文章目录
python处理二进制
python的struct模块可以将整型(或者其它类型)转化为byte数组.看下面的代码.
# coding: utf-8
from struct import *
# 包装成大端的byte数组
print(pack('>hhi', 1, 2, 3)) # b'\x00\x01\x00\x02\x00\x00\x00\x03'
pack(’>hhl’, 1, 2, 3)作用是以大端的方式把1(h表示2字节整型),2,3(i表示4字节整型),转化为对于的byte数组.大端小端的区别看参数资料2,>hhi的含义见参考资料1.输出为长度为8的byte数组,2个h的长度为4,1个i的长度为4,加起来一共是8.何为大端,一般存储是从低地址到高地址存储,如果先存高位,再存低位就是大端存储方式,简单理解就是大端存储符合我们平常的书写习惯,先写百位,再写十位,最后个位。
再体会下面代码的作用.
# coding: utf-8
from struct import *
# 包装成大端的byte数组
print(pack('>hhl', 1, 2, 3)) # b'\x00\x01\x00\x02\x00\x00\x00\x03'
mnist介绍
MNIST(Mixed National Institute of Standards and Technology database)是一个计算机视觉数据集,MNIST数据集来自美国国家标准与技术研究所, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). 训练集 (training set) 由来自 250 个不同人手写的数字构成, 其中 50% 是高中学生, 50% 来自人口普查局 (the Census Bureau) 的工作人员. 测试集(test set) 也是同样比例的手写数字数据. 该数据集中的图片表示0~9的手写阿拉伯数字。mnist包含一个训练集(一个训练图片文件和一个训练标签文件)和一个测试集(一个测试图片文件,一个测试标签文件),其中训练集有60000个样本,测试集有10000个样本。
MNIST是一个非常有名的手写体数字识别数据集,在很多资料中,这个数据集都会被用作深度学习的入门样例。
MNIST下载地址:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/, 从官方网站下载的数据是gz格式的压缩包,解压后可以得到原始文件。mnist数据集包含4个文件,分别对应60000个训练图片,60000个训练标签,10000个测试图片,10000个测试标签。数据集被分成两部分:60000 行的训练数据集(mnist.train)和10000行的测试数据集(mnist.test)。其中:60000 行的训练集分拆为 55000 行的训练集和 5000 行的验证集。
- train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz: 60000个训练图片 (9912422 bytes)
- train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz: 60000个训练标签 (28881 bytes)
- t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz: 10000个测试图片 (1648877 bytes)
- t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz: 10000个测试标签 (4542 bytes)
mnist显示
在MNIST数据集中的每一张图片都代表了0~9中的一个数字。图片的大小都为28*28,且数字都会出现在图片的正中间。
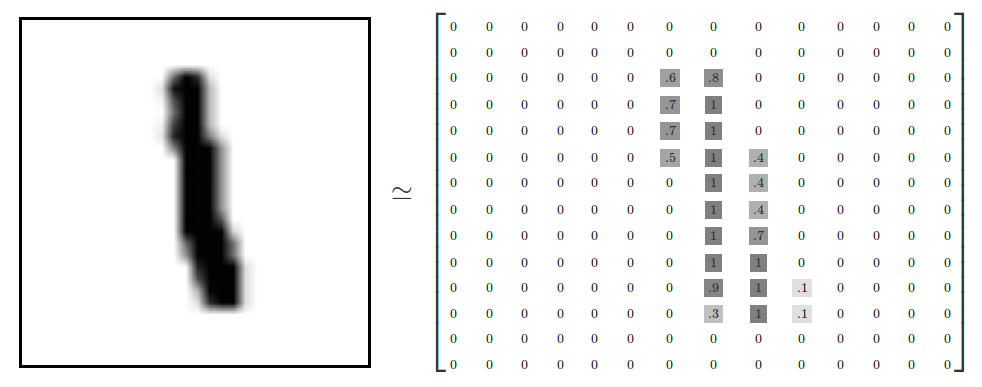
60000行的训练数据集是一个形状为 [60000, 784] 的张量,第一个维度数字用来索引图片,第二个维度数字用来索引每张图片中的像素点。在此张量里的每一个元素,都表示某张图片里的某个像素的强度值,值介于 0 和 1 之间。

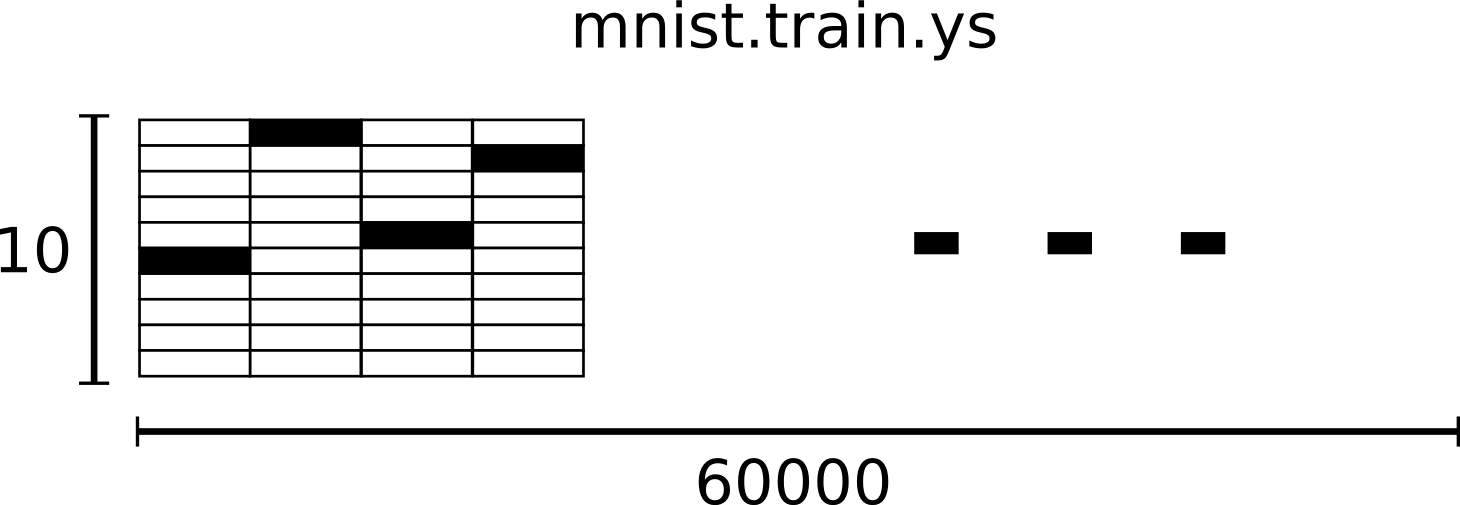
60000 行的训练数据集标签是介于 0 到 9 的数字,用来描述给定图片里表示的数字。称为 “one-hot vectors”。 一个 one-hot 向量除了某一位的数字是 1 以外其余各维度数字都是 0。所以在此教程中,数字 n 将表示成一个只有在第 n 维度(从 0 开始)数字为 1 的 10 维向量。比如,标签 0 将表示成 ( [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ] )。因此,其标签是一个 [60000, 10] 的数字矩阵。
以train-images.idx3-ubyte为例,train-images.idx3-ubyte是二进制文件.其格式为
| [offset] | [type] | [value] | [description] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 32 bit integer | 0x00000803(2051) | magic number #文件头魔数 |
| 4 | 32 bit integer | 60000 | number of images #图像个数 |
| 8 | 32 bit integer | 28 | number of rows #图像宽度 |
| 12 | 32 bit integer | 28 | number of columns #图像高度 |
| 16 | unsigned byte | ?? | pixel #图像像素值 |
| 17 | unsigned byte | ?? | pixel |
| …… | |||
| xxxx | unsigned byte | ?? | pixel |
文件大小满足:47040016Byte=600002828+16(Byte)
以train-labels.idx1-ubyte为例, train-labels.idx1-ubyte是二进制文件.其格式为
| [offset] | [type] | [value] | [description] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 32 bit integer | 0x00000801(2049) | magic number (MSB first) |
| 4 | 32 bit integer | 60000 | number of items |
| 8 | unsigned byte | ?? | label |
| 9 | unsigned byte | ?? | label |
| …… | |||
| xxxx | unsigned byte | ?? | label |
文件大小满足:60008Byte=60000*1+8(Byte)
前4个整型代表文件头的一些信息.之后的无符号byte数组才是图片的内容.所以要先越过前4个整型,然后再开始读取。
方法一:读取解压后的原始文件
代码如下:
import numpy as np
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
filename = r'mnist/t10k-images.idx3-ubyte'
binfile = open(filename, 'rb')
buf = binfile.read()
index = 0
magic, numImages, numRows, numColumns = struct.unpack_from('>IIII', buf, index) # 读取前4个字节的内容
index += struct.calcsize('>IIII')
im = struct.unpack_from('>784B', buf, index) # 以大端方式读取一张图上28*28=784
index += struct.calcsize('>784B')
binfile.close()
im = np.array(im)
im = im.reshape(28, 28)
fig = plt.figure()
plotwindow = fig.add_subplot(111)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
# plt.savefig("test.png") # 保存成文件
plt.close()
可以看到结果:

方法二:使用TensorFlow封装代码读取
【注意:此方法,对下载的数据集压缩包不需要解压,代码会自己解压。】
TensorFlow的封装让使用MNIST数据集变得更加方便。MNIST数据集是NIST数据集的一个子集,它包含了60000张图片作为训练数据,10000张图片作为测试数据。在MNIST数据集中的每一张图片都代表了0~9中的一个数字。图片的大小都为28*28,且数字都会出现在图片的正中间。
参考tensorflow中mnist模块的方法读取,代码如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
#1:默认等级,显示所有信息,2:只显示warning和Error,3:只显示Error
''' 读取MNIST数据方法一'''
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('mnist_gz',one_hot=True)
#每一张图片的标签被初始化成 一个 10 维的“one-hot”向量
'''1)获得数据集的个数'''
train_nums = mnist.train.num_examples
validation_nums = mnist.validation.num_examples
test_nums = mnist.test.num_examples
print('MNIST数据集的个数')
print('\t>>>train_nums=%d' % train_nums,'\n',
'\t>>>validation_nums=%d'% validation_nums,'\n',
'\t>>>test_nums=%d' % test_nums,'\n')
'''2)获得数据值'''
train_data = mnist.train.images #所有训练数据
val_data = mnist.validation.images #(5000,784)
test_data = mnist.test.images #(10000,784)
print('\t>>>训练集数据大小:',train_data.shape,'\n',
'\t>>>一副图像的大小:',train_data[0].shape)
'''3)获取标签值label=[0,0,...,0,1],是一个1*10的向量'''
train_labels = mnist.train.labels #(55000,10)
val_labels = mnist.validation.labels #(5000,10)
test_labels = mnist.test.labels #(10000,10)
print('\t>>>训练集标签数组大小:',train_labels.shape,'\n',
'\t>>>一副图像的标签大小:',train_labels[1].shape,'\n',
'\t>>>一副图像的标签值:',train_labels[0])
'''4)批量获取数据和标签【使用next_batch(batch_size)】'''
batch_size = 100 #每次批量训练100幅图像
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
print('使用mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)批量读取样本')
print('\t>>>批量读取100个样本:数据集大小=',batch_xs.shape,'\n',
'\t>>>批量读取100个样本:标签集大小=',batch_ys.shape)
#xs是图像数据(100,784);ys是标签(100,10)
'''5)显示图像'''
plt.figure()
for i in range(1000):
#im = train_data[i].reshape(28,28)
#im和im1不完全一样
im1 = batch_xs[i].reshape(28,28)
label = batch_ys[i].tolist().index(1)
plt.title('true number:%d'% label)
plt.imshow(im1,'gray')
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.show()

需求一:同时显示图片和标签,验证图片和标签一一对应
代码如下:
import numpy as np
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 训练集文件
train_images_idx3_ubyte_file = 'mnist/train-images.idx3-ubyte'
# 训练集标签文件
train_labels_idx1_ubyte_file = 'mnist/train-labels.idx1-ubyte'
# 测试集文件
test_images_idx3_ubyte_file = 'mnist/t10k-images.idx3-ubyte'
# 测试集标签文件
test_labels_idx1_ubyte_file = 'mnist/t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte'
def decode_idx3_ubyte(idx3_ubyte_file):
# 读取二进制数据
bin_data = open(idx3_ubyte_file, 'rb').read()
# 解析文件头信息,依次为魔法数、图片数量、每张图片高、每张图片宽
offset = 0
fmt_header = '>iiii' #因为数据结构中前4行的数据类型都是32位整型,所以采用i格式,但我们需要读取前4行数据,所以需要4个i。我们后面会看到标签集中,只使用2个ii。
magic_number, num_images, num_rows, num_cols = struct.unpack_from(fmt_header, bin_data, offset)
print('魔法数:%d, 图片数量: %d张, 图片大小: %d*%d' % (magic_number, num_images, num_rows, num_cols))
# 解析数据集
image_size = num_rows * num_cols
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_header) #获得数据在缓存中的指针位置,从前面介绍的数据结构可以看出,读取了前4行之后,指针位置(即偏移位置offset)指向0016。
print(offset)
fmt_image = '>' + str(image_size) + 'B' #图像数据像素值的类型为unsigned char型,对应的format格式为B。这里还有加上图像大小784,是为了读取784个B格式数据,如果没有则只会读取一个值(即一副图像中的一个像素值)
print(fmt_image,offset,struct.calcsize(fmt_image))
images = np.empty((num_images, num_rows, num_cols))
for i in range(num_images):
if (i + 1) % 10000 == 0:
print('已解析 %d' % (i + 1) + '张')
print(offset)
images[i] = np.array(struct.unpack_from(fmt_image, bin_data, offset)).reshape((num_rows, num_cols))
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_image)
return images
def decode_idx1_ubyte(idx1_ubyte_file):
# 读取二进制数据
bin_data = open(idx1_ubyte_file, 'rb').read()
# 解析文件头信息,依次为魔数和标签数
offset = 0
fmt_header = '>ii'
magic_number, num_images = struct.unpack_from(fmt_header, bin_data, offset)
print('魔法数:%d, 图片数量: %d张' % (magic_number, num_images))
# 解析数据集
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_header)
fmt_image = '>B'
labels = np.empty(num_images)
for i in range(num_images):
if (i + 1) % 10000 == 0:
print ('已解析 %d' % (i + 1) + '张')
labels[i] = struct.unpack_from(fmt_image, bin_data, offset)[0]
offset += struct.calcsize(fmt_image)
return labels
def load_train_images(idx_ubyte_file=train_images_idx3_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx3_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
def load_train_labels(idx_ubyte_file=train_labels_idx1_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx1_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
def load_test_images(idx_ubyte_file=test_images_idx3_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx3_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
def load_test_labels(idx_ubyte_file=test_labels_idx1_ubyte_file):
return decode_idx1_ubyte(idx_ubyte_file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_images = load_train_images()
train_labels = load_train_labels()
# tes_images = load_test_images()
# test_labels = load_test_labels()
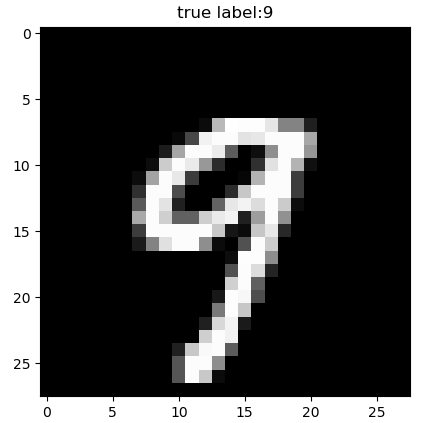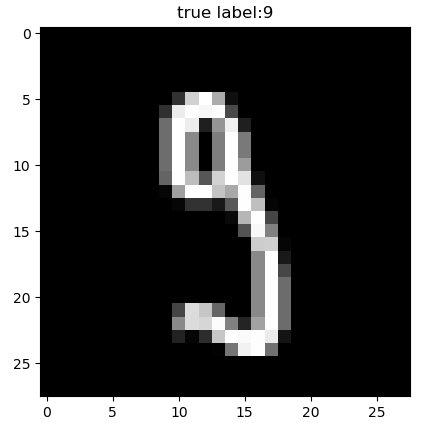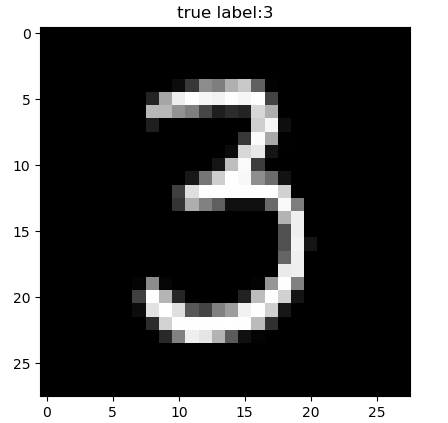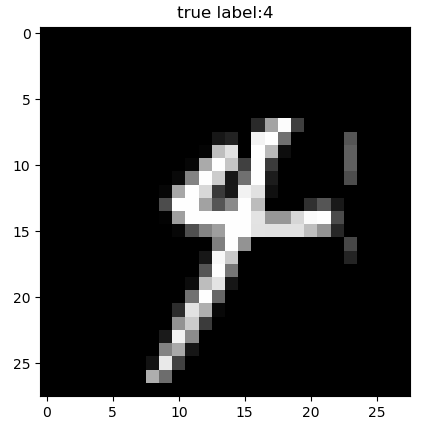
# 查看前一百个数据及其标签以读取是否正确
plt.figure()
for i in range(100):
plt.title("true label:%d"%train_labels[i])
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap='gray')
plt.savefig("test" + str(i) + ".png")
plt.pause(0.3)
print('done')
需求二、读取1-9等10个数字图片和不同形态的手写7
代码如下:
import os
import struct
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_mnist(path, kind='train'):
"""Load MNIST data from `path`"""
labels_path = os.path.join(path, '%s-labels.idx1-ubyte' % kind)
images_path = os.path.join(path, '%s-images.idx3-ubyte' % kind)
with open(labels_path, 'rb') as lbpath:
magic, n = struct.unpack('>II', lbpath.read(8))
labels = np.fromfile(lbpath, dtype=np.uint8)
with open(images_path, 'rb') as imgpath:
magic, num, rows, cols = struct.unpack('>IIII', imgpath.read(16))
images = np.fromfile(imgpath, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(len(labels), 784)
return images, labels
images, labels = load_mnist("mnist")
fig, ax = plt.subplots( nrows=2, ncols=5, sharex=True, sharey=True, )
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(10):
img = images[labels== i][0].reshape(28, 28)
ax[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
ax[0].set_xticks([])
ax[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots( nrows=8, ncols=8, sharex=True, sharey=True, )
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(64):
img = images[labels== 7][i].reshape(28, 28)
ax[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
ax[0].set_xticks([])
ax[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
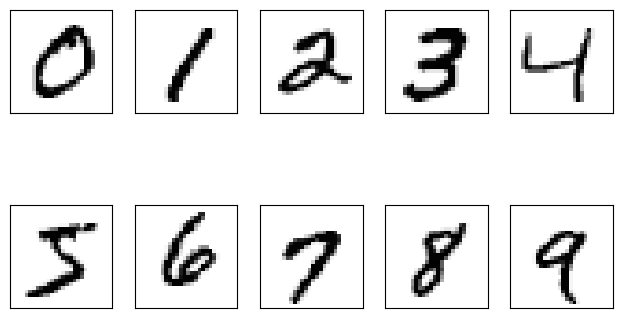
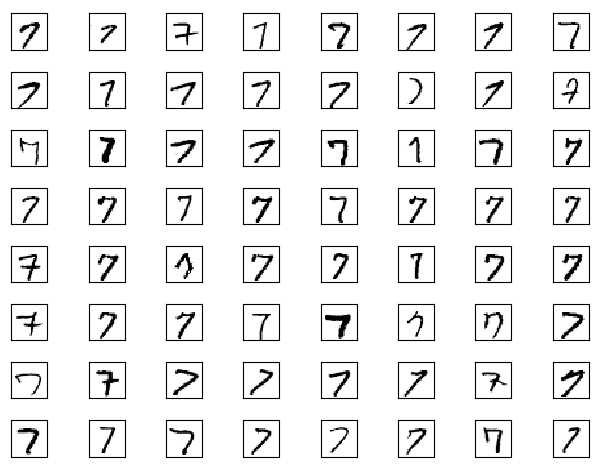
需求三:同时读取多个数字
import gzip
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
filepath = r"mnist_gz/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz"
def _read32(bytestream):
dt = numpy.dtype(numpy.uint32).newbyteorder('>')
return numpy.frombuffer(bytestream.read(4), dtype=dt)[0]
def imagine_arr(filepath, index):
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
with gzip.GzipFile(fileobj=f) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2051:
raise ValueError('Invalid magic number %d in MNIST image file: %s' % (magic, f.name))
num = _read32(bytestream) # 几张图片
rows = _read32(bytestream)
cols = _read32(bytestream)
if index >= num:
index = 0
bytestream.read(rows * cols * index)
buf = bytestream.read(rows * cols)
data = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.ubyte)
return data.reshape(rows, cols)
im = imagine_arr(filepath, 0) # 显示第0张
fig = plt.figure()
plotwindow = fig.add_subplot(111)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
plt.close()
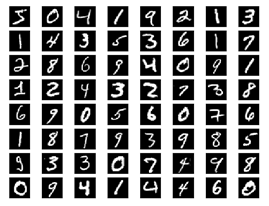
用的是numpy里面的方法。函数_read32作用是读取4个字节,以大端的方式转化成无符号整型.其余代码逻辑和之前的类似.
补充
注意:mnist目录下的文件是由mnist_gz下的文件解压得到的原始文件。