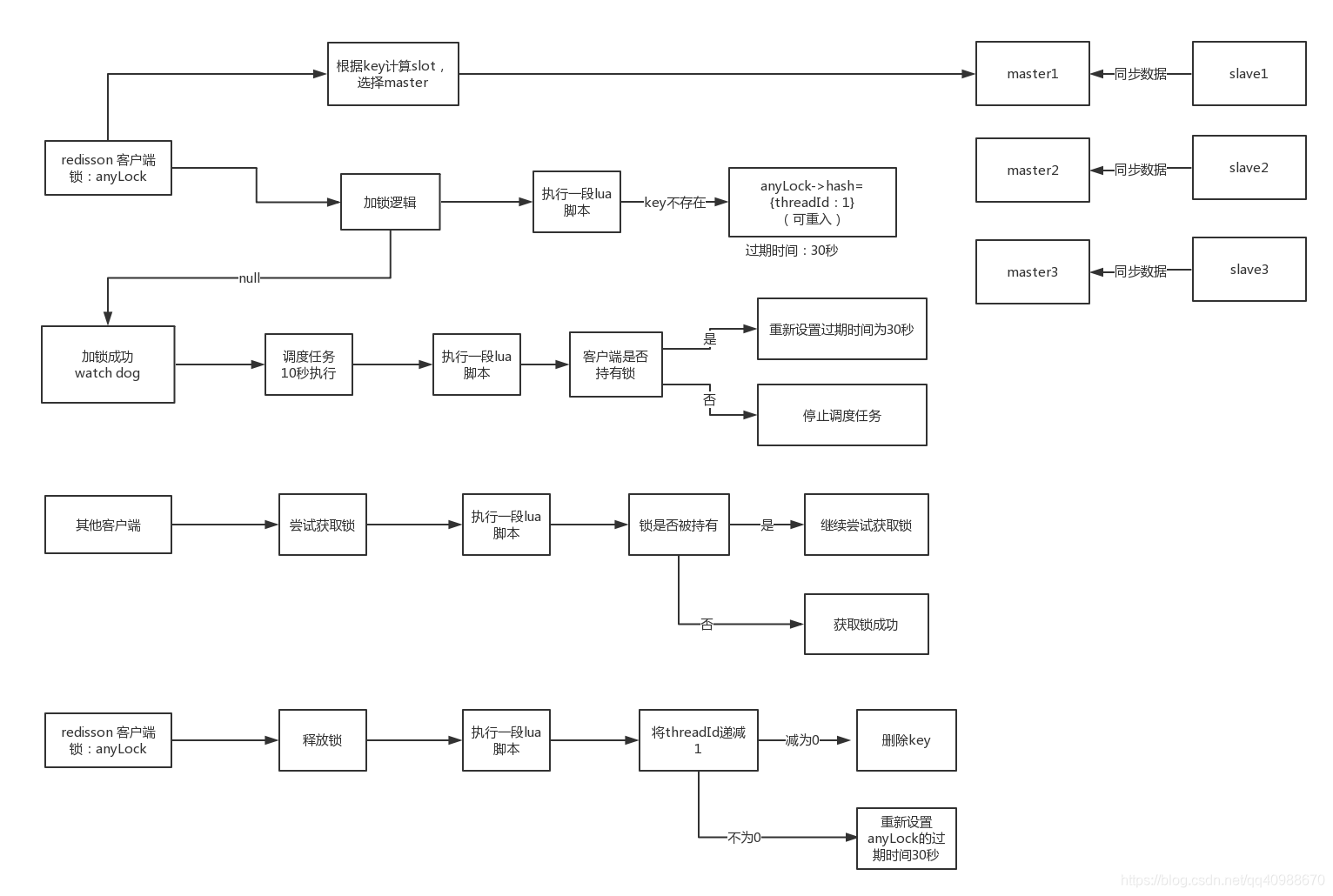
Redisson分布式锁源码剖析(非公平锁)
maven配置文件:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</dependency>
代码示例:
Config config = new Config();
config.useClusterServers()
.addNodeAddress("redis://192.168.31.114:7001")
.addNodeAddress("redis://192.168.31.184:7002")
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("anyLock"); //设置internalLockLeaseTime=30秒
lock.lock();
lock.unlock();
lock()方法源码剖析
核心源码:
1、根据加锁的key(anyLock)计算slot,选择redis master。evalWriteAsync方法。
2、执行加锁逻辑,核心是一段lua脚本。lua脚本逻辑:
lock()->RedisssonLock.lock()->lockInterruptibly()->tryAcquire()->tryAcquireAsync()->tryLockInnerAsync()
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
第一段逻辑:判断anyLock是否存在,如果不存在,设置一个map数据结构,key=anyLock->hash={threadId:1},设置key的过期时间30秒,最后返回null。
第二段逻辑:判断是否存在key=anyLock,并且threadId:1,如果存在,则把value累计1,即threadId:2。重新设置anyLock的过期时间30秒,最后返回null。(可重入锁)
第三段逻辑:返回anyLock的存活时间。(锁的互斥阻塞)
3、加锁成功后,10秒后启动一个调度任务,执行一段lua脚本,更新过期时间。
lock()->RedisssonLock.lock()->lockInterruptibly()->tryAcquire()->tryAcquireAsync()->scheduleExpirationRenewal()->renewExpirationAsync()
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
lua脚本逻辑:判断是否存在key=anyLock,并且threadId:1,如果存在,说明客户端还持有锁,重新设置anyLock的过期时间30秒。如果不存在,说明已经释放锁,停止调度任务。
4、如果其它线程来获取锁,如果加锁成功,就会直接返回,如果加锁失败,一直循环尝试获取锁。
lock()->RedisssonLock.lock()->lockInterruptibly()
try {
while (true) {
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
// waiting for message
if (ttl >= 0) {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
unlock()方法源码剖析
释放锁也是通过一段lua脚本。
unlock()->RedisssonLock.unlock()->unlockAsync()->unlockInnerAsync()
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end;" +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.unlockMessage, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
第一段逻辑:如果anyLock这个key不存在,将信息发送到指定的频道。
第二段逻辑:判断anyLock对应的hash数据结构中,当前这个线程是否对这个anyLock进行了加锁。
counter:递减anyLock的threadId:1。(因为锁的可重入性)
第三段逻辑:如果counter大于0,说明多次加锁,重新设置anyLock的过期时间30秒,返回的值是0。如果counter=0,说明只加了一次锁,会删除anyLock这个key。
Redisson 非公平锁的原理图