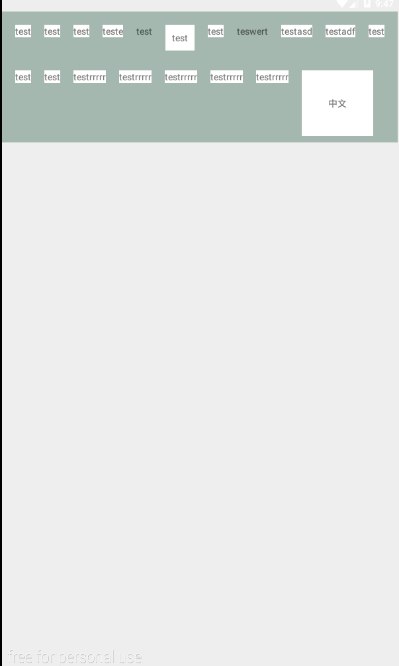
这段时间偷懒了,全去dota去了。都没有心情敲代码了。写了个流式布局。练习下自定义viewgroup,再准备写个圆形菜单来练习练习。
下面看看效果:
流式布局:
一 概述:
流式布局就将其子控件,从左往右进行排列。如果这一行能放下当前的控件(需要考虑margin,和控件的宽度)那么久在当前放下控件,如果放不下控件,就放到第二行去。
viewgroup中我们必须实现onMeasure(),和onLayout()。两个方法,onMeasure()是测量布局的尺寸的。onLayout()方法是控制子控件位置的。然后执行完了之后还会执行onDraw()。如果你还需要 绘画其他东西,就可以自己画。
二 源码解读:
好了,我们可以看看onMeasure()方法。
如果你自定义的是View类型的控件,如果你不重写onMeasure()方法那么wrap_content属性将不会有任何作用和match_parent一样的效果。
现在我们自定义的是viewgroup ,因为viewgroup是个抽象方法,我们必须实现onMeasure(),onLayout()。
onMeasure()方法中有两个参数int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec,这两个参数将对应的宽高的size,和mode都放进这两个参数中了。
获取方式如下:
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);这里的heightSize , widthSize 都是返回match_parent状态下的尺寸,或者精确的某个值。
widthMode,heightMode 如果是MeasureSpec.EXACTLY那么对应的是match_parent或者精确的值。
如果返回的是MeasureSpec.AT_MOST那么对应的wrap_content就是自适应。这个就需要我们手动进行计算了,并且还需要参考heightSize ,widthSize ,虽然我们是wrap_content,但是这两个值给我们的是match_parent对应的尺寸。所以我们自已适应的时候需要参考这两个值,不能超过他们,因为这是给我们最大的值了。最后还需要考虑到子控件的margin,和自己的padding属性。
贴出我的onMeasure
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
Log.e("xhc","onMeasure");
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
return;
}
//最后管padding
int childCount = getChildCount();
int measureWidth = 0, measureHeight = 0;
//一行中最高的一个控件
int heightMax = 0, widthMax = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
measureChild(view, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if ((measureWidth + params.rightMargin + params.leftMargin + view.getMeasuredWidth() + getPaddingRight()) <= widthSize) {
//这一行可以放下这个控件
measureWidth += (params.rightMargin + params.leftMargin + view.getMeasuredWidth());
if (heightMax < (view.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin)) {
heightMax = (view.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin);
}
} else {
//换行
if ((measureHeight + heightMax) < heightSize) {
//换行了 高度增加
measureHeight += heightMax;
Log.e("xhc","高度增加"+measureHeight);
heightMax = 0 ;
}
if (widthMax < measureWidth) {
//换成最宽的宽度;
widthMax = measureWidth;
}
//行宽重新开始
measureWidth = 0 ;
}
if(i == (childCount - 1)){
//这个是最后一行并且没到换行的地方需要把这一行的高度加进去
measureHeight += heightMax;
}
}
if (widthMax != 0) {
measureWidth = widthMax;
}
if (measureHeight == 0) {
measureHeight = heightMax;
}
if ((measureWidth + getPaddingLeft()) < widthSize) {
measureWidth += getPaddingLeft();
}
if ((measureWidth + getPaddingRight()) < widthSize) {
measureWidth += getPaddingRight();
}
if ((measureHeight + getPaddingTop()) < heightSize) {
measureHeight += getPaddingTop();
}
if ((measureHeight + getPaddingBottom()) < heightSize) {
measureHeight += getPaddingBottom();
}
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measureWidth = widthSize;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measureHeight = heightSize;
}
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth, measureHeight);
}在需要子控件的尺寸之前需要测量子控件
measureChild(view, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
注意:如果要将子控件的LayoutParams 转成 MarginLayoutParams 需要在viewgroup中添加
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}先判断这一行能否还能继续放下当前控件,因为最大的宽度就是widthSize,不能比他还大了。如果放不下了就移动到下一行去。并这一行的高度其实就是最高的控件的高度
if (heightMax < (view.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin)) {
heightMax = (view.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin);
}当移动到下一行就将测量的高度加上上一行最高的高度。
measureHeight += heightMax;并且判断是否是最宽的一行。如果是的话那么就把当前布局的宽度设置成这个宽度。
if (widthMax < measureWidth) {
//换成最宽的宽度;
widthMax = measureWidth;
}记住在最后一行的时候需要将自己的行的高度添加上去
if(i == (childCount - 1)){
//这个是最后一行并且没到换行的地方需要把这一行的高度加进去
measureHeight += heightMax;
}然后将自己的padding计算上去。
if ((measureWidth + getPaddingLeft()) < widthSize) {
measureWidth += getPaddingLeft();
}
if ((measureWidth + getPaddingRight()) < widthSize) {
measureWidth += getPaddingRight();
}
if ((measureHeight + getPaddingTop()) < heightSize) {
measureHeight += getPaddingTop();
}
if ((measureHeight + getPaddingBottom()) < heightSize) {
measureHeight += getPaddingBottom();
}最后在判断自己的layout_width , layout_height 属性对应的是否是MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,如果是的话就直接使用widthSize,heightSize最大的尺寸了。
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measureWidth = widthSize;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measureHeight = heightSize;
}最后设置尺寸
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth, measureHeight);然后我们来看看onLayout函数:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
Log.e("xhc","onLayout");
//注意父控件的padding,子空间的margin
int childCount = getChildCount();
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddintRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
int currentX = paddingLeft, currentY = paddingTop;
int heightMax = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childTotalWidth = params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin + child.getMeasuredWidth();
if ((paddintRight + currentX + childTotalWidth) <= getMeasuredWidth()) {
//这一行可以放下
int left = (currentX + params.leftMargin);
int top = (currentY + params.topMargin);
child.layout(left, top, left + child.getMeasuredWidth(), top + child.getMeasuredHeight());
currentX += (params.leftMargin + child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.rightMargin);
if (heightMax < (top + child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.bottomMargin)) {
heightMax = (top + child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.bottomMargin);
}
} else {
currentX = paddingLeft;
currentY += heightMax;
}
}
}这里的基本逻辑和onMeasure中一致。判断这一行是否能放下,能放下就放下(阿弥陀佛)
if ((paddintRight + currentX + childTotalWidth) <= getMeasuredWidth()) {
//这一行可以放下
int left = (currentX + params.leftMargin);
int top = (currentY + params.topMargin);
child.layout(left, top, left + child.getMeasuredWidth(), top + child.getMeasuredHeight());
}不能放下就到下一行去。
else {
currentX = paddingLeft;
currentY += heightMax;
}好了最后贴出源码地址:
加个好友共同学习(不是公众号):
因为小弟水平有限,如果有写的有问题,希望指出。