系列前言
参考文献:
- RNNLM - Recurrent Neural Network Language Modeling Toolkit(点此阅读)
- Recurrent neural network based language model(点此阅读)
- EXTENSIONS OF RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK LANGUAGE MODEL(点此阅读)
- Strategies for Training Large Scale Neural Network Language Models(点此阅读)
- STATISTICAL LANGUAGE MODELS BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS(点此阅读)
- A guide to recurrent neural networks and backpropagation(点此阅读)
- A Neural Probabilistic Language Model(点此阅读)
- Learning Long-Term Dependencies with Gradient Descent is Difficult(点此阅读)
- Can Artificial Neural Networks Learn Language Models?(点此阅读)
由于testNbest(), testGen()我没去看,剩下两个主干函数,一个是训练函数,另一个是测试函数,这两个函数都调用前面介绍过的函数。训练时,每当文件训练一遍完毕时,会马上将训练后的模型在valid文件上面试一下,看一下效果如何,如果这一遍训练的效果还不错的话,那么继续同样的学习率来训练文件,如果效果没太多打提升,就将学习率降低为一半,继续学习,直到没太大的提升就不再训练了。至于这个效果怎么看,是指训练打模型在valid上面的困惑度。测试函数是直接将训练好的模型在测试文件上计算所有的对数概率和,并换算成PPL,里面存着一个动态模型的概念,意思就是边测试的同时,还去更新网络的参数,这样测试文件也可以对模型参数进行更新。里面很重要的一个计算量是PPL, 下面的公式是PPL的公式,以便贴上来和程序代码部分对照:
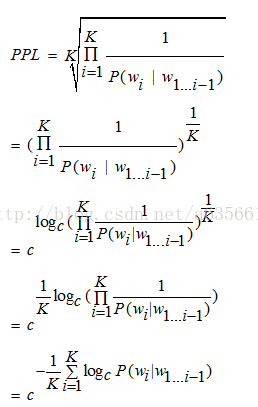
这是对一个序列w1w2w3...wk计算困惑度的公式,后面的c值在程序取的是10,后面会在代码中看到。下面就直接贴代码以及注释:
//训练网络
void CRnnLM::trainNet()
{
int a, b, word, last_word, wordcn;
char log_name[200];
FILE *fi, *flog;
//在time.h中 typedef long clock_t
clock_t start, now;
//log_name中字串是rnnlm_file.output.txt
sprintf(log_name, "%s.output.txt", rnnlm_file);
printf("Starting training using file %s\n", train_file);
starting_alpha=alpha;
//打开rnnlm_file文件
fi=fopen(rnnlm_file, "rb");
if (fi!=NULL) { //打开成功,即存在训练好的文件模型
fclose(fi);
printf("Restoring network from file to continue training...\n");
//将rnnlm_file中模型信息恢复
restoreNet();
}
else { //rnnlm_file打开失败
//从train_file中读数据,相关数据会装入vocab,vocab_hash
learnVocabFromTrainFile();
//分配内存,初始化网络
initNet();
//iter表示整个训练文件的训练次数
iter=0;
}
if (class_size>vocab_size) {
printf("WARNING: number of classes exceeds vocabulary size!\n");
}
//counter含义:当前训练的word是train_file的第counter个词
counter=train_cur_pos;
//saveNet();
//最外层循环,循环一遍表示整个训练文件完成一次训练,用iter指示
while (iter < maxIter) {
printf("Iter: %3d\tAlpha: %f\t ", iter, alpha);
//fflush(stdout)刷新标准输出缓冲区,把输出缓冲区里的东西打印到标准输出设备上
//即将上面要输出的内容立马输出
fflush(stdout);
//初始化bptt_history, history
if (bptt>0) for (a=0; a<bptt+bptt_block; a++) bptt_history[a]=0;
for (a=0; a<MAX_NGRAM_ORDER; a++) history[a]=0;
//TRAINING PHASE
//清除神经元的ac,er值
netFlush();
//打开训练文件
fi=fopen(train_file, "rb");
//在vocab中下标为0表示一个句子的结束即</s>
last_word=0;
//todo
if (counter>0) for (a=0; a<counter; a++) word=readWordIndex(fi); //this will skip words that were already learned if the training was interrupted
//记录每次语料库开始训练的时间
start=clock();
while (1) {
counter++;
//下面信息每训练1万个词语才输出
if ((counter%10000)==0) if ((debug_mode>1)) {
now=clock();
////train_words表示训练文件中的词数
if (train_words>0)
//输出的第一个%c,后面跟的是13表示回车键的ASCII,注意不同于换行键的10
//对熵我不太了解,所以不太明白train entropy具体含义
//Progress表示当前所训练的单词在整个训练文件中的位置,即训练进度
//Words/sec表示每一秒中训练了多少个word
printf("%cIter: %3d\tAlpha: %f\t TRAIN entropy: %.4f Progress: %.2f%% Words/sec: %.1f ", 13, iter, alpha, -logp/log10(2)/counter, counter/(real)train_words*100, counter/((double)(now-start)/1000000.0));
else
printf("%cIter: %3d\tAlpha: %f\t TRAIN entropy: %.4f Progress: %dK", 13, iter, alpha, -logp/log10(2)/counter, counter/1000);
fflush(stdout);
}
//表示每训练anti_k个word,会将网络信息保存到rnnlm_file
if ((anti_k>0) && ((counter%anti_k)==0)) {
train_cur_pos=counter;
//保存网络的所有信息到rnnlm_file
saveNet();
}
//读取下一个词,该函数返回下一个word在vocab中的下标
word=readWordIndex(fi); //read next word
//注意训练文件中第一个词时,即counter=1时,last_word表示一个句子的结束
computeNet(last_word, word); //compute probability distribution
if (feof(fi)) break; //end of file: test on validation data, iterate till convergence
//logp表示累计对数概率,即logp = log10w1 + log10w2 + log10w3...
if (word!=-1) logp+=log10(neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac * neu2[word].ac);
//第一个条件没看懂,第二个条件似乎isinf(x)C99新增加的数学函数,如果x无穷返回非0的宏值
//判断数值是否出错吧
if ((logp!=logp) || (isinf(logp))) {
printf("\nNumerical error %d %f %f\n", word, neu2[word].ac, neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac);
exit(1);
}
if (bptt>0) { //shift memory needed for bptt to next time step
////这里进行移动,结果就是bptt_history从下标0开始存放的是wt,wt-1,wt-2...
for (a=bptt+bptt_block-1; a>0; a--) bptt_history[a]=bptt_history[a-1];
bptt_history[0]=last_word;
//这里进行移动,结果就是bptt_hidden从下标0开始存放的是st,st-1,st-2...
for (a=bptt+bptt_block-1; a>0; a--) for (b=0; b<layer1_size; b++) {
bptt_hidden[a*layer1_size+b].ac=bptt_hidden[(a-1)*layer1_size+b].ac;
bptt_hidden[a*layer1_size+b].er=bptt_hidden[(a-1)*layer1_size+b].er;
}
}
//反向学习,调整参数
learnNet(last_word, word);
//将隐层神经元的ac值复制到输出层后layer1_size那部分,即s(t-1)
copyHiddenLayerToInput();
//准备对下一个词所在的输入层进行编码
if (last_word!=-1) neu0[last_word].ac=0; //delete previous activation
last_word=word;
//移动,结果就是history从下标0开始存放的是wt, wt-1,wt-2...
for (a=MAX_NGRAM_ORDER-1; a>0; a--) history[a]=history[a-1];
history[0]=last_word;
//word==0表示当前句子结束,independent非0,即表示要求每个句子独立训练
//这个控制表面是否将一个句子独立训练,如果independent==0,表面上一个句子对下一个句子的训练时算作历史信息的
//这控制还得看句子与句子之间的相关性如何了
if (independent && (word==0)) netReset();
}
//关闭文件(train_file)
fclose(fi);
now=clock();
//输出整个文件训练完毕的相关信息,具体见上面
printf("%cIter: %3d\tAlpha: %f\t TRAIN entropy: %.4f Words/sec: %.1f ", 13, iter, alpha, -logp/log10(2)/counter, counter/((double)(now-start)/1000000.0));
//训练文件只会进行一遍,然后保存
if (one_iter==1) { //no validation data are needed and network is always saved with modified weights
printf("\n");
logp=0;
////保存网络的所有信息到rnnlm_file
saveNet();
break;
}
//VALIDATION PHASE
//上面训练一遍,下面进行验证,使用early-stopping
//注意这里和上面TRAIN PHASE不同的是,下面的内容只是做计算,计算概率分布
//并且测试整个validation文件的概率,下面不会有learNet的部分,如果有是属于dynamic models
//清除神经元的ac,er值
netFlush();
//打开验证数据文件
fi=fopen(valid_file, "rb");
if (fi==NULL) {
printf("Valid file not found\n");
exit(1);
}
//ab方式打开文件:b表示二进制方式
//a表示若文件不存在,则会建立该文件,如果文件存在,写入的数据会被加到文件尾后
//log_name中字串是rnnlm_file.output.txt
flog=fopen(log_name, "ab");
if (flog==NULL) {
printf("Cannot open log file\n");
exit(1);
}
//fprintf(flog, "Index P(NET) Word\n");
//fprintf(flog, "----------------------------------\n");
last_word=0;
logp=0;
//wordcn的含义跟counter一样,只不过wordcn不包括OOV的词
wordcn=0;
while (1) {
//读取下一个词,该函数返回下一个word在vocab中的下标
word=readWordIndex(fi);
//计算下一个词的概率分布
computeNet(last_word, word);
if (feof(fi)) break; //end of file: report LOGP, PPL
if (word!=-1) {
//logp表示累计对数概率,即logp = log10w1 + log10w2 + log10w3...
logp+=log10(neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac * neu2[word].ac);
wordcn++;
}
/*if (word!=-1)
fprintf(flog, "%d\t%f\t%s\n", word, neu2[word].ac, vocab[word].word);
else
fprintf(flog, "-1\t0\t\tOOV\n");*/
//learnNet(last_word, word); //*** this will be in implemented for dynamic models
////将隐层神经元的ac值复制到输出层后layer1_size那部分,即s(t-1)
copyHiddenLayerToInput();
////准备对下一个词所在的输入层进行编码
if (last_word!=-1) neu0[last_word].ac=0; //delete previous activation
last_word=word;
//移动,结果就是history从下标0开始存放的是wt, wt-1,wt-2...
for (a=MAX_NGRAM_ORDER-1; a>0; a--) history[a]=history[a-1];
history[0]=last_word;
//word==0表示当前句子结束,independent非0,即表示要求每个句子独立训练
//这个控制表面是否将一个句子独立训练,如果independent==0,表面上一个句子对下一个句子的训练时算作历史信息的
if (independent && (word==0)) netReset();
}
fclose(fi);
//表示第iter次训练train_file
fprintf(flog, "\niter: %d\n", iter);
fprintf(flog, "valid log probability: %f\n", logp);
//这里实在没弄明白exp10()这个函数哪里来的,函数什么意思我也不能确定,希望明白的朋友告知一下~
//但是按照PPL定义来推导,不难发现exp10啥意思,见PPL公式,公式里面我们取常数c = 10即可
//所以exp10(x)就是10^(x)的意思吧
fprintf(flog, "PPL net: %f\n", exp10(-logp/(real)wordcn));
fclose(flog);
//entropy不太熟悉,这里没去了解了
printf("VALID entropy: %.4f\n", -logp/log10(2)/wordcn);
counter=0;
train_cur_pos=0;
//llogp前面的l表示上一次last
//这里的判断表示如果本次训练的结果没有上一次好,那么恢复到上一次
//否则保存当前网络
if (logp<llogp)
restoreWeights();
else
saveWeights();
//logp是越大说明训练得越好
//初始时min_improvement=1.003,alpha_divide=0
//这里表示如果本次训练的效果没有那么显著(提高min_improvement倍)则进入循环
//训练的效果比较显著时,不进入循环,alpha保持不变
//这里可以参考原论文第30页有更详细的说明
if (logp*min_improvement<llogp) {
//如果没显著的提高,打开alpha_divide控制
if (alpha_divide==0) alpha_divide=1;
else {
//如果没显著的提高,且alpha_divide开关是打开的,那么退出训练,这时说明训练得不错了
saveNet();
break;
}
}
//如果没有显著的提高,则将学习率降低一半
if (alpha_divide) alpha/=2;
llogp=logp;
logp=0;
iter++;
saveNet();
}
}
//测试网络
void CRnnLM::testNet()
{
int a, b, word, last_word, wordcn;
FILE *fi, *flog, *lmprob=NULL;
real prob_other, log_other, log_combine;
double d;
//将rnnlm_file中模型信息恢复
restoreNet();
//use_lmprob这个控制开关等于1时,表示使用其他训练好的语言模型
if (use_lmprob) {
//打开其他语言模型文件
lmprob=fopen(lmprob_file, "rb");
}
//TEST PHASE
//netFlush();
//打开测试文件
fi=fopen(test_file, "rb");
//sprintf(str, "%s.%s.output.txt", rnnlm_file, test_file);
//flog=fopen(str, "wb");
//stdout是一个文件指针,C己经在头文件中定义好的了,可以直接使用,把它赋给另一个文件指针,这样直接为标准输出
//printf其实就是fprintf的第一个参数设置为stdout
flog=stdout;
if (debug_mode>1) {
if (use_lmprob) {
fprintf(flog, "Index P(NET) P(LM) Word\n");
fprintf(flog, "--------------------------------------------------\n");
} else {
fprintf(flog, "Index P(NET) Word\n");
fprintf(flog, "----------------------------------\n");
}
}
//在vocab中下标为0表示一个句子的结束即</s>,即last_word初始时,即 等于 end of sentence
last_word=0;
//rnn对测试文件的对数累加概率
logp=0;
//其他语言模型对测试文件的对数累加概率
log_other=0;
//rnn与其他语言模型的结合对数累加概率
log_combine=0;
//其他语言模型某个词的概率
prob_other=0;
//wordcn的含义跟trainNet里面的counter一样,只不过wordcn不包括OOV的词
wordcn=0;
//将隐层神经元的ac值复制到输出层后layer1_size那部分,即s(t-1)
copyHiddenLayerToInput();
//清空历史信息
if (bptt>0) for (a=0; a<bptt+bptt_block; a++) bptt_history[a]=0;
for (a=0; a<MAX_NGRAM_ORDER; a++) history[a]=0;
if (independent) netReset();
while (1) {
//读取下一个词,该函数返回下一个word在vocab中的下标
word=readWordIndex(fi);
//计算下一个词的概率分布
computeNet(last_word, word);
if (feof(fi)) break; //end of file: report LOGP, PPL
if (use_lmprob) {
fscanf(lmprob, "%lf", &d);
prob_other=d;
goToDelimiter('\n', lmprob);
}
//log_combine通过系数lambda插值
if ((word!=-1) || (prob_other>0)) {
if (word==-1) {
//这里不太懂为啥要惩罚
logp+=-8; //some ad hoc penalty - when mixing different vocabularies, single model score is not real PPL
//插值
log_combine+=log10(0 * lambda + prob_other*(1-lambda));
} else {
//计算rnn累加对数概率
logp+=log10(neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac * neu2[word].ac);
//插值
log_combine+=log10(neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac * neu2[word].ac*lambda + prob_other*(1-lambda));
}
log_other+=log10(prob_other);
wordcn++;
}
if (debug_mode>1) {
if (use_lmprob) {
if (word!=-1) fprintf(flog, "%d\t%.10f\t%.10f\t%s", word, neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac *neu2[word].ac, prob_other, vocab[word].word);
else fprintf(flog, "-1\t0\t\t0\t\tOOV");
} else {
if (word!=-1) fprintf(flog, "%d\t%.10f\t%s", word, neu2[vocab[word].class_index+vocab_size].ac *neu2[word].ac, vocab[word].word);
else fprintf(flog, "-1\t0\t\tOOV");
}
fprintf(flog, "\n");
}
//这部分是 dynamic model 在测试时还能让rnn进行学习更新参数
if (dynamic>0) {
if (bptt>0) {
//将bptt_history往后移动一个位置,将最近的word装入bptt_history第一个位置
for (a=bptt+bptt_block-1; a>0; a--) bptt_history[a]=bptt_history[a-1];
bptt_history[0]=last_word;
//将bptt_hidden往后移动一个位置,将第一个位置留出来,第一个位置的赋值是在learnNet里面
for (a=bptt+bptt_block-1; a>0; a--) for (b=0; b<layer1_size; b++) {
bptt_hidden[a*layer1_size+b].ac=bptt_hidden[(a-1)*layer1_size+b].ac;
bptt_hidden[a*layer1_size+b].er=bptt_hidden[(a-1)*layer1_size+b].er;
}
}
//动态模型时的学习率
alpha=dynamic;
learnNet(last_word, word); //dynamic update
}
//将隐层神经元的ac值复制到输出层后layer1_size那部分,即s(t-1)
copyHiddenLayerToInput();
//准备对下一个词所在的输入层进行编码
if (last_word!=-1) neu0[last_word].ac=0; //delete previous activation
last_word=word;
//将ME部分的history往后移动一个位置,第一个位置放最近的词
for (a=MAX_NGRAM_ORDER-1; a>0; a--) history[a]=history[a-1];
history[0]=last_word;
//这个和前面同理
if (independent && (word==0)) netReset();
}
fclose(fi);
if (use_lmprob) fclose(lmprob);
//这里输出对测试文件的信息
//write to log file
if (debug_mode>0) {
fprintf(flog, "\ntest log probability: %f\n", logp);
if (use_lmprob) {
fprintf(flog, "test log probability given by other lm: %f\n", log_other);
fprintf(flog, "test log probability %f*rnn + %f*other_lm: %f\n", lambda, 1-lambda, log_combine);
}
fprintf(flog, "\nPPL net: %f\n", exp10(-logp/(real)wordcn));
if (use_lmprob) {
fprintf(flog, "PPL other: %f\n", exp10(-log_other/(real)wordcn));
fprintf(flog, "PPL combine: %f\n", exp10(-log_combine/(real)wordcn));
}
}
fclose(flog);
}
好了,rnnlm toolkit源码走读就暂告一段落了,内容肯定会很有多自己理解不正确的地方,还是一样欢迎明白的朋友指出,一起讨论,因为图解过于分散在每一篇了,最后我会在把rnnlm toolkit的内部数据结构图作为单独一篇文章全部贴出来。