1.不可重入锁和可重入锁
在java中synchronized和ReentrantLock都是可重入锁
可重入锁和不可重入锁的概念:在一个锁中再次获取这个锁,可以获取就是可重入锁(也叫做递归锁),不可获取就是不可重入锁(也交自旋锁)(个人理解)
例如:
public class TestLock {
private synchronized void method1(){
method2();
System.out.println("this is method2");
}
private synchronized void method2(){
System.out.println("this is method2");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestLock lock = new TestLock();
lock.method1();
}
}
运行结果

因为synchronized是可重入锁,所以在method1()中调用method2()可以调用并不会阻塞,如果是不可重入锁的话会被阻塞进入死锁
下面有一个不可重入锁的例子(摘自https://blog.csdn.net/u012545728/article/details/80843595)
public class Lock{
private boolean isLocked = false;
public synchronized void lock() throws InterruptedException{
while(isLocked){
wait();
}
isLocked = true;
}
public synchronized void unlock(){
isLocked = false;
notify();
}
}在一个线程执行lock()之后在执行lock()会被阻塞
2.ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock和synchronized的基本用法差不多,作用都是加锁,在jdk1.5之后性能也差不多
public class TestReentrantLock {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private void method1(){
lock.lock();
System.out.println("this is method1");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.unlock();
}
private void method2(){
lock.lock();
System.out.println("this is method2");
lock.unlock();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final TestReentrantLock reentrantLock = new TestReentrantLock();
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
reentrantLock.method1();
}
}.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
reentrantLock.method2();
}
}
但ReentrantLock的功能更为强大
1.响应中断式加锁

可以通过Thread.interrupt()来中断锁
public class TestReentrantLock2 {
static ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread =new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
lock1.lockInterruptibly();//以中断方式加锁
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
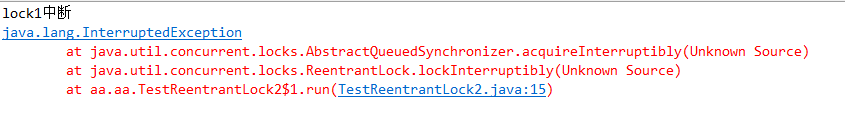
System.out.println("lock1中断");
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(lock1.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
System.out.println("lock1解锁");
lock1.unlock();
}
}
}
};
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
}
}运行结果
2.申请锁
ReentrantLock可以尝试获取锁tryLock(),如果获取成功返回true,否则返回false,此方法不加参数是立即获取,加时间参数是在多少时间内获取
public class TestReentrantLock3 extends Thread{
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if(lock.tryLock(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
System.out.println(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"得到了锁");
Thread.sleep(2000);
lock.unlock();
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"没有获取到锁");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestReentrantLock3 thread1 = new TestReentrantLock3();
TestReentrantLock3 thread2 = new TestReentrantLock3();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}3.公平锁
带布尔型参数的构造函数,true为公平锁,false为非公平锁。不带参数默认非公平锁。
公平锁是指多个等待的线程获取这个锁会按等待时间顺序获得。
public class TestReentrantLock4 extends Thread{
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取了锁");
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new TestReentrantLock4();
Thread thread2 = new TestReentrantLock4();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}运行结果

4.Condition
ReentrantLock中的newCondition()方法可以创建一个Condition对象,Condition对象可以来使线程wait(必须先执行lock.lock方法获得锁)
这里提一下:Condition类的await()方法和Object类的wait()都是是通过提前释放锁,重新去请求锁导致的阻塞,直到被singal()、notify()、singalAll()、notifyAll()再次获得锁继续执行
public class TestReentrantLock5 {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程等待");
condition.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程继续执行");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
lock.unlock();
}finally{
if(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("一秒后");
System.out.println(lock.isLocked());
lock.lock();
condition.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}运行结果

一个ReentrantLock对象可以创建多个Condition对象,每一个Condition对象的singal()方法和await()方法时一一对应的(不是单例)。