版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/Wqh_lrr/article/details/79850193
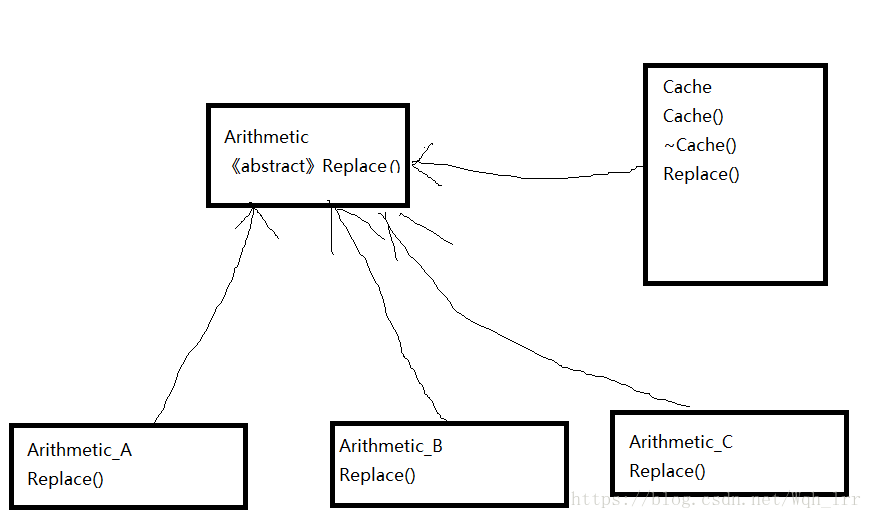
定义算法家族,分别封装起来,让他们之间可以相互替换,让算法变化,不会影响到用户。适合类中的成员以方法为主,算法经常变动,简化了单元测试(因为每个算法都有自己的类),可以通过自己的借口单独测试。策略模式和简单工厂模式基本相同,但简单工厂模式只能解决对象创建问题,对于经常变动的算法应该使用策略模式。
//策略模式
class Arithmetic
{
public:
virtual void Replace() = 0;
};
//三种具体的替换算法
class Arithmetic_A : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic A" << endl; }
};
class Arithmetic_B : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic B" << endl; }
};
class Arithmetic_C : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic C" << endl; }
};
//Cache需要用到替换算法
class Cache
{
private:
Arithmetic * ar;
public:
Cache(Arithmetic *temp) { ar = temp; }
~Cache() { delete ar; }
void Replace() { ar->Replace(); }
};
int main()
{
Cache *cache = new Cache(new Arithmetic_A);//暴露了算法的定义
cache->Replace();
Cache *cache_1 = new Cache(new Arithmetic_B);//暴露了算法的定义
cache_1->Replace();
Cache *cache_2 = new Cache(new Arithmetic_C);//暴露了算法的定义
cache_2->Replace();
return 0;
}策略模式与工厂模式结合:客户端只需访问Cache类,而不用知道其他任何信息,只需要知道算法的标签就行了,实现了低耦合。
enum CTYPE {RA, RB ,RC};
//策略模式
class Arithmetic
{
public:
virtual void Replace() = 0;
};
//三种具体的替换算法
class Arithmetic_A : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic A" << endl; }
};
class Arithmetic_B : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic B" << endl; }
};
class Arithmetic_C : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic C" << endl; }
};
//Cache需要用到替换算法
class Cache
{
private:
Arithmetic * ar;
public:
Cache(CTYPE temp)
{
if (temp == RA)
ar = new Arithmetic_A();
else if (temp == RB)
ar = new Arithmetic_B();
else if (temp == RC)
ar = new Arithmetic_C();
else
ar = NULL;
}
~Cache() { delete ar; }
void Replace() { ar->Replace(); }
};
int main()
{
Cache *cache = new Cache(RA);//Cache cache(RA); cache.Replace();
cache->Replace();
Cache *cache_1 = new Cache(RB);
cache_1->Replace();
Cache *cache_2 = new Cache(RC);
cache_2->Replace();
return 0;
}不需要传参数,直接调用指定算法
//策略模式
class Arithmetic
{
public:
virtual void Replace() = 0;
};
//三种具体的替换算法
class Arithmetic_A : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic A" << endl; }
};
class Arithmetic_B : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic B" << endl; }
};
class Arithmetic_C : public Arithmetic
{
public:
void Replace() { cout << "Arithmetic C" << endl; }
};
template <class ARI>
class Cache
{
private:
ARI ar;
public:
Cache(){}
~Cache() {}
void Replace() { ar.Replace(); }
};
int main()
{
Cache<Arithmetic_B> cache; //模板实参
cache.Replace();
return 0;
}
策略模式图