注:本文源码是JDK8的版本,与之前的版本有较大差异
ConcurrentHashMap是conccurrent家族中的一个类,由于它可以高效地支持并发操作,以及被广泛使用,经典的开源框架spring的底层数据结构就是使用ConcurrentHashMap实现的。与同是线程安全的老大哥HashTable相比,它已经更胜一筹,因此它的锁更加细化,而不是像HashTable一样为几乎每个方法都添加了synchronized锁,这样的锁无疑会影响到性能。
本文的分析的源码是JDK8的版本,与JDK6的版本有很大的差异。实现线程安全的思想也已经完全变了,它摒弃了Segment(锁段)的概念,而是启用了一种全新的方式实现,利用CAS算法。它沿用了与它同时期的HashMap版本的思想,底层依然由“数组”+链表+红黑树的方式思想,但是为了做到并发,又增加了很多辅助的类,例如TreeBin,Traverser等对象内部类。
1 重要的属性
首先来看几个重要的属性,与HashMap相同的就不再介绍了,这里重点解释一下sizeCtl这个属性。可以说它是ConcurrentHashMap中出镜率很高的一个属性,因为它是一个控制标识符,在不同的地方有不同用途,而且它的取值不同,也代表不同的含义。
- 负数代表正在进行初始化或扩容操作
- -1代表正在初始化
- -N 表示有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作
- 正数或0代表hash表还没有被初始化,这个数值表示初始化或下一次进行扩容的大小,这一点类似于扩容阈值的概念。还后面可以看到,它的值始终是当前ConcurrentHashMap容量的0.75倍,这与loadfactor是对应的。
- /**
- * 盛装Node元素的数组 它的大小是2的整数次幂
- * Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators.
- */
- transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
- /**
- * Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
- * table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
- * else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
- * when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
- * creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
- * next element count value upon which to resize the table.
- hash表初始化或扩容时的一个控制位标识量。
- 负数代表正在进行初始化或扩容操作
- -1代表正在初始化
- -N 表示有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作
- 正数或0代表hash表还没有被初始化,这个数值表示初始化或下一次进行扩容的大小
- */
- private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
- // 以下两个是用来控制扩容的时候 单线程进入的变量
- /**
- * The number of bits used for generation stamp in sizeCtl.
- * Must be at least 6 for 32bit arrays.
- */
- private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
- /**
- * The bit shift for recording size stamp in sizeCtl.
- */
- private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
- /*
- * Encodings for Node hash fields. See above for explanation.
- */
- static final int MOVED = -1; // hash值是-1,表示这是一个forwardNode节点
- static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash值是-2 表示这时一个TreeBin节点
2 重要的内部类
2.1 Node
Node是最核心的内部类,它包装了key-value键值对,所有插入ConcurrentHashMap的数据都包装在这里面。它与HashMap中的定义很相似,但是但是有一些差别它对value和next属性设置了volatile同步锁,它不允许调用setValue方法直接改变Node的value域,它增加了find方法辅助map.get()方法。
- static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
- final int hash;
- final K key;
- volatile V val;//带有同步锁的value
- volatile Node<K,V> next;//带有同步锁的next指针
- Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.val = val;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public final K getKey() { return key; }
- public final V getValue() { return val; }
- public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }
- public final String toString(){ return key + “=” + val; }
- //不允许直接改变value的值
- public final V setValue(V value) {
- throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
- }
- public final boolean equals(Object o) {
- Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
- return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
- (k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
- (v = e.getValue()) != null &&
- (k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
- (v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
- }
- /**
- * Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
- */
- Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
- Node<K,V> e = this;
- if (k != null) {
- do {
- K ek;
- if (e.hash == h &&
- ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
- return e;
- } while ((e = e.next) != null);
- }
- return null;
- }
- }
- 这个Node内部类与HashMap中定义的Node类很相似,但是有一些差别
- 它对value和next属性设置了volatile同步锁
- 它不允许调用setValue方法直接改变Node的value域
- 它增加了find方法辅助map.get()方法
2.2 TreeNode
树节点类,另外一个核心的数据结构。当链表长度过长的时候,会转换为TreeNode。但是与HashMap不相同的是,它并不是直接转换为红黑树,而是把这些结点包装成TreeNode放在TreeBin对象中,由TreeBin完成对红黑树的包装。而且TreeNode在ConcurrentHashMap集成自Node类,而并非HashMap中的集成自LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>类,也就是说TreeNode带有next指针,这样做的目的是方便基于TreeBin的访问。
2.3 TreeBin
这个类并不负责包装用户的key、value信息,而是包装的很多TreeNode节点。它代替了TreeNode的根节点,也就是说在实际的ConcurrentHashMap“数组”中,存放的是TreeBin对象,而不是TreeNode对象,这是与HashMap的区别。另外这个类还带有了读写锁。
这里仅贴出它的构造方法。可以看到在构造TreeBin节点时,仅仅指定了它的hash值为TREEBIN常量,这也就是个标识为。同时也看到我们熟悉的红黑树构造方法
- /**
- * Creates bin with initial set of nodes headed by b.
- */
- TreeBin(TreeNode<K,V> b) {
- super(TREEBIN, null, null, null);
- this.first = b;
- TreeNode<K,V> r = null;
- for (TreeNode<K,V> x = b, next; x != null; x = next) {
- next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
- x.left = x.right = null;
- if (r == null) {
- x.parent = null;
- x.red = false;
- r = x;
- }
- else {
- K k = x.key;
- int h = x.hash;
- Class<?> kc = null;
- for (TreeNode<K,V> p = r;;) {
- int dir, ph;
- K pk = p.key;
- if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
- dir = -1;
- else if (ph < h)
- dir = 1;
- else if ((kc == null &&
- (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
- (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
- dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
- TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
- if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
- x.parent = xp;
- if (dir <= 0)
- xp.left = x;
- else
- xp.right = x;
- r = balanceInsertion(r, x);
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- this.root = r;
- assert checkInvariants(root);
- }
2.5 ForwardingNode
一个用于连接两个table的节点类。它包含一个nextTable指针,用于指向下一张表。而且这个节点的key value next指针全部为null,它的hash值为-1. 这里面定义的find的方法是从nextTable里进行查询节点,而不是以自身为头节点进行查找
- /**
- * A node inserted at head of bins during transfer operations.
- */
- static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
- final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
- ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
- super(MOVED, null, null, null);
- this.nextTable = tab;
- }
- Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
- // loop to avoid arbitrarily deep recursion on forwarding nodes
- outer: for (Node<K,V>[] tab = nextTable;;) {
- Node<K,V> e; int n;
- if (k == null || tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
- (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) == null)
- return null;
- for (;;) {
- int eh; K ek;
- if ((eh = e.hash) == h &&
- ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
- return e;
- if (eh < 0) {
- if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) {
- tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable;
- continue outer;
- }
- else
- return e.find(h, k);
- }
- if ((e = e.next) == null)
- return null;
- }
- }
- }
- }
3 Unsafe与CAS
在ConcurrentHashMap中,随处可以看到U, 大量使用了U.compareAndSwapXXX的方法,这个方法是利用一个CAS算法实现无锁化的修改值的操作,他可以大大降低锁代理的性能消耗。这个算法的基本思想就是不断地去比较当前内存中的变量值与你指定的一个变量值是否相等,如果相等,则接受你指定的修改的值,否则拒绝你的操作。因为当前线程中的值已经不是最新的值,你的修改很可能会覆盖掉其他线程修改的结果。这一点与乐观锁,SVN的思想是比较类似的。
3.1 unsafe静态块
unsafe代码块控制了一些属性的修改工作,比如最常用的SIZECTL 。 在这一版本的concurrentHashMap中,大量应用来的CAS方法进行变量、属性的修改工作。 利用CAS进行无锁操作,可以大大提高性能。
- private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U;
- private static final long SIZECTL;
- private static final long TRANSFERINDEX;
- private static final long BASECOUNT;
- private static final long CELLSBUSY;
- private static final long CELLVALUE;
- private static final long ABASE;
- private static final int ASHIFT;
- static {
- try {
- U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
- Class<?> k = ConcurrentHashMap.class;
- SIZECTL = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”sizeCtl”));
- TRANSFERINDEX = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”transferIndex”));
- BASECOUNT = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”baseCount”));
- CELLSBUSY = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”cellsBusy”));
- Class<?> ck = CounterCell.class;
- CELLVALUE = U.objectFieldOffset
- (ck.getDeclaredField(”value”));
- Class<?> ak = Node[].class;
- ABASE = U.arrayBaseOffset(ak);
- int scale = U.arrayIndexScale(ak);
- if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0)
- throw new Error(“data type scale not a power of two”);
- ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new Error(e);
- }
- }
3.2 三个核心方法
ConcurrentHashMap定义了三个原子操作,用于对指定位置的节点进行操作。正是这些原子操作保证了ConcurrentHashMap的线程安全。
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
- //获得在i位置上的Node节点
- static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
- return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
- }
- //利用CAS算法设置i位置上的Node节点。之所以能实现并发是因为他指定了原来这个节点的值是多少
- //在CAS算法中,会比较内存中的值与你指定的这个值是否相等,如果相等才接受你的修改,否则拒绝你的修改
- //因此当前线程中的值并不是最新的值,这种修改可能会覆盖掉其他线程的修改结果 有点类似于SVN
- static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
- Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
- return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
- }
- //利用volatile方法设置节点位置的值
- static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) {
- U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v);
- }
4 初始化方法initTable
对于ConcurrentHashMap来说,调用它的构造方法仅仅是设置了一些参数而已。而整个table的初始化是在向ConcurrentHashMap中插入元素的时候发生的。如调用put、computeIfAbsent、compute、merge等方法的时候,调用时机是检查table==null。
初始化方法主要应用了关键属性sizeCtl 如果这个值〈0,表示其他线程正在进行初始化,就放弃这个操作。在这也可以看出ConcurrentHashMap的初始化只能由一个线程完成。如果获得了初始化权限,就用CAS方法将sizeCtl置为-1,防止其他线程进入。初始化数组后,将sizeCtl的值改为0.75*n
- /**
- * Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
- */
- private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
- Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
- while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
- //sizeCtl表示有其他线程正在进行初始化操作,把线程挂起。对于table的初始化工作,只能有一个线程在进行。
- if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
- Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {//利用CAS方法把sizectl的值置为-1 表示本线程正在进行初始化
- try {
- if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
- int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
- Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
- table = tab = nt;
- sc = n - (n >>> 2);//相当于0.75*n 设置一个扩容的阈值
- }
- } finally {
- sizeCtl = sc;
- }
- break;
- }
- }
- return tab;
- }
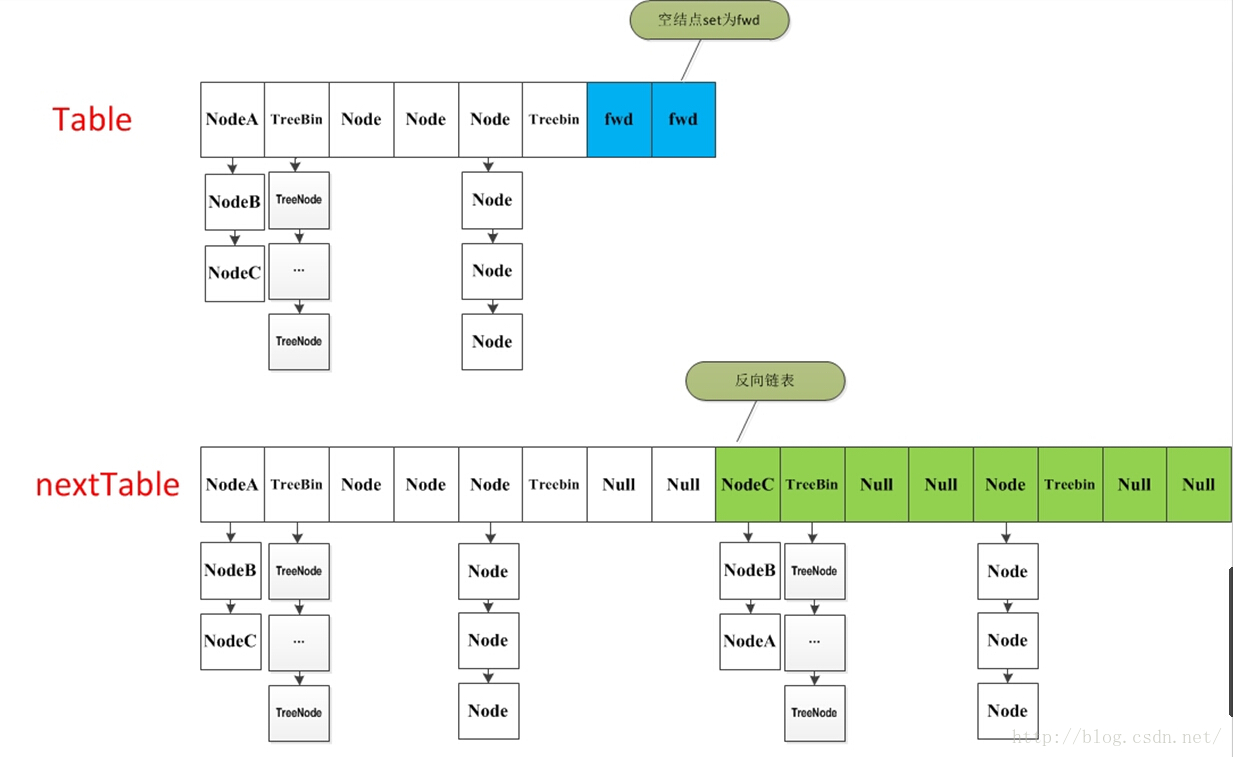
5 扩容方法 transfer
当ConcurrentHashMap容量不足的时候,需要对table进行扩容。这个方法的基本思想跟HashMap是很像的,但是由于它是支持并发扩容的,所以要复杂的多。原因是它支持多线程进行扩容操作,而并没有加锁。我想这样做的目的不仅仅是为了满足concurrent的要求,而是希望利用并发处理去减少扩容带来的时间影响。因为在扩容的时候,总是会涉及到从一个“数组”到另一个“数组”拷贝的操作,如果这个操作能够并发进行,那真真是极好的了。
整个扩容操作分为两个部分-
第一部分是构建一个nextTable,它的容量是原来的两倍,这个操作是单线程完成的。这个单线程的保证是通过RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT这个常量经过一次运算来保证的,这个地方在后面会有提到;
- 第二个部分就是将原来table中的元素复制到nextTable中,这里允许多线程进行操作。
先来看一下单线程是如何完成的:
它的大体思想就是遍历、复制的过程。首先根据运算得到需要遍历的次数i,然后利用tabAt方法获得i位置的元素:
-
如果这个位置为空,就在原table中的i位置放入forwardNode节点,这个也是触发并发扩容的关键点;
-
如果这个位置是Node节点(fh>=0),如果它是一个链表的头节点,就构造一个反序链表,把他们分别放在nextTable的i和i+n的位置上
-
如果这个位置是TreeBin节点(fh<0),也做一个反序处理,并且判断是否需要untreefi,把处理的结果分别放在nextTable的i和i+n的位置上
- 遍历过所有的节点以后就完成了复制工作,这时让nextTable作为新的table,并且更新sizeCtl为新容量的0.75倍 ,完成扩容。
在代码的69行有一个判断,如果遍历到的节点是forward节点,就向后继续遍历,再加上给节点上锁的机制,就完成了多线程的控制。多线程遍历节点,处理了一个节点,就把对应点的值set为forward,另一个线程看到forward,就向后遍历。这样交叉就完成了复制工作。而且还很好的解决了线程安全的问题。 这个方法的设计实在是让我膜拜。
- /**
- * 一个过渡的table表 只有在扩容的时候才会使用
- */
- private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
- /**
- * Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See
- * above for explanation.
- */
- private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
- int n = tab.length, stride;
- if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
- stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
- if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
- try {
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
- Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];//构造一个nextTable对象 它的容量是原来的两倍
- nextTab = nt;
- } catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
- sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- return;
- }
- nextTable = nextTab;
- transferIndex = n;
- }
- int nextn = nextTab.length;
- ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);//构造一个连节点指针 用于标志位
- boolean advance = true;//并发扩容的关键属性 如果等于true 说明这个节点已经处理过
- boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
- for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
- Node<K,V> f; int fh;
- //这个while循环体的作用就是在控制i– 通过i–可以依次遍历原hash表中的节点
- while (advance) {
- int nextIndex, nextBound;
- if (–i >= bound || finishing)
- advance = false;
- else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
- i = -1;
- advance = false;
- }
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
- (this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
- nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
- nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
- bound = nextBound;
- i = nextIndex - 1;
- advance = false;
- }
- }
- if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
- int sc;
- if (finishing) {
- //如果所有的节点都已经完成复制工作 就把nextTable赋值给table 清空临时对象nextTable
- nextTable = null;
- table = nextTab;
- sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);//扩容阈值设置为原来容量的1.5倍 依然相当于现在容量的0.75倍
- return;
- }
- //利用CAS方法更新这个扩容阈值,在这里面sizectl值减一,说明新加入一个线程参与到扩容操作
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
- if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
- return;
- finishing = advance = true;
- i = n; // recheck before commit
- }
- }
- //如果遍历到的节点为空 则放入ForwardingNode指针
- else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
- advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
- //如果遍历到ForwardingNode节点 说明这个点已经被处理过了 直接跳过 这里是控制并发扩容的核心
- else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
- advance = true; // already processed
- else {
- //节点上锁
- synchronized (f) {
- if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
- Node<K,V> ln, hn;
- //如果fh>=0 证明这是一个Node节点
- if (fh >= 0) {
- int runBit = fh & n;
- //以下的部分在完成的工作是构造两个链表 一个是原链表 另一个是原链表的反序排列
- Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
- for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
- int b = p.hash & n;
- if (b != runBit) {
- runBit = b;
- lastRun = p;
- }
- }
- if (runBit == 0) {
- ln = lastRun;
- hn = null;
- }
- else {
- hn = lastRun;
- ln = null;
- }
- for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
- int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
- if ((ph & n) == 0)
- ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
- else
- hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
- }
- //在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
- //在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
- //在table的i位置上插入forwardNode节点 表示已经处理过该节点
- setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
- //设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i–操作
- advance = true;
- }
- //对TreeBin对象进行处理 与上面的过程类似
- else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
- TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
- TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
- TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
- int lc = 0, hc = 0;
- //构造正序和反序两个链表
- for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
- int h = e.hash;
- TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
- (h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
- if ((h & n) == 0) {
- if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
- lo = p;
- else
- loTail.next = p;
- loTail = p;
- ++lc;
- }
- else {
- if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
- hi = p;
- else
- hiTail.next = p;
- hiTail = p;
- ++hc;
- }
- }
- //如果扩容后已经不再需要tree的结构 反向转换为链表结构
- ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
- (hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
- hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
- (lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
- //在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
- //在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
- //在table的i位置上插入forwardNode节点 表示已经处理过该节点
- setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
- //设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i–操作
- advance = true;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
6 Put方法
前面的所有的介绍其实都为这个方法做铺垫。ConcurrentHashMap最常用的就是put和get两个方法。现在来介绍put方法,这个put方法依然沿用HashMap的put方法的思想,根据hash值计算这个新插入的点在table中的位置i,如果i位置是空的,直接放进去,否则进行判断,如果i位置是树节点,按照树的方式插入新的节点,否则把i插入到链表的末尾。ConcurrentHashMap中依然沿用这个思想,有一个最重要的不同点就是ConcurrentHashMap不允许key或value为null值。另外由于涉及到多线程,put方法就要复杂一点。在多线程中可能有以下两个情况
-
如果一个或多个线程正在对ConcurrentHashMap进行扩容操作,当前线程也要进入扩容的操作中。这个扩容的操作之所以能被检测到,是因为transfer方法中在空结点上插入forward节点,如果检测到需要插入的位置被forward节点占有,就帮助进行扩容;
-
如果检测到要插入的节点是非空且不是forward节点,就对这个节点加锁,这样就保证了线程安全。尽管这个有一些影响效率,但是还是会比hashTable的synchronized要好得多。
整体流程就是首先定义不允许key或value为null的情况放入 对于每一个放入的值,首先利用spread方法对key的hashcode进行一次hash计算,由此来确定这个值在table中的位置。
如果这个位置是空的,那么直接放入,而且不需要加锁操作。
如果这个位置存在结点,说明发生了hash碰撞,首先判断这个节点的类型。如果是链表节点(fh>0),则得到的结点就是hash值相同的节点组成的链表的头节点。需要依次向后遍历确定这个新加入的值所在位置。如果遇到hash值与key值都与新加入节点是一致的情况,则只需要更新value值即可。否则依次向后遍历,直到链表尾插入这个结点。 如果加入这个节点以后链表长度大于8,就把这个链表转换成红黑树。如果这个节点的类型已经是树节点的话,直接调用树节点的插入方法进行插入新的值。- public V put(K key, V value) {
- return putVal(key, value, false);
- }
- /** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
- final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
- //不允许 key或value为null
- if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- //计算hash值
- int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
- int binCount = 0;
- //死循环 何时插入成功 何时跳出
- for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
- Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
- //如果table为空的话,初始化table
- if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
- tab = initTable();
- //根据hash值计算出在table里面的位置
- else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
- //如果这个位置没有值 ,直接放进去,不需要加锁
- if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
- new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
- break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
- }
- //当遇到表连接点时,需要进行整合表的操作
- else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
- tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
- else {
- V oldVal = null;
- //结点上锁 这里的结点可以理解为hash值相同组成的链表的头结点
- synchronized (f) {
- if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
- //fh〉0 说明这个节点是一个链表的节点 不是树的节点
- if (fh >= 0) {
- binCount = 1;
- //在这里遍历链表所有的结点
- for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
- K ek;
- //如果hash值和key值相同 则修改对应结点的value值
- if (e.hash == hash &&
- ((ek = e.key) == key ||
- (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
- oldVal = e.val;
- if (!onlyIfAbsent)
- e.val = value;
- break;
- }
- Node<K,V> pred = e;
- //如果遍历到了最后一个结点,那么就证明新的节点需要插入 就把它插入在链表尾部
- if ((e = e.next) == null) {
- pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
- value, null);
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //如果这个节点是树节点,就按照树的方式插入值
- else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
- Node<K,V> p;
- binCount = 2;
- if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
- value)) != null) {
- oldVal = p.val;
- if (!onlyIfAbsent)
- p.val = value;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- if (binCount != 0) {
- //如果链表长度已经达到临界值8 就需要把链表转换为树结构
- if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
- treeifyBin(tab, i);
- if (oldVal != null)
- return oldVal;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量+1
- addCount(1L, binCount);
- return null;
- }
6.1 helpTransfer方法
这是一个协助扩容的方法。这个方法被调用的时候,当前ConcurrentHashMap一定已经有了nextTable对象,首先拿到这个nextTable对象,调用transfer方法。回看上面的transfer方法可以看到,当本线程进入扩容方法的时候会直接进入复制阶段。
- /**
- * Helps transfer if a resize is in progress.
- */
- final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
- Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
- if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
- (nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
- int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);//计算一个操作校验码
- while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
- (sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
- if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
- sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
- break;
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
- transfer(tab, nextTab);
- break;
- }
- }
- return nextTab;
- }
- return table;
- }
6.2 treeifyBin方法
这个方法用于将过长的链表转换为TreeBin对象。但是他并不是直接转换,而是进行一次容量判断,如果容量没有达到转换的要求,直接进行扩容操作并返回;如果满足条件才链表的结构抓换为TreeBin ,这与HashMap不同的是,它并没有把TreeNode直接放入红黑树,而是利用了TreeBin这个小容器来封装所有的TreeNode.
- private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
- Node<K,V> b; int n, sc;
- if (tab != null) {
- if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)//如果table.length<64 就扩大一倍 返回
- tryPresize(n << 1);
- else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
- synchronized (b) {
- if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {
- TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
- //构造了一个TreeBin对象 把所有Node节点包装成TreeNode放进去
- for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {
- TreeNode<K,V> p =
- new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,
- null, null);//这里只是利用了TreeNode封装 而没有利用TreeNode的next域和parent域
- if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
- hd = p;
- else
- tl.next = p;
- tl = p;
- }
- //在原来index的位置 用TreeBin替换掉原来的Node对象
- setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
7 get方法
get方法比较简单,给定一个key来确定value的时候,必须满足两个条件 key相同 hash值相同,对于节点可能在链表或树上的情况,需要分别去查找.
- public V get(Object key) {
- Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
- //计算hash值
- int h = spread(key.hashCode());
- //根据hash值确定节点位置
- if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
- (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
- //如果搜索到的节点key与传入的key相同且不为null,直接返回这个节点
- if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
- if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
- return e.val;
- }
- //如果eh<0 说明这个节点在树上 直接寻找
- else if (eh < 0)
- return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
- //否则遍历链表 找到对应的值并返回
- while ((e = e.next) != null) {
- if (e.hash == h &&
- ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
- return e.val;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
8 Size相关的方法
对于ConcurrentHashMap来说,这个table里到底装了多少东西其实是个不确定的数量,因为不可能在调用size()方法的时候像GC的“stop the world”一样让其他线程都停下来让你去统计,因此只能说这个数量是个估计值。对于这个估计值,ConcurrentHashMap也是大费周章才计算出来的。
8.1 辅助定义
为了统计元素个数,ConcurrentHashMap定义了一些变量和一个内部类
- /**
- * A padded cell for distributing counts. Adapted from LongAdder
- * and Striped64. See their internal docs for explanation.
- */
- @sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
- volatile long value;
- CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
- }
- /******************************************/
- /**
- * 实际上保存的是hashmap中的元素个数 利用CAS锁进行更新
- 但它并不用返回当前hashmap的元素个数
- */
- private transient volatile long baseCount;
- /**
- * Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells.
- */
- private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
- /**
- * Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
- */
- private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
8.2 mappingCount与Size方法
mappingCount与size方法的类似 从Java工程师给出的注释来看,应该使用mappingCount代替size方法 两个方法都没有直接返回basecount 而是统计一次这个值,而这个值其实也是一个大概的数值,因此可能在统计的时候有其他线程正在执行插入或删除操作。
- public int size() {
- long n = sumCount();
- return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
- (n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
- (int)n);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the number of mappings. This method should be used
- * instead of {@link #size} because a ConcurrentHashMap may
- * contain more mappings than can be represented as an int. The
- * value returned is an estimate; the actual count may differ if
- * there are concurrent insertions or removals.
- *
- * @return the number of mappings
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public long mappingCount() {
- long n = sumCount();
- return (n < 0L) ? 0L : n; // ignore transient negative values
- }
- final long sumCount() {
- CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;
- long sum = baseCount;
- if (as != null) {
- for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
- if ((a = as[i]) != null)
- sum += a.value;//所有counter的值求和
- }
- }
- return sum;
- }
8.3 addCount方法
在put方法结尾处调用了addCount方法,把当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素个数+1这个方法一共做了两件事,更新baseCount的值,检测是否进行扩容。
- private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
- CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
- //利用CAS方法更新baseCount的值
- if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
- !U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
- CounterCell a; long v; int m;
- boolean uncontended = true;
- if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
- (a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
- !(uncontended =
- U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
- fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
- return;
- }
- if (check <= 1)
- return;
- s = sumCount();
- }
- //如果check值大于等于0 则需要检验是否需要进行扩容操作
- if (check >= 0) {
- Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
- while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
- (n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
- int rs = resizeStamp(n);
- //
- if (sc < 0) {
- if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
- sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
- transferIndex <= 0)
- break;
- //如果已经有其他线程在执行扩容操作
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
- transfer(tab, nt);
- }
- //当前线程是唯一的或是第一个发起扩容的线程 此时nextTable=null
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
- (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
- transfer(tab, null);
- s = sumCount();
- }
- }
- }
(未完待续。。。)
注:本文源码是JDK8的版本,与之前的版本有较大差异
ConcurrentHashMap是conccurrent家族中的一个类,由于它可以高效地支持并发操作,以及被广泛使用,经典的开源框架spring的底层数据结构就是使用ConcurrentHashMap实现的。与同是线程安全的老大哥HashTable相比,它已经更胜一筹,因此它的锁更加细化,而不是像HashTable一样为几乎每个方法都添加了synchronized锁,这样的锁无疑会影响到性能。
本文的分析的源码是JDK8的版本,与JDK6的版本有很大的差异。实现线程安全的思想也已经完全变了,它摒弃了Segment(锁段)的概念,而是启用了一种全新的方式实现,利用CAS算法。它沿用了与它同时期的HashMap版本的思想,底层依然由“数组”+链表+红黑树的方式思想,但是为了做到并发,又增加了很多辅助的类,例如TreeBin,Traverser等对象内部类。
1 重要的属性
首先来看几个重要的属性,与HashMap相同的就不再介绍了,这里重点解释一下sizeCtl这个属性。可以说它是ConcurrentHashMap中出镜率很高的一个属性,因为它是一个控制标识符,在不同的地方有不同用途,而且它的取值不同,也代表不同的含义。
- 负数代表正在进行初始化或扩容操作
- -1代表正在初始化
- -N 表示有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作
- 正数或0代表hash表还没有被初始化,这个数值表示初始化或下一次进行扩容的大小,这一点类似于扩容阈值的概念。还后面可以看到,它的值始终是当前ConcurrentHashMap容量的0.75倍,这与loadfactor是对应的。
- /**
- * 盛装Node元素的数组 它的大小是2的整数次幂
- * Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators.
- */
- transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
- /**
- * Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
- * table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
- * else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
- * when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
- * creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
- * next element count value upon which to resize the table.
- hash表初始化或扩容时的一个控制位标识量。
- 负数代表正在进行初始化或扩容操作
- -1代表正在初始化
- -N 表示有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作
- 正数或0代表hash表还没有被初始化,这个数值表示初始化或下一次进行扩容的大小
- */
- private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
- // 以下两个是用来控制扩容的时候 单线程进入的变量
- /**
- * The number of bits used for generation stamp in sizeCtl.
- * Must be at least 6 for 32bit arrays.
- */
- private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
- /**
- * The bit shift for recording size stamp in sizeCtl.
- */
- private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
- /*
- * Encodings for Node hash fields. See above for explanation.
- */
- static final int MOVED = -1; // hash值是-1,表示这是一个forwardNode节点
- static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash值是-2 表示这时一个TreeBin节点
2 重要的内部类
2.1 Node
Node是最核心的内部类,它包装了key-value键值对,所有插入ConcurrentHashMap的数据都包装在这里面。它与HashMap中的定义很相似,但是但是有一些差别它对value和next属性设置了volatile同步锁,它不允许调用setValue方法直接改变Node的value域,它增加了find方法辅助map.get()方法。
- static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
- final int hash;
- final K key;
- volatile V val;//带有同步锁的value
- volatile Node<K,V> next;//带有同步锁的next指针
- Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.val = val;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public final K getKey() { return key; }
- public final V getValue() { return val; }
- public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }
- public final String toString(){ return key + “=” + val; }
- //不允许直接改变value的值
- public final V setValue(V value) {
- throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
- }
- public final boolean equals(Object o) {
- Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
- return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
- (k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
- (v = e.getValue()) != null &&
- (k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
- (v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
- }
- /**
- * Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
- */
- Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
- Node<K,V> e = this;
- if (k != null) {
- do {
- K ek;
- if (e.hash == h &&
- ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
- return e;
- } while ((e = e.next) != null);
- }
- return null;
- }
- }
- 这个Node内部类与HashMap中定义的Node类很相似,但是有一些差别
- 它对value和next属性设置了volatile同步锁
- 它不允许调用setValue方法直接改变Node的value域
- 它增加了find方法辅助map.get()方法
2.2 TreeNode
树节点类,另外一个核心的数据结构。当链表长度过长的时候,会转换为TreeNode。但是与HashMap不相同的是,它并不是直接转换为红黑树,而是把这些结点包装成TreeNode放在TreeBin对象中,由TreeBin完成对红黑树的包装。而且TreeNode在ConcurrentHashMap集成自Node类,而并非HashMap中的集成自LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>类,也就是说TreeNode带有next指针,这样做的目的是方便基于TreeBin的访问。
2.3 TreeBin
这个类并不负责包装用户的key、value信息,而是包装的很多TreeNode节点。它代替了TreeNode的根节点,也就是说在实际的ConcurrentHashMap“数组”中,存放的是TreeBin对象,而不是TreeNode对象,这是与HashMap的区别。另外这个类还带有了读写锁。
这里仅贴出它的构造方法。可以看到在构造TreeBin节点时,仅仅指定了它的hash值为TREEBIN常量,这也就是个标识为。同时也看到我们熟悉的红黑树构造方法
- /**
- * Creates bin with initial set of nodes headed by b.
- */
- TreeBin(TreeNode<K,V> b) {
- super(TREEBIN, null, null, null);
- this.first = b;
- TreeNode<K,V> r = null;
- for (TreeNode<K,V> x = b, next; x != null; x = next) {
- next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
- x.left = x.right = null;
- if (r == null) {
- x.parent = null;
- x.red = false;
- r = x;
- }
- else {
- K k = x.key;
- int h = x.hash;
- Class<?> kc = null;
- for (TreeNode<K,V> p = r;;) {
- int dir, ph;
- K pk = p.key;
- if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
- dir = -1;
- else if (ph < h)
- dir = 1;
- else if ((kc == null &&
- (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
- (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
- dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
- TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
- if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
- x.parent = xp;
- if (dir <= 0)
- xp.left = x;
- else
- xp.right = x;
- r = balanceInsertion(r, x);
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- this.root = r;
- assert checkInvariants(root);
- }
2.5 ForwardingNode
一个用于连接两个table的节点类。它包含一个nextTable指针,用于指向下一张表。而且这个节点的key value next指针全部为null,它的hash值为-1. 这里面定义的find的方法是从nextTable里进行查询节点,而不是以自身为头节点进行查找
- /**
- * A node inserted at head of bins during transfer operations.
- */
- static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
- final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
- ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
- super(MOVED, null, null, null);
- this.nextTable = tab;
- }
- Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
- // loop to avoid arbitrarily deep recursion on forwarding nodes
- outer: for (Node<K,V>[] tab = nextTable;;) {
- Node<K,V> e; int n;
- if (k == null || tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
- (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) == null)
- return null;
- for (;;) {
- int eh; K ek;
- if ((eh = e.hash) == h &&
- ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
- return e;
- if (eh < 0) {
- if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) {
- tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable;
- continue outer;
- }
- else
- return e.find(h, k);
- }
- if ((e = e.next) == null)
- return null;
- }
- }
- }
- }
3 Unsafe与CAS
在ConcurrentHashMap中,随处可以看到U, 大量使用了U.compareAndSwapXXX的方法,这个方法是利用一个CAS算法实现无锁化的修改值的操作,他可以大大降低锁代理的性能消耗。这个算法的基本思想就是不断地去比较当前内存中的变量值与你指定的一个变量值是否相等,如果相等,则接受你指定的修改的值,否则拒绝你的操作。因为当前线程中的值已经不是最新的值,你的修改很可能会覆盖掉其他线程修改的结果。这一点与乐观锁,SVN的思想是比较类似的。
3.1 unsafe静态块
unsafe代码块控制了一些属性的修改工作,比如最常用的SIZECTL 。 在这一版本的concurrentHashMap中,大量应用来的CAS方法进行变量、属性的修改工作。 利用CAS进行无锁操作,可以大大提高性能。
- private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U;
- private static final long SIZECTL;
- private static final long TRANSFERINDEX;
- private static final long BASECOUNT;
- private static final long CELLSBUSY;
- private static final long CELLVALUE;
- private static final long ABASE;
- private static final int ASHIFT;
- static {
- try {
- U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
- Class<?> k = ConcurrentHashMap.class;
- SIZECTL = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”sizeCtl”));
- TRANSFERINDEX = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”transferIndex”));
- BASECOUNT = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”baseCount”));
- CELLSBUSY = U.objectFieldOffset
- (k.getDeclaredField(”cellsBusy”));
- Class<?> ck = CounterCell.class;
- CELLVALUE = U.objectFieldOffset
- (ck.getDeclaredField(”value”));
- Class<?> ak = Node[].class;
- ABASE = U.arrayBaseOffset(ak);
- int scale = U.arrayIndexScale(ak);
- if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0)
- throw new Error(“data type scale not a power of two”);
- ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new Error(e);
- }
- }
3.2 三个核心方法
ConcurrentHashMap定义了三个原子操作,用于对指定位置的节点进行操作。正是这些原子操作保证了ConcurrentHashMap的线程安全。
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
- //获得在i位置上的Node节点
- static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
- return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
- }
- //利用CAS算法设置i位置上的Node节点。之所以能实现并发是因为他指定了原来这个节点的值是多少
- //在CAS算法中,会比较内存中的值与你指定的这个值是否相等,如果相等才接受你的修改,否则拒绝你的修改
- //因此当前线程中的值并不是最新的值,这种修改可能会覆盖掉其他线程的修改结果 有点类似于SVN
- static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
- Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
- return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
- }
- //利用volatile方法设置节点位置的值
- static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) {
- U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v);
- }
4 初始化方法initTable
对于ConcurrentHashMap来说,调用它的构造方法仅仅是设置了一些参数而已。而整个table的初始化是在向ConcurrentHashMap中插入元素的时候发生的。如调用put、computeIfAbsent、compute、merge等方法的时候,调用时机是检查table==null。
初始化方法主要应用了关键属性sizeCtl 如果这个值〈0,表示其他线程正在进行初始化,就放弃这个操作。在这也可以看出ConcurrentHashMap的初始化只能由一个线程完成。如果获得了初始化权限,就用CAS方法将sizeCtl置为-1,防止其他线程进入。初始化数组后,将sizeCtl的值改为0.75*n
- /**
- * Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
- */
- private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
- Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
- while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
- //sizeCtl表示有其他线程正在进行初始化操作,把线程挂起。对于table的初始化工作,只能有一个线程在进行。
- if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
- Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {//利用CAS方法把sizectl的值置为-1 表示本线程正在进行初始化
- try {
- if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
- int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
- Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
- table = tab = nt;
- sc = n - (n >>> 2);//相当于0.75*n 设置一个扩容的阈值
- }
- } finally {
- sizeCtl = sc;
- }
- break;
- }
- }
- return tab;
- }
5 扩容方法 transfer
当ConcurrentHashMap容量不足的时候,需要对table进行扩容。这个方法的基本思想跟HashMap是很像的,但是由于它是支持并发扩容的,所以要复杂的多。原因是它支持多线程进行扩容操作,而并没有加锁。我想这样做的目的不仅仅是为了满足concurrent的要求,而是希望利用并发处理去减少扩容带来的时间影响。因为在扩容的时候,总是会涉及到从一个“数组”到另一个“数组”拷贝的操作,如果这个操作能够并发进行,那真真是极好的了。
整个扩容操作分为两个部分-
第一部分是构建一个nextTable,它的容量是原来的两倍,这个操作是单线程完成的。这个单线程的保证是通过RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT这个常量经过一次运算来保证的,这个地方在后面会有提到;
- 第二个部分就是将原来table中的元素复制到nextTable中,这里允许多线程进行操作。
先来看一下单线程是如何完成的:
它的大体思想就是遍历、复制的过程。首先根据运算得到需要遍历的次数i,然后利用tabAt方法获得i位置的元素:
-
如果这个位置为空,就在原table中的i位置放入forwardNode节点,这个也是触发并发扩容的关键点;
-
如果这个位置是Node节点(fh>=0),如果它是一个链表的头节点,就构造一个反序链表,把他们分别放在nextTable的i和i+n的位置上
-
如果这个位置是TreeBin节点(fh<0),也做一个反序处理,并且判断是否需要untreefi,把处理的结果分别放在nextTable的i和i+n的位置上
- 遍历过所有的节点以后就完成了复制工作,这时让nextTable作为新的table,并且更新sizeCtl为新容量的0.75倍 ,完成扩容。
在代码的69行有一个判断,如果遍历到的节点是forward节点,就向后继续遍历,再加上给节点上锁的机制,就完成了多线程的控制。多线程遍历节点,处理了一个节点,就把对应点的值set为forward,另一个线程看到forward,就向后遍历。这样交叉就完成了复制工作。而且还很好的解决了线程安全的问题。 这个方法的设计实在是让我膜拜。
- /**
- * 一个过渡的table表 只有在扩容的时候才会使用
- */
- private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
- /**
- * Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See
- * above for explanation.
- */
- private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
- int n = tab.length, stride;
- if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
- stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
- if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
- try {
- @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
- Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];//构造一个nextTable对象 它的容量是原来的两倍
- nextTab = nt;
- } catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
- sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- return;
- }
- nextTable = nextTab;
- transferIndex = n;
- }
- int nextn = nextTab.length;
- ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);//构造一个连节点指针 用于标志位
- boolean advance = true;//并发扩容的关键属性 如果等于true 说明这个节点已经处理过
- boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
- for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
- Node<K,V> f; int fh;
- //这个while循环体的作用就是在控制i– 通过i–可以依次遍历原hash表中的节点
- while (advance) {
- int nextIndex, nextBound;
- if (–i >= bound || finishing)
- advance = false;
- else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
- i = -1;
- advance = false;
- }
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
- (this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
- nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
- nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
- bound = nextBound;
- i = nextIndex - 1;
- advance = false;
- }
- }
- if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
- int sc;
- if (finishing) {
- //如果所有的节点都已经完成复制工作 就把nextTable赋值给table 清空临时对象nextTable
- nextTable = null;
- table = nextTab;
- sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);//扩容阈值设置为原来容量的1.5倍 依然相当于现在容量的0.75倍
- return;
- }
- //利用CAS方法更新这个扩容阈值,在这里面sizectl值减一,说明新加入一个线程参与到扩容操作
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
- if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
- return;
- finishing = advance = true;
- i = n; // recheck before commit
- }
- }
- //如果遍历到的节点为空 则放入ForwardingNode指针
- else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
- advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
- //如果遍历到ForwardingNode节点 说明这个点已经被处理过了 直接跳过 这里是控制并发扩容的核心
- else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
- advance = true; // already processed
- else {
- //节点上锁
- synchronized (f) {
- if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
- Node<K,V> ln, hn;
- //如果fh>=0 证明这是一个Node节点
- if (fh >= 0) {
- int runBit = fh & n;
- //以下的部分在完成的工作是构造两个链表 一个是原链表 另一个是原链表的反序排列
- Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
- for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
- int b = p.hash & n;
- if (b != runBit) {
- runBit = b;
- lastRun = p;
- }
- }
- if (runBit == 0) {
- ln = lastRun;
- hn = null;
- }
- else {
- hn = lastRun;
- ln = null;
- }
- for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
- int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
- if ((ph & n) == 0)
- ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
- else
- hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
- }
- //在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
- //在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
- //在table的i位置上插入forwardNode节点 表示已经处理过该节点
- setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
- //设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i–操作
- advance = true;
- }
- //对TreeBin对象进行处理 与上面的过程类似
- else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
- TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
- TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
- TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
- int lc = 0, hc = 0;
- //构造正序和反序两个链表
- for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
- int h = e.hash;
- TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
- (h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
- if ((h & n) == 0) {
- if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
- lo = p;
- else
- loTail.next = p;
- loTail = p;
- ++lc;
- }
- else {
- if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
- hi = p;
- else
- hiTail.next = p;
- hiTail = p;
- ++hc;
- }
- }
- //如果扩容后已经不再需要tree的结构 反向转换为链表结构
- ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
- (hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
- hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
- (lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
- //在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
- //在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表
- setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
- //在table的i位置上插入forwardNode节点 表示已经处理过该节点
- setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
- //设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i–操作
- advance = true;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
6 Put方法
前面的所有的介绍其实都为这个方法做铺垫。ConcurrentHashMap最常用的就是put和get两个方法。现在来介绍put方法,这个put方法依然沿用HashMap的put方法的思想,根据hash值计算这个新插入的点在table中的位置i,如果i位置是空的,直接放进去,否则进行判断,如果i位置是树节点,按照树的方式插入新的节点,否则把i插入到链表的末尾。ConcurrentHashMap中依然沿用这个思想,有一个最重要的不同点就是ConcurrentHashMap不允许key或value为null值。另外由于涉及到多线程,put方法就要复杂一点。在多线程中可能有以下两个情况
-
如果一个或多个线程正在对ConcurrentHashMap进行扩容操作,当前线程也要进入扩容的操作中。这个扩容的操作之所以能被检测到,是因为transfer方法中在空结点上插入forward节点,如果检测到需要插入的位置被forward节点占有,就帮助进行扩容;
-
如果检测到要插入的节点是非空且不是forward节点,就对这个节点加锁,这样就保证了线程安全。尽管这个有一些影响效率,但是还是会比hashTable的synchronized要好得多。
整体流程就是首先定义不允许key或value为null的情况放入 对于每一个放入的值,首先利用spread方法对key的hashcode进行一次hash计算,由此来确定这个值在table中的位置。
如果这个位置是空的,那么直接放入,而且不需要加锁操作。
如果这个位置存在结点,说明发生了hash碰撞,首先判断这个节点的类型。如果是链表节点(fh>0),则得到的结点就是hash值相同的节点组成的链表的头节点。需要依次向后遍历确定这个新加入的值所在位置。如果遇到hash值与key值都与新加入节点是一致的情况,则只需要更新value值即可。否则依次向后遍历,直到链表尾插入这个结点。 如果加入这个节点以后链表长度大于8,就把这个链表转换成红黑树。如果这个节点的类型已经是树节点的话,直接调用树节点的插入方法进行插入新的值。- public V put(K key, V value) {
- return putVal(key, value, false);
- }
- /** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
- final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
- //不允许 key或value为null
- if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- //计算hash值
- int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
- int binCount = 0;
- //死循环 何时插入成功 何时跳出
- for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
- Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
- //如果table为空的话,初始化table
- if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
- tab = initTable();
- //根据hash值计算出在table里面的位置
- else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
- //如果这个位置没有值 ,直接放进去,不需要加锁
- if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
- new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
- break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
- }
- //当遇到表连接点时,需要进行整合表的操作
- else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
- tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
- else {
- V oldVal = null;
- //结点上锁 这里的结点可以理解为hash值相同组成的链表的头结点
- synchronized (f) {
- if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
- //fh〉0 说明这个节点是一个链表的节点 不是树的节点
- if (fh >= 0) {
- binCount = 1;
- //在这里遍历链表所有的结点
- for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
- K ek;
- //如果hash值和key值相同 则修改对应结点的value值
- if (e.hash == hash &&
- ((ek = e.key) == key ||
- (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
- oldVal = e.val;
- if (!onlyIfAbsent)
- e.val = value;
- break;
- }
- Node<K,V> pred = e;
- //如果遍历到了最后一个结点,那么就证明新的节点需要插入 就把它插入在链表尾部
- if ((e = e.next) == null) {
- pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
- value, null);
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //如果这个节点是树节点,就按照树的方式插入值
- else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
- Node<K,V> p;
- binCount = 2;
- if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
- value)) != null) {
- oldVal = p.val;
- if (!onlyIfAbsent)
- p.val = value;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- if (binCount != 0) {
- //如果链表长度已经达到临界值8 就需要把链表转换为树结构
- if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
- treeifyBin(tab, i);
- if (oldVal != null)
- return oldVal;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量+1
- addCount(1L, binCount);
- return null;
- }
6.1 helpTransfer方法
这是一个协助扩容的方法。这个方法被调用的时候,当前ConcurrentHashMap一定已经有了nextTable对象,首先拿到这个nextTable对象,调用transfer方法。回看上面的transfer方法可以看到,当本线程进入扩容方法的时候会直接进入复制阶段。
- /**
- * Helps transfer if a resize is in progress.
- */
- final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
- Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
- if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
- (nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
- int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);//计算一个操作校验码
- while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
- (sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
- if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
- sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
- break;
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
- transfer(tab, nextTab);
- break;
- }
- }
- return nextTab;
- }
- return table;
- }
6.2 treeifyBin方法
这个方法用于将过长的链表转换为TreeBin对象。但是他并不是直接转换,而是进行一次容量判断,如果容量没有达到转换的要求,直接进行扩容操作并返回;如果满足条件才链表的结构抓换为TreeBin ,这与HashMap不同的是,它并没有把TreeNode直接放入红黑树,而是利用了TreeBin这个小容器来封装所有的TreeNode.
- private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
- Node<K,V> b; int n, sc;
- if (tab != null) {
- if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)//如果table.length<64 就扩大一倍 返回
- tryPresize(n << 1);
- else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
- synchronized (b) {
- if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {
- TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
- //构造了一个TreeBin对象 把所有Node节点包装成TreeNode放进去
- for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {
- TreeNode<K,V> p =
- new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,
- null, null);//这里只是利用了TreeNode封装 而没有利用TreeNode的next域和parent域
- if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
- hd = p;
- else
- tl.next = p;
- tl = p;
- }
- //在原来index的位置 用TreeBin替换掉原来的Node对象
- setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
7 get方法
get方法比较简单,给定一个key来确定value的时候,必须满足两个条件 key相同 hash值相同,对于节点可能在链表或树上的情况,需要分别去查找.
- public V get(Object key) {
- Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
- //计算hash值
- int h = spread(key.hashCode());
- //根据hash值确定节点位置
- if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
- (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
- //如果搜索到的节点key与传入的key相同且不为null,直接返回这个节点
- if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
- if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
- return e.val;
- }
- //如果eh<0 说明这个节点在树上 直接寻找
- else if (eh < 0)
- return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
- //否则遍历链表 找到对应的值并返回
- while ((e = e.next) != null) {
- if (e.hash == h &&
- ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
- return e.val;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
8 Size相关的方法
对于ConcurrentHashMap来说,这个table里到底装了多少东西其实是个不确定的数量,因为不可能在调用size()方法的时候像GC的“stop the world”一样让其他线程都停下来让你去统计,因此只能说这个数量是个估计值。对于这个估计值,ConcurrentHashMap也是大费周章才计算出来的。
8.1 辅助定义
为了统计元素个数,ConcurrentHashMap定义了一些变量和一个内部类
- /**
- * A padded cell for distributing counts. Adapted from LongAdder
- * and Striped64. See their internal docs for explanation.
- */
- @sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
- volatile long value;
- CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
- }
- /******************************************/
- /**
- * 实际上保存的是hashmap中的元素个数 利用CAS锁进行更新
- 但它并不用返回当前hashmap的元素个数
- */
- private transient volatile long baseCount;
- /**
- * Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells.
- */
- private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
- /**
- * Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
- */
- private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
8.2 mappingCount与Size方法
mappingCount与size方法的类似 从Java工程师给出的注释来看,应该使用mappingCount代替size方法 两个方法都没有直接返回basecount 而是统计一次这个值,而这个值其实也是一个大概的数值,因此可能在统计的时候有其他线程正在执行插入或删除操作。
- public int size() {
- long n = sumCount();
- return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
- (n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
- (int)n);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the number of mappings. This method should be used
- * instead of {@link #size} because a ConcurrentHashMap may
- * contain more mappings than can be represented as an int. The
- * value returned is an estimate; the actual count may differ if
- * there are concurrent insertions or removals.
- *
- * @return the number of mappings
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public long mappingCount() {
- long n = sumCount();
- return (n < 0L) ? 0L : n; // ignore transient negative values
- }
- final long sumCount() {
- CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;
- long sum = baseCount;
- if (as != null) {
- for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
- if ((a = as[i]) != null)
- sum += a.value;//所有counter的值求和
- }
- }
- return sum;
- }
8.3 addCount方法
在put方法结尾处调用了addCount方法,把当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素个数+1这个方法一共做了两件事,更新baseCount的值,检测是否进行扩容。
- private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
- CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
- //利用CAS方法更新baseCount的值
- if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
- !U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
- CounterCell a; long v; int m;
- boolean uncontended = true;
- if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
- (a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
- !(uncontended =
- U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
- fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
- return;
- }
- if (check <= 1)
- return;
- s = sumCount();
- }
- //如果check值大于等于0 则需要检验是否需要进行扩容操作
- if (check >= 0) {
- Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
- while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
- (n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
- int rs = resizeStamp(n);
- //
- if (sc < 0) {
- if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
- sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
- transferIndex <= 0)
- break;
- //如果已经有其他线程在执行扩容操作
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
- transfer(tab, nt);
- }
- //当前线程是唯一的或是第一个发起扩容的线程 此时nextTable=null
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
- (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
- transfer(tab, null);
- s = sumCount();
- }
- }
- }
(未完待续。。。)