版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/pfl_327/article/details/85805143
子函数调用
- 子函数
定义:能被其他程序调用,在实现某种功能后能自动返回到调用程序去的程序。其最后一条指令一定是返回指令,故能保证重新返回到调用它的程序中去。也可调用其他子程序,甚至可自身调用(如递归)。 - 函数的调用形式
函数调用的一般格式为:(在main函数中)
<函数名> ([<实际参数列表>]); - 函数声明
函数声明的一般格式:
<返回类型><函数名> ([<形参类型1>][<形参1>],[<形参类型2>][<形参2>]…);
例:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
void putin(int); //函数原型声明
int number;
printf("请输入数字:\n");
scanf("%d",&number);
putin(number); //调用子函数putin()
return 0;
}
void putin(int number)
{
printf("%c\n",'number'); //将输入的数的ascll码输出
return ;
}
运行结果:

注:
个人自己的理解:
1.在函数声明的时候,个人比较喜欢放到头文件的下面。声明时不是按照函数原型声明(省略形参),而是详细的都列出来,因为在用函数原型声明的时候很容易出错,倒不如直接全部声明。
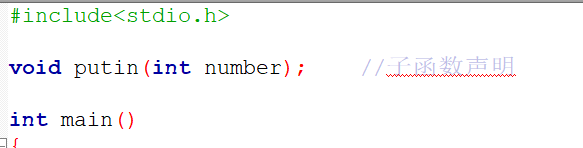
2.在函数调用的时候倒是没有什么不一样的,基本上就是这个模板.
最后在放个你让我看的例子;
法一:
#include<stdio.h>
//声明子函数
void name(char student_name[20]);
void place(char student_hometown[20]);
int main()
{
char student_name[20];
char student_hometown[20]; //定义两个字符变量
//调用子函数
name(student_name);
place(student_hometown);
//界面化实现
printf("*******************************\n");
printf("Welcome! %s \n",student_name);
printf("come from:%s!\n",student_hometown);
printf("*******************************\n");
return 0;
}
//name子函数
void name(char student_name[20])
{
printf("Enter your name:\n");
scanf("%s",student_name);
return ; //纯属个人习惯,没有也是对的
}
//place子函数
void place(char student_hometown[20])
{
printf("Enter your hometown:\n");
scanf("%s",student_hometown);
return ;
}
法二:
#include<stdio.h>
//声明子函数
/*
void name(char student_name[20]);
void place(char student_hometown[20]);
*/
//name子函数
void name(char student_name[20])
{
printf("Enter your name:\n");
scanf("%s",student_name);
return ; //纯属个人习惯,没有也是对的
}
//place子函数
void place(char student_hometown[20])
{
printf("Enter your hometown:\n");
scanf("%s",student_hometown);
return ;
}
int main()
{
char student_name[20];
char student_hometown[20]; //定义两个字符变量
//调用子函数
name(student_name);
place(student_hometown);
//界面化实现
printf("*******************************\n");
printf("Welcome! %s \n",student_name);
printf("come from:%s!\n",student_hometown);
printf("*******************************\n");
return 0;
}
注:其实法二,并不算是一种方法。只是把所有的子函数放在了main函数的上边就不需要声明了。
遇到的一些问题:
1.尽量不要在声明的时候省略形参。
2.注意一下关于字符串的处理,值得深入研究字符串。
3.注释打一下,既是练打字,还能让自己更了解