本文参考了【张鸿洋的博客】: Android 手把手教您自定义ViewGroup(一)和Android 自定义ViewGroup 实战篇 -> 实现FlowLayout
在很多应用里面,我们能看到类似于这样的流式
用现有的控件我们实现这种动态适应的布局很麻烦,对于如何比较简单的去实现这种布局,就需要我们去自定义ViewGroup了
实现步骤
一、新建一个FlowLayout类,继承ViewGroup,并重写generateLayoutParams方法
重写generateLayoutParams是为了设置布局的LayoutParams,在这里,我们用系统的MarginLayoutParams就可以了
//设置布局的LayoutParams,用系统的MarginLayoutParams就行
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}二、重写onMeasure方法
重写onMeasure方法是为了根据子控件去计算布局的宽高,并进行设置
//根据childView的高宽,计算布局的宽高,并进行设置
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获取布局的父容器为它设置的测量模式和大小
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//最后计算的布局宽高
int width = 0, height = 0;
//每一行的宽高
int lineWidth = 0, lineHeight = 0;
//循环childView
for (int i = 0, count = getChildCount(); i < count; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
//计算当前childView的高和宽
measureChild(view, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//得到childView的LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
//得到childView所占的宽度和高度
int childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
if (childWidth > widthSize) {
params.width = widthSize - params.leftMargin - params.rightMargin;
view.setLayoutParams(params);
measureChild(view, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
params = (MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
int childHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight() + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
//如果加入当前childView的宽度会超出父容器计算的宽度话,则需要开启新的一行,累加height
//否则累加当前行的宽高
if (lineWidth + childWidth > widthSize) {
//取宽度最大值
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);
//累加height
height += lineHeight;
//记录下一行的宽高
lineWidth = childWidth;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
//如果是最后一个,则将当前行的宽度与width做比较,累加height
if (i == count - 1) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, width);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
//设置布局的宽高
setMeasuredDimension((widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? widthSize : width),
(heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? heightSize : height));
}三、重写onLayout方法
重写onLayout方法是为了对布局所有的子控件进行重新排版,对他们的位置进行设置
//对所有的childView位置和大小进行设置
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int widht = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
//记录的高度
int recordHeight = 0;
//每行的宽高
int lineWidth = 0, lineHeight = 0;
//每个childView的坐标
int left = 0, top = 0, right = 0, bottom = 0;
//循环childView
for (int i = 0, count = getChildCount(); i < count; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
//得到childView的LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
//得到childView宽高
int childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
if (childWidth + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin + lineWidth > widht) {
recordHeight = recordHeight + lineHeight;
left = params.leftMargin;
right = left + childWidth;
top = recordHeight + params.topMargin;
bottom = top + childHeight;
lineWidth = childWidth + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
lineHeight = childHeight + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
} else {
left = lineWidth + params.leftMargin;
right = left + childWidth;
top = recordHeight + params.topMargin;
bottom = top + childHeight;
lineWidth = lineWidth + childWidth + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin);
}
view.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}四、代码中使用
至此,我们的流式布局已经写完,现在去用他进行布局
布局文件activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.krubo.flowlayout.MainActivity">
<com.krubo.flowlayout.FlowLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="遍历所有的childView"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="用于设置allViews的值"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="根据"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="childView"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="所有的"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="遍历"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="到此完成了所有的childView的绘制区域的确定,到此,我们的FlowLayout的代码也结束了~~静下心来看一看是不是也不难"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="静下心"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="用于设置allViews的值"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="根据"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="childView"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="所有的"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="#dddddd"
android:text="遍历"/>
</com.krubo.flowlayout.FlowLayout>
</LinearLayout>
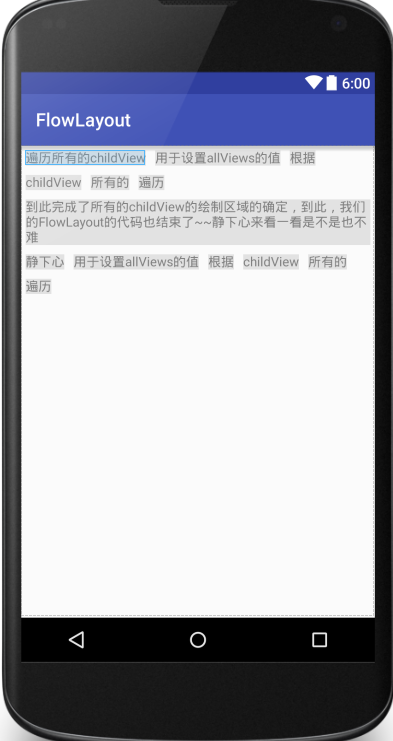
运行后的效果图如下