConfig(); // Let concrete implementations initialize themselves. try { initDao(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex); } } protected abstract void checkDaoConfig() throws IllegalArgumentException; protected void initDao() throws Exception { } }
一看典型的模板设计模式,真正处理的在子类中。这里我们关心的是checkDaoConfig(),看看子类MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig这个到底干了啥。
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> { protected void checkDaoConfig() { super.checkDaoConfig();//调用父类的方法,父类就是检查sqlSession是否为null。null的话抛出异常 notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required"); // 通过sqlSession获取MybatisConfiguration Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration(); if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) { try { // 将mapperInterface注册到configuration中。 configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e); throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } } }
MybatisConfiguration#addMapper干的就是将类型类型注册到我们Mapper容器中,便于后续取
public class MybatisConfiguration extends Configuration { public final MybatisMapperRegistry mybatisMapperRegistry = new MybatisMapperRegistry(this); public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { mybatisMapperRegistry.addMapper(type); } }
-
接下来就要看看
MybatisMapperRegistry#addMapper注册到底干了何事。猜猜应该就是自定义无XML的sql生产注入。哪些是自定义?就是我们BaseMapper中的那一堆方法。
public class MybatisMapperRegistry extends MapperRegistry { // 感觉这个属性变量名没有起好。这个就是用来存储我们mapper接口和mapper对应代理工厂类的一个关系。 private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>(); public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) { // 注入过就不再执行了。 if (hasMapper(type)) { return; } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { // 这里先记着,后面查看我们MapperProxy代理用的着哦 knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); // mybatisMapper注解构建器 MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); // 解析 parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } } } }
接下来看看MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder#parse方法。
public class MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder extends MapperAnnotationBuilder { ... public void parse() { String resource = type.toString(); if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { // 加载xml loadXmlResource(); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName()); parseCache(); parseCacheRef(); Method[] methods = type.getMethods(); // 类型是否是BaseMapper if (BaseMapper.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) { GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type); } for (Method method : methods) { try { // issue #237 if (!method.isBridge()) { parseStatement(method); } } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method)); } } } parsePendingMethods(); } ... }
在上面的parse方法中,我们重点关心GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type);这一段实现。我们现在基本上服务中的dao都是实现BaseMapper。这里面就是对我们sql的生产并且注入到configuration中。具体看下面的代码
public class AutoSqlInjector implements ISqlInjector { // 注入到builderAssistant public void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass) { String className = mapperClass.toString(); Set<String> mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration()); // 判断之前是否注入过 if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className)) { // 注入 inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass); // 加入到缓存中 mapperRegistryCache.add(className); } } // md,单独看这段代码感觉有点线程不安全的感觉。 public void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass) { this.configuration = builderAssistant.getConfiguration(); this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant; this.languageDriver = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance(); /** * 驼峰设置 PLUS 配置 > 原始配置 */ GlobalConfiguration globalCache = this.getGlobalConfig(); if (!globalCache.isDbColumnUnderline()) { globalCache.setDbColumnUnderline(configuration.isMapUnderscoreToCamelCase()); } Class<?> modelClass = extractModelClass(mapperClass); if (null != modelClass) { /** * 初始化 SQL 解析 */ if (globalCache.isSqlParserCache()) { PluginUtils.initSqlParserInfoCache(mapperClass); } // 这里获取tableInfo. 这里你会看到我们@TableName了。。 TableInfo table = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass); //生成sql注入sql injectSql(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, table); } } // 看到这个方法里面的injectXXXX是不是和我们BaseMapper里的一样呢。对这里挨着一个个的去实现。 protected void injectSql(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo table) { /** * #148 表信息包含主键,注入主键相关方法 */ if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(table.getKeyProperty())) { /** 删除 */ this.injectDeleteByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectDeleteByIdSql(true, mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 修改 */ this.injectUpdateByIdSql(true, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectUpdateByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 查询 */ this.injectSelectByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectByIdSql(true, mapperClass, modelClass, table); } else { // 表不包含主键时 给予警告 logger.warn(String.format("%s ,Not found @TableId annotation, Cannot use Mybatis-Plus 'xxById' Method.", modelClass.toString())); } /** * 正常注入无需主键方法 */ /** 插入 */ this.injectInsertOneSql(true, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectInsertOneSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 删除 */ this.injectDeleteSql(mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectDeleteByMapSql(mapperClass, table); /** 修改 */ this.injectUpdateSql(mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 查询 */ this.injectSelectByMapSql(mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectOneSql(mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectCountSql(mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectListSql(SqlMethod.SELECT_LIST, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectListSql(SqlMethod.SELECT_PAGE, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectMapsSql(SqlMethod.SELECT_MAPS, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectMapsSql(SqlMethod.SELECT_MAPS_PAGE, mapperClass, modelClass, table); this.injectSelectObjsSql(SqlMethod.SELECT_OBJS, mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 自定义方法 */ this.inject(configuration, builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, table); } }
看到上面的AutoSqlInjector#injectSql这个方法,你会发觉到就和BaseMapper中一样了。这里就是将那些方法解析生成并注入。下面将以AutoSqlInjector#injectSelectCountSql为例,看看他到底咋个搞得。
protected void injectSelectCountSql(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo table) { // 从枚举中获取到sqlMethod SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_COUNT; // 将sqlMethod.getSql() 格式化 String sql = String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), table.getTableName(), sqlWhereEntityWrapper(table)); // 得到SqlSource SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql, modelClass); // 注入 this.addSelectMappedStatement(mapperClass, sqlMethod.getMethod(), sqlSource, Integer.class, null); } // 这个方法将是根据实体类,构造一堆条件。构造出来得条件,后续执行我们得sql后会根据OGNL,也将会通过反射机制调用我们得get方法,惨了,所以最上面我们出现得NPE就问题来了。为null当然会NPE出现了。 protected String sqlWhereEntityWrapper(TableInfo table) { StringBuilder where = new StringBuilder(128); where.append("\n<where>"); where.append("\n<if test=\"ew!=null\">"); where.append("\n<if test=\"ew.entity!=null\">"); if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(table.getKeyProperty())) { where.append("\n<if test=\"ew.entity.").append(table.getKeyProperty()).append("!=null\">\n"); where.append(table.getKeyColumn()).append("=#{ew.entity.").append(table.getKeyProperty()).append("}"); where.append("\n</if>"); } List<TableFieldInfo> fieldList = table.getFieldList(); for (TableFieldInfo fieldInfo : fieldList) { where.append(convertIfTag(fieldInfo, "ew.entity.", false)); where.append(" AND ").append(this.sqlCondition(fieldInfo.getCondition(), fieldInfo.getColumn(), "ew.entity." + fieldInfo.getEl())); where.append(convertIfTag(fieldInfo, true)); } where.append("\n</if>"); where.append("\n<if test=\"ew!=null and ew.sqlSegment!=null and ew.notEmptyOfWhere\">\n${ew.sqlSegment}\n</if>"); where.append("\n</if>"); where.append("\n</where>"); where.append("\n<if test=\"ew!=null and ew.sqlSegment!=null and ew.emptyOfWhere\">\n${ew.sqlSegment}\n</if>"); return where.toString(); }
MapperProxy生产实现
在上面得分析代码得时候,在扫描得时候将我们BeanDefinition中得beanClass设置为MapperFactoryBean,
MapperFactoryBean实现FactoryBean。实现FactoryBean得好处是什么?我们先看看spring容器启动这个流程
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean { ... // 这个就是spring容器启动得核心流程都在这里。 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } } ... }
所以这里我们重点看finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory),这个方法主要是完成BeanFactory中得非懒加载Bean得初始化工作,在这也将会注入依赖得bean,依赖注入得时候,调用AbstractBeanFactory#getBean(String, Class<T>),具体可以详细看看。在后续会判断此Bean是否是FactoryBean得类型,如果是会调用FactoryBean#getObject();那么现在我们再回到MapperFactoryBean#getObject()实现。
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> { ... public T getObject() throws Exception { //这里通过MybatisSqlSessionTemplate去获取我们得Mapper代理。 return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface); } ... } public class MybatisSqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean { public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this); } } public class MybatisConfiguration extends Configuration { public final MybatisMapperRegistry mybatisMapperRegistry = new MybatisMapperRegistry(this); ... //在注册器中获取 public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mybatisMapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } ... } public class MybatisMapperRegistry extends MapperRegistry { private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>(); // 这里从之前说的knownMappers这个命名感觉不好的缓存中获取MapperProxyFactory代理工厂方法。 public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MybatisPlusMapperRegistry."); } try { // 通过代理工厂再实例化。我们得MapperProxy代理 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } }
代理工厂
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { return mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() { return methodCache; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } }
MapperProxy代理代码如下
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L; private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method); if (mapperMethod == null) { mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()); methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); } return mapperMethod; } @UsesJava7 private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class .getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); if (!constructor.isAccessible()) { constructor.setAccessible(true); } final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); return constructor .newInstance(declaringClass, MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED | MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC) .unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args); } /** * Backport of java.lang.reflect.Method#isDefault() */ private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) { return (method.getModifiers() & (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface(); } }
至此我们sql生产以及MapperProxy代理生产就分析完了。
总结
跟着源码看下,学习到东西还是很多得。
-
设计模式:代理、工厂、模板、委派等
-
spring容器初始化流程
-
spring中很多扩展点等等
一个很简单问题,解决是解决了,但是解决了并不代表你从中学到了什么。