今天在慕课网学习了“快乐动起来呀”老师的《ES6快速入门》
https://www.imooc.com/learn/955
1.课程介绍:
ES使用情况:
jquery==》ES3
vue==》ES6
recat==》ES6
课程优点:
同样的问题,用ES3,ES5,ES6,三种方法对比学习,能很快了解ES6的优势。
对ES6冰山一角的5个认识:
1)常量
2)作用域
3)箭头函数
4)默认参数
5)对象代理
2.环境搭建
要简单的了解三个技术:Git,webpack,js
对于Git:要先了解https://github.com/cucygh/fe-material
对于webpack:我没有去看这块内容,但是要使用较新版chrome来实现的。
对于js:最好先了解ES3,ES5之后学习ES6,会发现ES6的强大之处。
3.常量
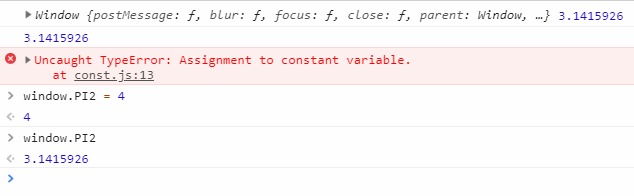
ES5中的常量,把常量绑定在全局对象window中。
// 给对象一个属性,让属性只读 Object.defineProperty(window,"PI2",{ value:3.1415926, writable:false, }) console.log(window,PI2);
控台输出显示赋值无效。
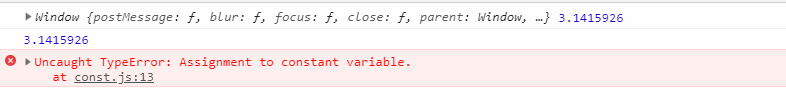
ES6中实现常量。
const PI = 3.1415926;
console.log(PI);
PI = 4;
赋值为4:弹出Assignment to constant variable.
4.作用域
ES5中的作用域
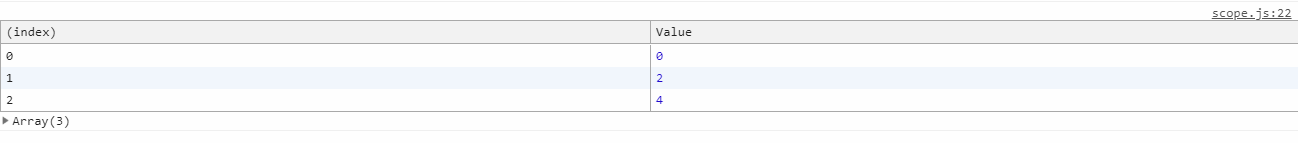
const callbacks = []; for(var i=0; i<=2;i++ ){ callbacks[i] = function(){ return i*2; } } console.table([ callbacks[0](), callbacks[1](), callbacks[2](), ]);
显示结果:所有value都是6,在for循环内使用的var声明变量,被变量提升到了for循环之外的前面了,callbacks[i]中的i=0,但是function函数中因为闭包,return中的i并没有取值为0,返回的是一个表达式。在console的时候去执行,那是i已经等于3,所以无论怎么执行,都是输出3*2。

ES6的作用域
const callbacks2 = []; for(let j = 0;j<=2;j++){ callbacks2[j] = function(){ return j*2; } } console.table([ callbacks2[0](), callbacks2[1](), callbacks2[2](), ]);
显示结果:let声明的变量,有一个块作用域,function函数中的闭包可以使用,for循环每次执行都可以生成这个作用域。
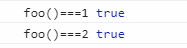
在ES5保证一块代码的独立的实现:
(function(){ var foo = function(){ return 1 } console.log("foo()===1",foo()===1); (function(){ var foo = function(){ return 2 } console.log("foo()===2",foo()===2); })(); })();
显示结果:
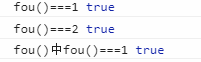
ES6中的实现:
{ function fou(){ return 1; } console.log('fou()===1',fou()===1); { function fou(){ return 2; } console.log('fou()===2',fou()===2); } console.log('fou()中fou()===1',fou()===1); }
显示结果:
5.箭头函数
声明和写法:
{ // ES3,ES5中遍历的声明 var evens = [1,2,3,4,5,6]; var odds= evens.map(function(v){ return v+1; }); console.log(evens,odds); } { //ES6 let evens = [1,2,3,4,5,6]; let odds = evens.map(v => v+1); console.log(evens,odds); } { ()=>{ } } //(args1,args2),括号内只有一个参数的时候可以省略(),{return a+b}中表达式作为返回值,可以省略{}。
箭头函数和普通函数的区别在于this的绑定。
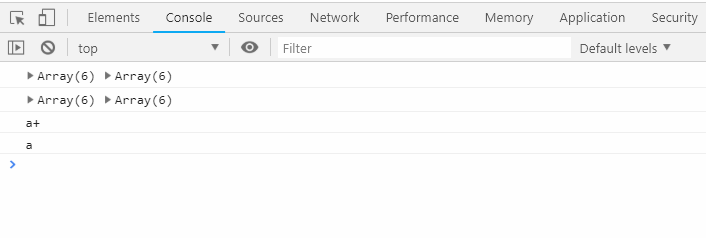
// ES3,ES5 // this的指向:是该函数被调用的对象 { var factory=function(){ this.a='a'; this.b='b'; this.c={ a:'a+', b:function(){ return this.a; } } } console.log(new factory().c.b()); }; //ES6 // 箭头函数的指向:是定义时this的指向。 // b在定义函数的时候,return 中的this指向函数体中的this,函数体中的this指向构造函数的实例, // 构造函数的this指向factory这个实例,new factory的实例就是this.a。 //为了解决ES5中this指向不明确,避免在运行的时候this指向不确定。 { var factory=function(){ this.a='a', this.b='b', this.c={ a:'a+', b:()=>{ return this.a } } } console.log(new factory().c.b()); }
输出结果:
6.默认参数
举例
// ES3、ES5中默认参数写法 { function f(x,y,z){ if(y===undefined){ y=7; } if(z===undefined){ z=42; } return x+y+z; } console.log(f(1,3)); } //ES6默认参数 { function f(x,y=7,z=42){ return x+y+z; } console.log(f(1,3)); }
参数默认必选性检查
{ function checkParameter(){ throw new Error('can\'t be empty'); } function f(x=checkParameter(),y=7,z=42){ return x+y+z; } console.log(f(1)); try{ f(); }catch(e){ console.log(e); }finally{ } }
可变参数求和
//ES3,ES5可变参数求和 { function f(){ var a =Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); var sum = 0; a.forEach(function(item){ sum+=item*1; }) return sum; } console.log(f(1,2,3,4,6)); } // ES6可变参数 { function f(...a){ var sum=0; a.forEach(item=>{ sum+=item*1; }); return sum; } console.log(f(1,2,3,4,6)); }
输出结果:

合并数组
// ES5合并数组 { var params=['hello',true,7]; var other=[1,2].concat(params); console.log(other); } //ES6利用扩展运算符合并数组 { var params=['hello',7,true]; var other=[1,2,...params]; console.log(other); }
7.对象代理(解决Javascript中私有变量的问题)
// ES3中的数据保护 { var Person=function(){ var data={ name:'es3', sex:'male', age:15 } // 读取 this.get=function(key){ return data[key]; } this.set=function(key,value){ if(key!='sex'){ data[key]=value; } } } // 声明一个实例 var person=new Person(); //读取 console.table({ name:person.get('name'), sex:person.get('sex'), age:person.get('age') }); // 修改 person.set('name','es3-cname'); console.table({ name:person.get('name'), sex:person.get('sex'), age:person.get('age') }); person.set('sex','female'); console.table({ name:person.get('name'), sex:person.get('sex'), age:person.get('age') }); } //ES5 { var Person = { name:'es5', age:15 }; Object.defineProperty(Person,'sex',{ writable:false, value:'male' }); console.table({ name:Person.name, age:Person.age, sex:Person.sex }); Person.name='es5-cname'; console.table({ name:Person.name, age:Person.age, sex:Person.sex }); Person.sex='female'; console.table({ name:Person.name, age:Person.age, sex:Person.sex }); } //ES6 { let Person={ name:'es6', sex:'male', age:15 }; let person = new Proxy(Person,{ get(target,key){ return target[key]; }, set(target,key,value){ if(key!=='sex'){ target[key]=value; } } }); console.table({ name:person.name, sex:person.sex, age:person.age }); person.name='es6-cname'; person.sex = 'female'; console.table({ name:person.name, sex:person.sex, age:person.age }); }
8.ES6其余内容