SpringBoot项目整合动态数据源(读写分离)
1.配置多个数据源,根据业务需求访问不同的数据,指定对应的策略:增加,删除,修改操作访问对应数据,查询访问对应数据,不同数据库做好的数据一致性的处理。由于此方法相对易懂,简单,不做过多介绍。
2. 动态切换数据源,根据配置的文件,业务动态切换访问的数据库:此方案通过Spring的AOP,AspactJ来实现动态织入,通过编程继承实现Spring中的AbstractRoutingDataSource,来实现数据库访问的动态切换,不仅可以方便扩展,不影响现有程序,而且对于此功能的增删也比较容易。
3. 通过mycat来实现读写分离:使用mycat提供的读写分离功能,mycat连接多个数据库,数据源只需要连接mycat,对于开发人员而言他还是连接了一个数据库(实际是mysql的mycat中间件),而且也不需要根据不同 业务来选择不同的库,这样就不会有多余的代码产生。
详细参考配置
动态数据源核心配置
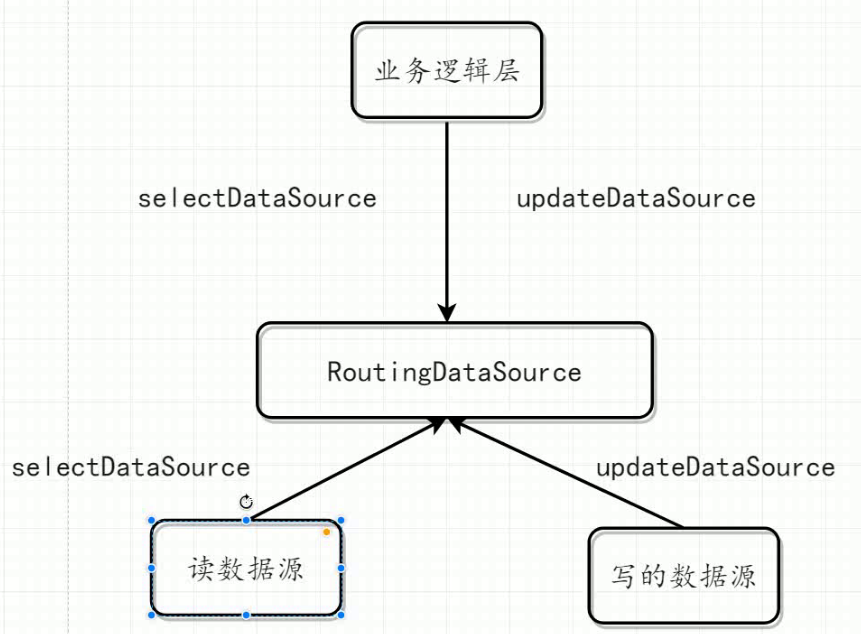
在Spring 2.0.1中引入了AbstractRoutingDataSource, 该类充当了DataSource的路由中介, 能有在运行时, 根据某种key值来动态切换到真正的DataSource上。
1.项目中需要集成多个数据源分别为读和写的数据源,绑定不同的key。
2.采用AOP技术进行拦截业务逻辑层方法,判断方法的前缀是否需要写或者读的操作
3.如果方法的前缀是写的操作的时候,直接切换为写的数据源,反之切换为读的数据源
也可以自己定义注解进行封装
项目中有两个数据源 分别为读和写的数据源
使用AOP技术判断业务逻辑方法的前缀,如果前缀为比如select get find等。直接走RoutingDataSource
如果是写的话,传递一个key给RoutingDataSource指明使用写的数据源
下面是两个数据源,读的数据源和写的数据源。都需要设置一个key。然后注册存放到RoutingDataSource。
使用AOP技术拦截业务逻辑层的方法,判断方法的前缀是否为读或者写的操作
如果是写的操作,会给RoutingDataSource传递一个key 哈哈懂得了吧
环境配置:
1.创建读和写的数据源
2.将读和写的数据源注册到RoutiongDataSource
3.使用AOP技术拦截业务逻辑层,判断方法的前缀是否需要做读或者写
pom:
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.0.23</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
配置代码:
通过ThreadLocal 保存本地多数据源
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Primary public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Autowired @Qualifier("selectDataSource") //获取读的数据源 private DataSource selectDataSource; @Autowired @Qualifier("updateDataSource") //获取写的数据源 private DataSource updateDataSource; /** * 这个是主要的方法,返回的是生效的数据源名称 */ @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { System.out.println("DataSourceContextHolder:::" + DataSourceContextHolder.getDbType()); return DataSourceContextHolder.getDbType(); } /** * 配置数据源信息 注册数据源的操作 最终注入到datasource数据源中 */ @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("selectDataSource", selectDataSource); map.put("updateDataSource", updateDataSource); setTargetDataSources(map); setDefaultTargetDataSource(updateDataSource); super.afterPropertiesSet(); } }
配置多个数据源:
import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /* * 配置多个数据源 */ @Configuration public class DataSourceConfig { // 创建可读数据源 @Bean(name = "selectDataSource") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.select") // application.properteis中对应属性的前缀 public DataSource dataSource1() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } // 创建可写数据源 @Bean(name = "updateDataSource") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.update") // application.properteis中对应属性的前缀 public DataSource dataSource2() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } }
将数据源注册到RoutingDataSource中
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Primary public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Autowired @Qualifier("selectDataSource") //获取读的数据源 private DataSource selectDataSource; @Autowired @Qualifier("updateDataSource") //获取写的数据源 private DataSource updateDataSource; /** * 这个是主要的方法,返回的是生效的数据源名称 */ @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { System.out.println("DataSourceContextHolder:::" + DataSourceContextHolder.getDbType()); return DataSourceContextHolder.getDbType(); } /** * 配置数据源信息 注册数据源的操作 最终注入到datasource数据源中 */ @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("selectDataSource", selectDataSource); map.put("updateDataSource", updateDataSource); setTargetDataSources(map); setDefaultTargetDataSource(updateDataSource); super.afterPropertiesSet(); } }
然后对于AOP的编写配置:
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.mayikt.config.DataSourceContextHolder; @Aspect @Component @Lazy(false) @Order(0) // Order设定AOP执行顺序 使之在数据库事务上先执行 动态数据源事务先执行的 public class SwitchDataSourceAOP { // 这里切到你的方法目录 @Before("execution(* com.mayikt.service.*.*(..))") //扫包范围是业务逻辑层 public void process(JoinPoint joinPoint) { String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); //通过反射获取到方法名称 if (methodName.startsWith("get") || methodName.startsWith("count") || methodName.startsWith("find") || methodName.startsWith("list") || methodName.startsWith("select") || methodName.startsWith("check")) { // 读 DataSourceContextHolder.setDbType("selectDataSource"); } else { // 切换dataSource DataSourceContextHolder.setDbType("updateDataSource"); } } }
启动:
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.toov5.mapper") public class AppMybatis { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(AppMybatis.class, args); } }
yml:
spring:
datasource:
###可读数据源
select:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.91.7:8066/mycat_testdb
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: user
password: user
####可写数据源
update:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.91.7:8066/mycat_testdb
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
注意数据源的配置:是MyCat的域名和端口
Controller:
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity; import com.mayikt.service.UserService; @RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping("/findUser") public List<UserEntity> findUser() { return userService.findUser(); } @RequestMapping("/insertUser") public List<UserEntity> insertUser(String userName) { return userService.insertUser(userName); } }
entity:
public class UserEntity { private String userName; public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } }
service:
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity; import com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper; @Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; public List<UserEntity> findUser() { return userMapper.findUser(); } public List<UserEntity> insertUser(String userName) { return userMapper.insertUser(userName); } }
mapper:
import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity; public interface UserMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM user_info ") public List<UserEntity> findUser(); @Select("insert into user_info values (null,#{userName}); ") public List<UserEntity> insertUser(@Param("userName") String userName); }