\(\color{#0066ff}{ 题目描述 }\)
对Samuel星球的探险已经取得了非常巨大的成就,于是科学家们将目光投向了Samuel星球所在的星系——一个巨大的由千百万星球构成的Samuel星系。
星际空间站的Samuel II巨型计算机经过长期探测,已经锁定了Samuel星系中许多星球的空间坐标,并对这些星球从1开始编号1、2、3……。
一些先遣飞船已经出发,在星球之间开辟探险航线。
探险航线是双向的,例如从1号星球到3号星球开辟探险航线,那么从3号星球到1号星球也可以使用这条航线。
例如下图所示:
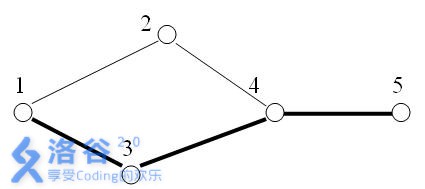
在5个星球之间,有5条探险航线。
A、B两星球之间,如果某条航线不存在,就无法从A星球抵达B星球,我们则称这条航线为关键航线。
显然上图中,1号与5号星球之间的关键航线有1条:即为4-5航线。
然而,在宇宙中一些未知的磁暴和行星的冲撞,使得已有的某些航线被破坏,随着越来越多的航线被破坏,探险飞船又不能及时回复这些航线,可见两个星球之间的关键航线会越来越多。
假设在上图中,航线4-2(从4号星球到2号星球)被破坏。此时,1号与5号星球之间的关键航线就有3条:1-3,3-4,4-5。
小联的任务是,不断关注航线被破坏的情况,并随时给出两个星球之间的关键航线数目。现在请你帮助完成。
\(\color{#0066ff}{输入格式}\)
第一行有两个整数N,M。表示有N个星球(1< N < 30000),初始时已经有M条航线(1 < M < 100000)。随后有M行,每行有两个不相同的整数A、B表示在星球A与B之间存在一条航线。接下来每行有三个整数C、A、B。C为1表示询问当前星球A和星球B之间有多少条关键航线;C为0表示在星球A和星球B之间的航线被破坏,当后面再遇到C为1的情况时,表示询问航线被破坏后,关键路径的情况,且航线破坏后不可恢复; C为-1表示输入文件结束,这时该行没有A,B的值。被破坏的航线数目与询问的次数总和不超过40000。
\(\color{#0066ff}{输出格式}\)
对每个C为1的询问,输出一行一个整数表示关键航线数目。
\(\color{#0066ff}{输入样例}\)
5 5
1 2
1 3
3 4
4 5
4 2
1 1 5
0 4 2
1 5 1
-1\(\color{#0066ff}{输出样例}\)
1
3\(\color{#0066ff}{数据范围与提示}\)
我们保证无论航线如何被破坏,任意时刻任意两个星球都能够相互到达。在整个数据中,任意两个星球之间最多只可能存在一条直接的航线。
\(\color{#0066ff}{ 题解 }\)
正序删边我们不好维护这种东西,考虑离线倒序加边
一旦出现环,我们就暴力缩点,用ufs来维护所属的双连通分量
显然树链上每个点代表一个双连通分量,那么答案就是点数- 1
在连边的时候,如果不成环,直接连即可,如果成环,暴力dfs把所有点的ufs的父亲设为当前点
那它们原来的父亲不就无效了吗,所以access的时候,把父亲设为ufs的父亲即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
LL in() {
char ch; LL x = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return x * f;
}
const int maxn = 3e4 + 9;
const int maxm = 1e5 + 9;
struct node {
node *ch[2], *fa;
int siz, rev;
node(int siz = 1, int rev = 0): siz(siz), rev(rev) { ch[0] = ch[1] = fa = NULL; }
void trn() { std::swap(ch[0], ch[1]), rev ^= 1; }
void upd() {
siz = 1;
if(ch[0]) siz += ch[0]->siz;
if(ch[1]) siz += ch[1]->siz;
}
void dwn() {
if(!rev) return;
if(ch[0]) ch[0]->trn();
if(ch[1]) ch[1]->trn();
rev = 0;
}
bool ntr() { return fa && (fa->ch[0] == this || fa->ch[1] == this); }
bool isr() { return fa->ch[1] == this; }
}pool[maxn];
int fa[maxn];
void rot(node *x) {
node *y = x->fa, *z = y->fa;
bool k = x->isr(); node *w = x->ch[!k];
if(y->ntr()) z->ch[y->isr()] = x;
(x->ch[!k] = y)->ch[k] = w;
(y->fa = x)->fa = z;
if(w) w->fa = y;
y->upd(), x->upd();
}
void splay(node *o) {
static node *st[maxn];
int top;
st[top = 1] = o;
while(st[top]->ntr()) st[top + 1] = st[top]->fa, top++;
while(top) st[top--]->dwn();
while(o->ntr()) {
if(o->fa->ntr()) rot(o->isr() ^ o->fa->isr()? o : o->fa);
rot(o);
}
}
int findset(int x) { return x == fa[x]? fa[x] : fa[x] = findset(fa[x]); }
void access(node *x) {
for(node *y = NULL; x;) {
splay(x), x->ch[1] = y, x->upd();
y = x;
if(x->fa) x = x->fa = pool + findset(x->fa - pool);
else x = x->fa;
}
}
void makeroot(node *o) { access(o), splay(o), o->trn(); }
node *findroot(node *o) {
access(o), splay(o);
while(o->dwn(), o->ch[0]) o = o->ch[0];
return splay(o), o;
}
void del(node *o, int f) { if(o) fa[o - pool] = f, del(o->ch[0], f), del(o->ch[1], f); }
void out();
void link(int l, int r) {
if(l == r) return;
node *x = pool + l, *y = pool + r;
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) != x) return (void)(x->fa = y);
del(x->ch[1], x - pool);
if(x->ch[1]) x->ch[1] = NULL;
x->upd();
}
int query(int l, int r) {
node *x = pool + l, *y = pool + r;
makeroot(x), access(y), splay(y);
return y->siz - 1;
}
using std::pair;
using std::make_pair;
pair<int, int> e[maxm], q[maxm];
std::map<pair<int, int>, int> mp;
bool vis[maxm];
int id[maxm], n, m, ans[maxn];
int main() {
n = in(), m = in();
int x, y;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
x = in(), y = in();
if(x > y) std::swap(x, y);
mp[e[i] = make_pair(x, y)] = i;
}
int num = 0;
while(~(id[++num] = in())) {
x = in(), y = in();
if(x > y) std::swap(x, y);
q[num] = make_pair(x, y);
if(id[num] == 0) vis[mp[q[num]]] = true;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) if(!vis[i]) link(findset(e[i].first), findset(e[i].second));
int v = 0;
for(int i = num - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
x = findset(q[i].first), y = findset(q[i].second);
if(id[i] == 1) ans[++v] = query(x, y);
else link(x, y);
}
for(int i = v; i >= 1; i--) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}