ConcurrentHashMap源码学习
自从学习了AQS之后,想着重新读一下ConcurrentHashMap的源码来加深下理解,所以有了这篇文章,针对ConcurrentHashMap常用的方法进行分析。
0,基础知识以及一些字段的含义
1.8中的ConcurrentHashMap使用了比较多的CAS操作,例如设置每个tab。设置一些变量值,用UnSafe类来操作。
这三个字段值表示了特殊的Hash值, -1时说明这个节点正在transfer(resize), -2则说明该节点已经是一个树结构的根。 -3
static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
sizeCtl,顾名思义就是size Control,控制了大小转变的参数,当初始化时,会默认赋值为0.75cap,每次扩容完成后也是0.75Cap,在扩容中会变成负数,如,初始化为-1,或者为-(1+扩容线程的数量)。
/**
* Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
* table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
* else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
* when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
* creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
* next element count value upon which to resize the table.
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
transferIndex table里下一个去转换的节点。
/**
* The next table index (plus one) to split while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
1,put方法的流程
put方法与hashMap的流程很类似。
为空则初始化
不为空,则计算该key的hash出来的位置,如果该位置Node为null,则CAS给该节点赋值。
然后比较特殊的一点是,防止正在扩容的操作,如果发现正在扩容,则helpTransfer。
如果没有在扩容,则锁住该节点,正常遍历链表查询,没有则插入到最后,如果链表太长,则转化为红黑树。
最后增加新节点后,增加size,然后判断是否扩容。
看一下Node节点以及Node节点的子类:
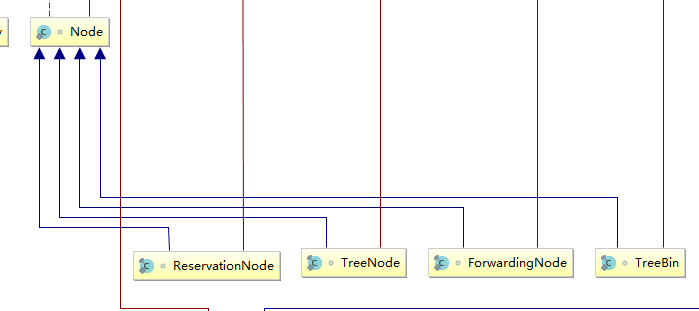
上图是ConcurrentHashMap的uml图中的一点关于Node节点的,一共有四个实现:TreeNode和ForwardingNode以及 TreeBin,ReservationNode。
Node为正常存储时的节点类型。
TreeBin为链表转化为树结构时的树的根节点。
TreeNode为转化为树结构时的树的子节点。
ReservationNode为调用compute方法和computeIfAbsent方法时的占位节点,占位是为了防止多线程下的错误,当然也可以自旋+cas解决,1.8貌似是对 sychronized 进行了优化,很多可以用自旋+cas的都用了sychronized来解决。
下面看正常put过程中,如下图:
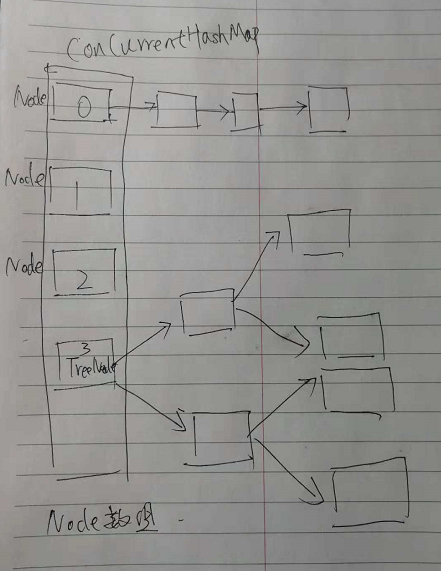
ConcurrentHashMap 的数据结构是Node数组,但是部分的Node会变成他的实现类,在链表长度超过8时,形成树形结构,树的根为TreeBin,TreeBin上不存key value,指向后续的TreeNode节点。快速查找。
接着看看扩容时的变化,如下图:
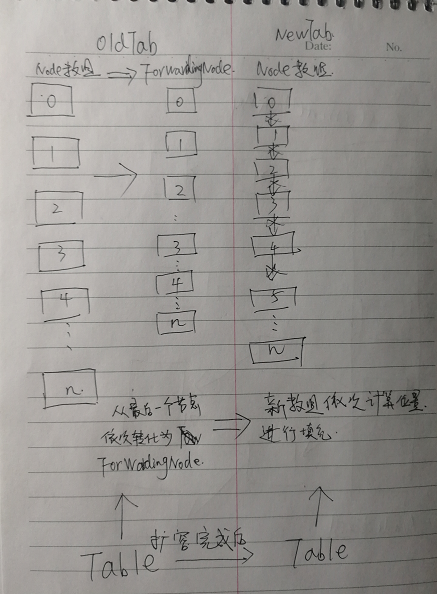
首先会先创建一个NewTab,但是这时候ConcurrentHashMap 的table还是只想oldTab的,接着依次从最后一个节点开始转变,如果节点无值,直接把该节点转化为ForwardingNode,如果有值,则将Node链表上的值依次转移到NewTab中。
逐渐的,oldTab中的Node数组会变成ForwardingNode数组。而newTab数组则转移完成。
此时,ConcurrentHashMap的table会指向newTab。废弃之前的oldTab。
需要注意的是,在转移的过程中,如果put,则会先helpTransfer后put
转移的过程中,如果get,则会用ForwardingNode的find方法来查找所有已有的节点进行返回。
2,get方法的流程
get方法比较简单,除了**“转移的过程中,如果get,则会用ForwardingNode的find方法来查找所有已有的节点进行返回。”**这一点以外,就是Node节点的next和value都设置为volatile,保证数据的可见性。
3,计算size方法
代码如下:
public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
(int)n);
}
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
可以看出来,ConcurrentHashMap的size是靠baseCount和CounterCell求和得到。那么这两个值是怎么赋值的呢?
回顾之前put时的最后一步,addCount方法中,如下列代码所示,counterCells == null时,如果CAS无误,则baseCount计算中所有节点的个数。
但是在并发环境下,CAS失败,则会进入if条件体:调用fullAddCount方法来设置CounterCell里的值。
@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
volatile long value;
CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
}。
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
简单看下fullAddCount方法的内容:
自旋判断,如果 counterCells 已经不为空,则给counterCell的值进行修改,成功则break;
如果 cellsBusy 为0,则用CAS修改这个值为1,然后对counterCells开始修改,修改完毕cellsBusy重新变成0,成功则break;
如果上一步判断仍然不成立,则试着修改baseCount的值,成功则break;
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}