首先,我们创建一个数据库shopping,并插入几条记录()因为这个练习是用来练习servlet,所以我们用session来存值,并没有在数据库创建用户表和购物车表
use master
go
if exists (select * from sysdatabases where name='shopping')
drop database shopping
--创建数据库
create database shopping
use shopping
--创建商品表
create table shop
(
shopId int identity(1,1),
shopName varchar(20) not null,
price money
)
--添加商品
insert into shop
select '魔界剑圣异界纵横',360 union all
select '斗破苍穹',360 union all
select '武动乾坤',250 union all
select '大主宰',260 union all
select '元尊',180然后我们开始写java代码,项目的主题构造如下:
创建底层的链接数据库方法(BaseDao.java),我这里把增删改查的方法给抽出来了一写他们都有的代码,这样写方法时就会省事
package com.ruanyuan.Dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class BaseDao {
//驱动
private static final String DRIVER="com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver";
//数据库的URL
private static final String URL="jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;DatabaseName=Shopping";
//数据库的用户名
private static final String USERNAME="sa";
//数据库的密码
private static final String PASSWORD="sa";
//连接对象
protected Connection conn;
//预编译PreparedStatement对象
protected PreparedStatement pstmt;
//结束集ResultSet对象
protected ResultSet rs;
// 数据库连接
protected void getConnection() {
try {
// 注册sql驱动
Class.forName(DRIVER);
// 加载驱动并且得到连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 释放资源
protected void closeResource() {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();// 释放结果集
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (pstmt != null) {
try {
pstmt.close();// 释放预编译的命令对象
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();// 释放连接对象
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 增 删 改 的通用方法
* @param sql
* @param paras
* @return
*/
protected int execUpdate(String sql, String[] paras) {
int count = 0;// 受影响的行数
try {
// 连接数据库
this.getConnection();
// 基于sql语句构建PreparedStatement对象
pstmt=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 遍历参数数组,并将值赋给PrepareStatement对象
if (paras != null && paras.length > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < paras.length; i++) {
pstmt.setString(i + 1, paras[i]);
}
}
// 执行SQL语句
count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
this.closeResource();
}
return count;
}/**
* 查询 的通用方法
*/
protected ResultSet execQuery(String sql,String[] paras){
try {
//连接数据库
this.getConnection();
//基于SQL语句创建PreparedStantment对象
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//将SQL语句参数数组中的值依次赋给预执行语句
if(paras!=null&¶s.length>0){
for (int i = 0; i < paras.length; i++) {
pstmt.setString(i + 1, paras[i]);
}
}
//执行SQL语句
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果集
return rs;
}接下来我们封装一个shop类
package com.ruanyuan.entity;
public class Shop {
private int shopId;
private String shopName;
private int price;
private int count;
public int getShopId() {
return shopId;
}
public void setShopId(int shopId) {
this.shopId = shopId;
}
public String getShopName() {
return shopName;
}
public void setShopName(String shopName) {
this.shopName = shopName;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
}
然后我们开始写方法,我们在一进入网页时,需要展示所有商品,在购买后跳转到购物车界面,我们需要根据商品id查询出购买的商品名称
代码如下:(从代码可以看出,我们继承了连接数据库的BaseDao,在写每个方法时,我们调用父类的方法super.来调用)
package com.ruanyuan.Dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.ruanyuan.entity.Shop;
public class ShopDao extends BaseDao {
//all商品
public List<Shop> allshop(){
String sql="select * from shop";
List<Shop> list =new ArrayList<Shop>();
try {
super.execQuery(sql, null);
while(rs.next()){
Shop shop = new Shop();
shop.setShopId(rs.getInt("shopId"));
shop.setPrice(rs.getInt("price"));
shop.setShopName(rs.getString("shopName"));
list.add(shop);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{super.closeResource();}
return list;
}
//id查找
public Shop searchById(int shopId){
Shop shop=new Shop();
String sql="select * from shop where shopId=?";
String[] paras={String.valueOf(shopId)};
try {
super.execQuery(sql, paras);
if(rs.next()){
shop.setShopId(rs.getInt("shopId"));
shop.setPrice(rs.getInt("price"));
shop.setShopName(rs.getString("shopName"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return shop;
}
}
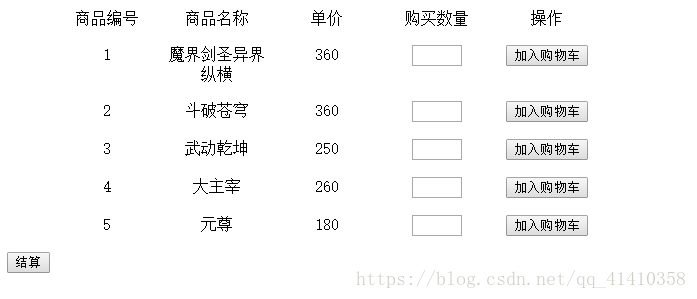
然后我们搭建页面,index.jsp,这里我们用了java小脚本,也是为了方便,没有再写成servlet
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ page import="com.ruanyuan.Dao.*"%>
<%@ page import="com.ruanyuan.entity.*"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
<style type="text/css">
.float_ul{
list-style-type: none;
}
ul li{
float: left;
padding-left: 10px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<%
ShopDao shopdao = new ShopDao();
List<Shop> list=shopdao.allshop();
request.setAttribute("list",list);
%>
<body>
<ul class="float_ul">
<li>商品编号</li>
<li>商品名称</li>
<li>单价</li>
<li>购买数量</li>
<li>操作</li>
</ul>
<div style="clear: both;" ></div>
<c:forEach var="shop" items="${list}">
<form action="shopservlet" method="post">
<ul class="float_ul">
<li>${shop.shopId }<input type="hidden" value="${shop.shopId }" name="itemID"/></li>
<li>${shop.shopName }</li>
<li>${shop.price }</li>
<li><input type="text" name="ShopCount" value="" style="width: 50px;"/></li>
<li><input type="submit" value="加入购物车"/></li>
</ul>
<div style="clear: both;" ></div>
</form>
</c:forEach>
<input type="button" value="结算" onclick="location.href='account.jsp'">
</body>
</html>
运行界面如下:
当我们输入购买数量,点击加入购物车时,会跳转到shopservlet,(这里我们需要存商品id,和商品信息,所以我们用了HsahMap)
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ShopDao shopdao = new ShopDao();
int itemID=Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("itemID"));//获取商品id
int buyCount=Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("ShopCount"));//获取商品购买数量
HttpSession session = request.getSession();//创建一个session
HashMap<Integer, Shop> shopCart = null;
if(session.getAttribute("SelectedGoods")==null){//判断是否第一次跳转到servlet
shopCart = new HashMap<Integer,Shop>();
}else{
shopCart = (HashMap<Integer,Shop>) session.getAttribute("SelectedGoods");
}
//判断购物车中是否存在已经购买的商品,如果存在,则只增加数据,否则添加新的购买条目
if(shopCart.containsKey(itemID)){
int oldCount = (Integer)shopCart.get(itemID).getCount();
Shop shop=shopdao.searchById(itemID);
shop.setCount(oldCount+buyCount);
shopCart.put(itemID, shop);
}else{
Shop shop=shopdao.searchById(itemID);
shop.setCount(buyCount);
shopCart.put(itemID, shop);
}
//将购买的商品保存到session
session.setAttribute("SelectedGoods", shopCart);
response.sendRedirect("index.jsp");//重定向到index.jsp
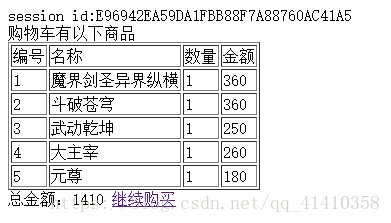
}当我们点击结算时,跳转到account.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
session id:<%=session.getId() %><br/>
<c:if test="${empty sessionScope.SelectedGoods}">
<h1>未购买任何商品</h1>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${not empty sessionScope.SelectedGoods}">
购物车有以下商品<br/>
<c:set var="total" value="0"></c:set>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>编号</td><td>名称</td><td>数量</td><td>金额</td></tr>
<c:forEach items="${sessionScope.SelectedGoods}" var="good">
<tr><td>${good.key}</td><td>${good.value.shopName }</td><td>${good.value.count}</td><td>${good.value.count*good.value.price }</td></tr>
<c:set var="total" value="${total+good.value.count*good.value.price }"></c:set>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</c:if>
总金额:${total }
<a href="index.jsp">继续购买</a>
</body>
</html>
现在我们每个商品各买了一次,结算界面如下: