文章目录
- Spring Boot - Thymeleaf模板简介以及集成
Spring Boot - Thymeleaf模板简介以及集成
正所谓工欲善其事必先利其器,这里我们就来先大概了解一下Thymeleaf的一些特性和使用。
1.什么是Thymeleaf?
Thymeleaf官网
Thymeleaf使用官方文档
Spring+Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是一个流行的模板引擎,该模板引擎采用Java语言开发。模板引擎只是一个技术名词,是跨领域跨平台的概念,在Java语言体系下有模板引擎,在C#、PHP等语言体系下也有各自的模板引擎。Thymeleaf是一个和Freemarker、Velocity、Beetl类似的模板引擎,在过去的Java Web开发中,我们往往会选择使用Jsp去完成页面的动态渲染,但是Thymeleaf的出现使它完全替代了JSP。新版的Spring中更推荐使用Thymeleaf去用作前端模版引擎,并且Spring Boot对Thymeleaf也提供了很好的集成。
既然官方也更加推荐使用Thymeleaf作为模板引擎,那必然是存在与其他模板引擎相比较的优点:
- Thymeleaf 对网络环境不存在严格的要求,既能用于Web环境下,也能用于非Web环境下。在非Web环境下,他能直接显示模板上的静态数据;在Web环境下,它能像Jsp一样从后台接收数据并替换掉模板上的静态数据。它是基于HTML的,以HTML标签为载体,Thymeleaf要寄托在HTML标签下实现
- Thymeleaf 开箱即用的特性,可以处理六种模板,每种模板都称为模板模式:两种标记模板模式(HTML和XML),三种文本模板模式(TEXT,JAVASCRIPT和CSS)和一种无操作模板模式(RAW)。它提供自身标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果。既可以保留原有JSTL以及标签的作用,同时又可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
2.标准表达式
每种模板引擎都有自己的表达式,Thymeleaf标准表达式主要有四种:
- 变量表达式
- 第选择或星号表达式
- URL表达式
- 消息表达式/资源表达式
下面先来介绍这些标准表达式,里面会涉及一些Thymeleaf的常用标签属性,后面会介绍。
2.1 变量表达式
语法:
${...}
变量表达式即OGNL表达式或Spring EL表达式,变量表达式用于访问容器(例如:tomcat)上下环境中的变量,功能与JSTL中${}相同,Thymeleaf中的变量表达式用${变量名}方式获取数据。例如:${user.name}
<p>
<span th:text="${user.name}">Jack</span>
<span th:text="${user.age}">18</span>
</p>
2.2 选择表达式/星号表达式
语法:
*{...}
选择表达式也叫星号表达式,可使用th:object属性绑定对象之后使用,实际绑定一个选择的对象代替上下文变量容器。选择表达式操作的是选定的对象,而不是整个环境变量映射。
<!-- 选择表达式:先使用th:object绑定对象 后用*可直接获取对象属性-->
<p th:object="${user}">
<span th:text="*{name}">Jack</span>
<span th:text="*{age}">18</span>
</p>
选择表达式可以和变量表达式可以混合使用,并且只要没有选定对象,选择表达式
*{}与变量表达式${}的语法作用是完全一样的。`
<!-- 标准变量表达式和选择表达式可以混用-->
<p th:object="${user}">
<span th:text="${user.name}">Jack</span>
<span th:text="*{age}">18</span>
</p>
<!--不使用th:object绑定对象,也可直接使用*{}获取属性-->
<p>
<span th:text="*{user.name}">Jack</span>
<span th:text="*{user.age}">18</span>
</p>
2.3 URL表达式
语法:
@{...}
URL表达式可用于<script src="..."> <link href="..."> <a href="...">等,URL表达式指的是把上下文信息添加到URL中,这个过程通常称为URL重写。
这里我们可以通过很多种方式去设置参数,例如下面示例:
- 第一种是通过我们常规的字符串拼接,这里用单引号将常量标明通过字符串拼接的方式动态重写URL。
- 第二种通过括号()将参数以及参数值填充至地址后面
- 第三种用||(高级文本连接)将所有内容包含起来,在里面可以直接使用以上标准表达式达到拼接效果
第一种方式和以前使用JSP的时候可能更加接近,这里第二种和第三种更加增强了动态URL的可读性并且减少了拼接的复杂度,并且这里也可以指定相对路径或者绝对路径。
<!-- http://localhost:8080/user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="https://blog.csdn.net" th:href="@{'http://localhost:8080/user?name='+${user.name}+'$age='+${user.age}}">点击一下</a>
<a href="https://blog.csdn.net" th:href="@{'http://localhost:8080/user(name=${user.name},age=${user.age})'}">点击一下</a>
<!-- http://localhost:8080/user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="https://blog.csdn.ne" th:href="@{|http://localhost:8080/user?name=${user.name}$age=${user.age}|}">点击一下</a>
<!-- user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="https://blog.csdn.ne" th:href="@{'user?name='+${user.name}+'$age='+${user.age}}">点击一下(相对页面)</a>
<!-- /springboot-thymeleaf/user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="https://blog.csdn.ne" th:href="@{'/user?name='+${user.name}+'$age='+${user.age}}">点击一下(相对项目)</a>
2.4 消息表达式/资源表达式
语法:
#{...}
消息表达式也叫资源表达式,通常用于显示页面静态文本,可以将静态文本维护在properties配置文件用Key索引Value方便维护,做国际化等功能。
若使用消息表达式做国际化功能,我们首先需要不同的配置文件,这里我们在statics/messages下建三个配置文件
messages.properties
main.msg=默认消息
second.msg=独有信息
messages_zh_CN.properties
main.msg=消息表达式
messages_en_US.properties
main.msg=msg expression
由于我们项目是Spring Boot构建项目,所以需要在application配置文件中配置扫描国际化配置文件路径
application.properties
#国际化配置文件
spring.messages.basename=statics/messages/messages
接下来我们就可以使用
#{}去获取数据
<!-- 信息表达式 -->
<p>
<span th:text="#{main.msg}">example</span>
<span th:text="#{second.msg}">example</span>
</p>
很简单我们就可以实现国家化的功能,这里大家需要注意的是关于国际化的配置文件存在优先级别的,假如存在以下三个配置文件,那么下面文件会从上往下为高至低的优先级去匹配。
messages_zh_CN.properties
messages_zh.properties
messages.properties
3.常用标签属性
在之前的介绍中,我们已经接触到了一些Thymeleaf的常见标签属性,那么我们来看看Thymeleaf还给我们提供了哪些功能的标签属性。
| 标签 | 功能 | 示例 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| th:id | id声明,替换id | <input th:id="'user' + ${user.id}"/> |
|
| th:text | 文本替换 | <p th:text="${msg}">description</p> |
<td th:text="7+8">2019</td> |
| th:utext | 支持html文本替换 | <p th:utext="${htmlcontent}">html</p> |
|
| th:object | 替换对象,用于数据对象绑定 | <div th:object="${user}"> |
|
| th:value | 属性赋值 | <input th:value="${user.name}" /> |
|
| th:with | 变量赋值运算 | <div th:with="flag=${user.count}%2==0"></div> |
|
| th:style | 设置样式 | <div th:style="'display:none;'">style</div> |
|
| th:onclick | 点击事件 | th:onclick="'myOnclick()'" |
|
| th:if | 判断条件 | <span th:if="${display} eq true" th:text="${display}">true</span> |
<div th:if="${user} != null and ${check} != null">show</div> |
| th:unless | 与th:if判断相反 | <span th:unless="${display} eq true" th:text="${display}">false</span> |
|
| th:each | 对象遍历,功能类似jstl中的<c:forEach>标签 |
<p th:each="user,iterStat:${userList}"> |
|
| th:href | 超链接,类似<a>标签的href 属性 |
<a th:href="@{/login}" th:unless=${session.user != null}>Login</a> /> |
|
| th:switch | 多路选择,配合th:case使用 | <div th:switch="${user.sex}"> |
|
| th:case | th:switch的分支 | <span th:case="1">男</span><span th:case="2">女</span><span th:case="*">未知</span> |
|
| th:fragment | 布局标签,声明该属性的div为模板片段,常用与头文件、页尾文件的引入。常与th:include,th:replace组合使用。 |
<div th: fragment="copy" >fragment</div> |
<div th: include=" /templates/footer : : copy" ></div> |
| th:include | 布局标签,替换内容到引入的文件 | <head th:include="layout :: htmlhead" th:with="title='include'"></head> /> |
|
| th:replace | 布局标签,替换整个标签到引入的文件 | <div th:replace="fragments/header :: title"></div> |
|
| th:selected | 选择框选中 | th:selected="(${user.id} == ${target.id})" |
|
| th:src | 用于外部资源引入,类似于<script>标签的src属性 |
<img class="img-responsive" alt="App Logo" th:src="@{/img/logo.png}" /> |
|
| th:inline | 内联文本、内联脚本 | <div th:inline="text"> [[${user.name}]]</div> |
<script th:inline="javascript" type="text/javascript">console.log([[${user.name}]]);</script> |
| th:action | 定义后台控制器路径,类似<form>标签的action属性 |
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}"> |
|
| th:remove | 删除某个属性 1.all:删除包含标签和所有的孩子。2.body:不包含标记删除,但删除其所有的孩子。3.tag:包含标记的删除,但不删除它的孩子。4.all-but-first:删除所有包含标签的孩子,除了第一个。5.none:什么也不做。这个值是有用的动态评估。 | <tr th:remove="all"> |
|
| th:attr | 设置标签属性,多个属性可以用逗号分隔 | <span th:text="${user.name}" th:attr="age=${user.age},sex=${user.sex}"> |
3.1 常用标签属性使用
ThymeleafController.java
@RequestMapping(value = "/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","thymeleaf controller...");
model.addAttribute("user",new User("jackson",20));
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
HashMap<Integer, Object> userMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i ++){
User user = new User("jackson" + i, (int) (Math.random() * 10) + i);
users.add(user);
userMap.put(i,user);
}
model.addAttribute("userList",users);
model.addAttribute("userMap",userMap);
model.addAttribute("display",true);
model.addAttribute("sex",1);
return "index";
}
在我们使用Thymeleaf模板时,遍历是我们开发中经常遇见的,在以前使用JSP时,我们使用c:foreach标签可以轻松完成数组集合的遍历,这里也一样,Thymeleaf提供了th:each标签属性很方便地也能达到遍历的效果。
th:each遍历
对于array以及list数组,Thymeleaf提供了很多遍历帮助变量:
- index:当前迭代对象index(0开始)
- count:当前迭代对象个数(1开始)
- size:被迭代对象大小
- current:当前迭代变量
- even/odd:布尔值,当前循环是否奇数/偶数
- first:布尔值,当前循环是否第一个
- last:布尔值,当前循环是否最后一个
注意:循环体信息iterStat若不定义,则默认采用迭代变量+Stat,这里为userStat(若iterStat未定义)
<p th:each="user,iterStat:${userList}">
<span th:text="${user.name}">杰克逊</span>
<span th:text="${user.age}">18</span>
<span th:text="${iterStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${iterStat.size}"></span>
<span th:text="${iterStat.first}"></span>
</p>
<!-- Map类型遍历 -->
<p th:each="map:${userMap}">
<span th:text="${map.key}">key</span>
<span th:text="${map.value}">value</span>
<span th:text="${map.value.name}">杰克逊</span>
<span th:text="${map.value.age}">18</span>
</p>
th:switch/th:case 多路开关
<span th:switch="${user.sex}">
<span th:case="1">男</span>
<span th:case="2">女</span>
<span th:case="*">未知</span>
</span>
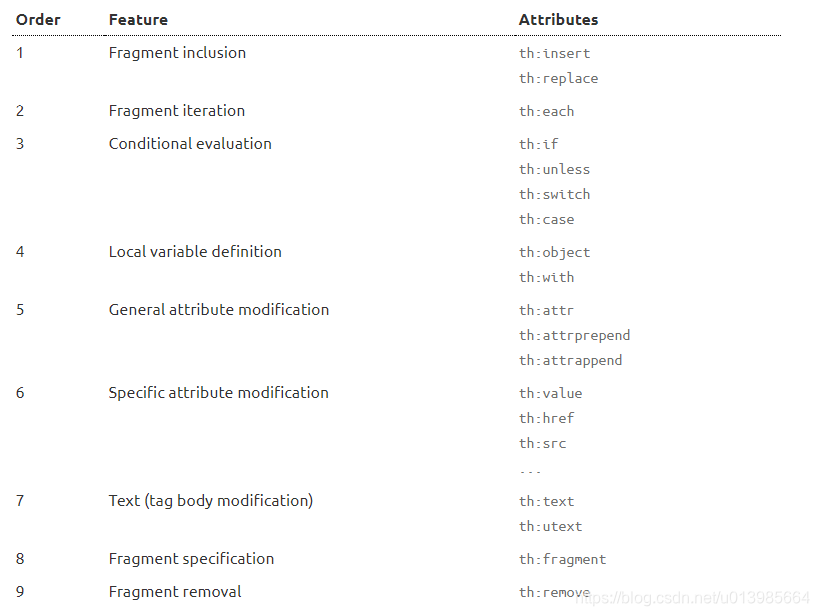
3.2 常用标签属性优先级
由于一个标签中可以添加多个属性,那么当然会有一个优先级的问题,这里我们可以看到官方文档给我们列举出了各个标签属性的优先级,大家组合使用的时候需要注意
4.表达式支持语法
为了更好地使用Thymeleaf模板,我们对其支持的语法进行了解可以更加提升我们开发的效率,所有以下特征都可以被组合嵌套使用,这里我们看一下支持的语法有哪些。
4.1 字面量(literals)
文本字面量:用单引号’ '包围的字符串为文本字面量 例:
'api/user', 'hello world'
数字字面量:0, 88.8
布尔字面量:true, false
空字面量:null
4.2 文本操作(Text operations)
字符串连接: 即字面量拼接,用 + 连接多个字面量 例:
'当前在线用户:'+${user.online}+'位'文本替换:使用 | 减少字符串拼接,更为优雅 例:
|当前在线用户${user.online}位|
4.3 算术运算(Arithmetic operations)
二元运算符:
+, -, *, /, %
三元运算符:?:例:<span th:if="${sex} eq 1?'男':'女'">未知</span>
关系比较:>, <, >=, <= (gt, lt, ge, le)
等值运算符:==, != (eq, ne)
4.4 布尔操作(Boolean operations)
一元运算符:
!, not
二元运算符:and, or
4.5 条件运算符(Conditional operators)
If-then:
(if) ? (then)
If-then-else:(if) ? (then) : (else)
4.6 表达式上下文内置对象
在使用Thymeleaf模板时我们仍能通过表达式去获取某些上下文内置对象,保持更高的灵活性。
#ctx:上下文对象。
#vars: 上下文变量。
#locale:上下文区域设置。
#request: HttpServletRequest对象(`2.x版本使用#httpServletRequest)。
#response: HttpServletResponse对象(2.x版本使用#httpServletResponse)。
#session: HttpSession对象(2.x版本使用#httpSession)。
#servletContext: ServletContext对象。
以上内置对象我们可以在Thymeleaf引擎模板中直接使用:
<span th:text="${#request.getContextPath()}"></span>
4.7 表达式功能内置对象
除了上面的上下文内置对象,Thymeleaf模板引擎也提供了一组功能性的内置对象,例如集合、时间、数值等处理都可以用这些对象轻松完成,也是通过
#调用,这里我们简单介绍几个,完整的对象和使用各位可以查看官方文档Thymeleaf官方文档-表达式功能性内置对象
- #dates:日期处理对象,使用和java.util.Date对象一致 例:
<span th:text="${#dates.format('2018/12/28','yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">时间功能对象</span>- #numbers:格式化数字的功能性内置对象
- #strings:字符串处理功能性内置对象 例:
${#strings.contains('jackson','on')}
所有的这里不一一列出,各位可以通过上面连接去官方文档里面查看,更加详细
5.集成Thymeleaf
首先对于Spring Boot的Web项目有几点是需要我们知道的:
- 静态资源(css、js、图片等)默认放在resources/static下面。如果要修改默认存放目录,可以通过设置属性 spring.mvc.static-path-pattern来实现。
- 模板文件默认放在 templates目录下,Spring boot支持使用模板来开发web应用,支持的模板类型包括
FreeMarker、Groovy、Thymeleaf、Mustache
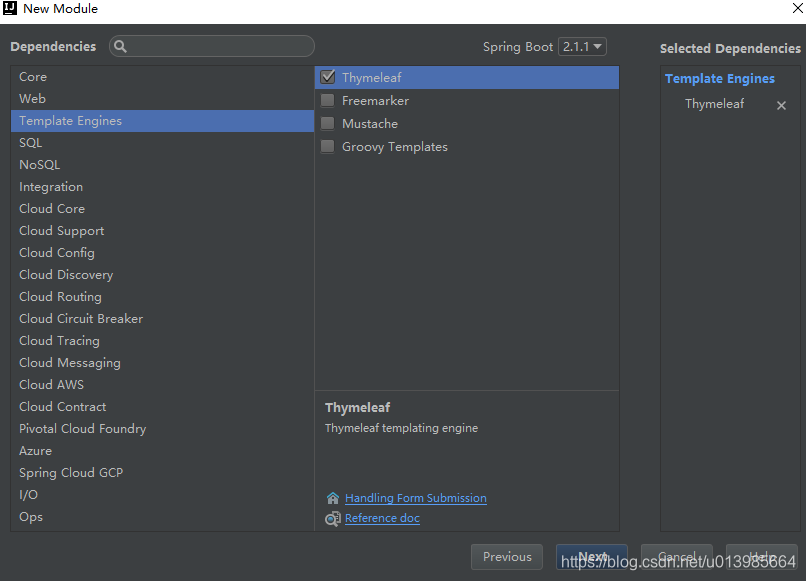
5.1 添加pom依赖
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-thymeleaf</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- springboot web起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- spring boot 整合thymeleaf起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 取消标签严格验证 设置spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGAYHTML5需要引入以下依赖-->
<!-- <dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId>
<artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.unbescape</groupId>
<artifactId>unbescape</artifactId>
<version>1.1.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>-->
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/webapp</directory>
<targetPath>META-INF/resources</targetPath>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
5.2 配置文件
这里我们不需要配置什么过多的属性就可以直接去使用Thymeleaf模板引擎,特别方便
application
# 开发阶段,建议关闭thymeleaf缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
# 使用遗留的html5 去除html标签严格验证
# spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot-thymeleaf
5.3 使用
ThymeleafController.java
package com.springboot.controller;
import com.springboot.repository.entity.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author hzk
* @date 2018/12/27
*/
@Controller
public class ThymeleafController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","thymeleaf controller...");
model.addAttribute("user",new User("jackson",20));
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
HashMap<Integer, Object> userMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i ++){
User user = new User("jackson" + i, (int) (Math.random() * 10) + i);
users.add(user);
userMap.put(i,user);
}
model.addAttribute("userList",users);
model.addAttribute("userMap",userMap);
model.addAttribute("display",true);
model.addAttribute("sex",1);
return "index";
}
}
我们可以通过上面controller填充好数据然后转发到index.html模板页面,所以我们需要在templates目录下放置index.html文件,这里只需要将
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">加上即可使用Thymeleaf。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 标准变量表达式 -->
<p th:text="${msg}">
index....
</p>
<p>
<span th:text="${user.name}">杰克逊</span>
<span th:text="${user.age}">18</span>
</p>
<!-- 选择变量表达式:先使用th:object绑定对象 后用*可直接获取对象属性-->
<p th:object="${user}">
<span th:text="*{name}">杰克逊a</span>
<span th:text="*{age}">18a</span>
</p>
<!-- 标准变量表达式和选择变量表达式可以混用-->
<p th:object="${user}">
<span th:text="${user.name}">杰克逊b</span>
<span th:text="*{age}">18b</span>
</p>
<!--不使用th:object绑定对象,也可直接使用*{}获取属性-->
<p>
<span th:text="*{user.name}">杰克逊c</span>
<span th:text="*{user.age}">18c</span>
</p>
<!-- 信息表达式 -->
<p>
<span th:text="#{main.msg}">example</span>
<span th:text="#{second.msg}">example</span>
</p>
<!-- url表达式 -->
<p>
<!-- http://localhost:8080/user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" th:href="@{'http://localhost:8080/user?name='+${user.name}+'$age='+${user.age}}">点击一下</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" th:href="@{'http://localhost:8080/user(name=${user.name},age=${user.age})'}">点击一下(设置参数)</a>
<!-- http://localhost:8080/user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" th:href="@{|http://localhost:8080/user?name=${user.name}$age=${user.age}|}">点击一下</a>
<!-- user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" th:href="@{'user?name='+${user.name}+'$age='+${user.age}}">点击一下(相对页面)</a>
<!-- /springboot-thymeleaf/user?name=jackson$age=20 -->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" th:href="@{'/user?name='+${user.name}+'$age='+${user.age}}">点击一下(相对项目)</a>
</p>
<!-- list/数组 th:each 遍历属性
index:当前迭代对象index(0开始)
count:当前迭代对象个数(1开始)
size:被迭代对象大小
current:当前迭代变量
even/odd:布尔值,当前循环是否奇数/偶数
first:布尔值,当前循环是否第一个
last:布尔值,当前循环是否最后一个
注意:循环体信息iterStat若不定义,则默认采用迭代变量+Stat,这里为userStat-->
<p th:each="user,iterStat:${userList}">
<span th:text="${user.name}">杰克逊</span>
<span th:text="${user.age}">18</span>
<span th:text="${iterStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${iterStat.size}"></span>
<span th:text="${iterStat.first}"></span>
</p>
<!-- Map类型遍历 -->
<p th:each="map:${userMap}">
<span th:text="${map.key}">key</span>
<span th:text="${map.value}">value</span>
<span th:text="${map.value.name}">杰克逊</span>
<span th:text="${map.value.age}">18</span>
</p>
<!-- 条件判断 == / eq 字符串需要''
th:unless 与之相反 -->
<p>
<span th:if="${display} eq true" th:text="${display}">
th:if
</span>
<span th:unless="${display} eq true" th:text="${display}">
th:unless
</span>
<span th:switch="${sex}">
<span th:case="1">1</span>
<span th:case="2">2</span>
<span th:case="*">未知</span>
</span>
</p>
<!-- th:attr 设置标签属性 -->
<p>
<span th:text="${user.name}" th:attr="age=${user.age},sex=${user.sex}"></span>
</p>
<!-- th:style设置样式 -->
<div th:style="'display:none;'">
ttt
</div>
<!-- 内联文本 用内联表达式可以获取属性
<div th:text="${user.name}">
jack
</div> 与此效果一致-->
<div th:inline="text">
[[${user.name}]]
</div>
<!-- 内敛脚本 th:inline="javascript" -->
<script th:inline="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var user = [[${user.name}]];
console.log(user);
</script>
<script th:src="@{/js/index.js}"></script>
<!-- 字面量 -->
<p>
<span th:text="'a'+'b'">文本字面量 ''</span>
<span th:text="2018+1">数字字面量</span>
<span th:if="${users == null}">
null字面量
</span>
</p>
<!-- 字符串拼接 -->
<p>
<span th:text="'第一种拼接方式'+${user.name}">第一种</span>
<span th:text="|第二种拼接方式${user.name}|">第二种</span>
</p>
<!--<p>
<span th:if="${sex} eq 1?'男':'女'">不清楚</span>
</p>-->
<!-- 运算关系判断
算数运算: + - * / %
关系比较: > < >= <= (gt lt ge le)
相等判断: == != (eq ne)-->
<!-- #request(相当于HttpServletRequest 2.x使用#httpServletRequest)
#session(相当于HttpSession 2.x使用#httpSession) ...
表达式基本内置对象-->
<p>
<span th:text="${#request.getContextPath()}"></span>
</p>
<!-- 功能内置对象 #dates #strings #object #lists .....
模板引擎提供一组功能性内置对象,可以在模板中直接使用这些功能对象提供的功能方法,以#开头引用-->
<p>
<span th:text="${#dates.format('2018/12/28','yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">时间功能对象</span>
</p>
</body>
</html>
我们可以感受到Spring Boot集成Thymeleaf没有很多繁琐的操作,甚至很简单就可以去使用该模板引擎。更多的是我们对Thymeleaf特性的了解和功能的使用需要花一些时间,官方文档上面还是很齐全的,所以大家可以有时间多看一看官方文档提供的信息。