Java Classes:
- Use a qualifier, a class keywords, an identifier, and a pair of {}
public class Hello{
public Hello(){
public int myInt;
private float myFloat;
//This is a constructor
}
}
- Whenever a class is instantiated, meaning memory is allocated, the constructor is called.
- The constructor in Java has the same name as the class, and no return type.
- One of the primary uses of a constructor is the initialization of member variables.
- Like a C structure, a Class can contain different fields of data.
- These fields can be made “public” or “private”
- The same as C++, private data members cannot be accessed without using a function.
- Typically, the private data members have a “get” function to get the data.
int getData()
- And a set function in order to assign the data.
void setData(int myParameter)
Collection Data Types
• Vector-A self-expanding linked list.
Deprecated and obsolete.
• HashTable-know this one for the future!
Deprecated and obsolete. (in Java)
• Enumeration-Vectors and other types turn into an enumerated series.
Not used so much anymore
• ArrayList-acts like an array, with a get function
Inheritance:
- An inheritance means the new class contains all the accessible abilities and traits of its parent class
- The parent class is the superclass
- The child class is the subclass
protected Data Members:
Protected Data Members:
*Not public, not private, but protected
- Protected data members
- Private data members are not shared between superclass and subclass
- Public data members are shared between superclass and subclass
- Protected data members are shared between subclass, superclass, and classes of the same package.
Sample code:(keyword: Extend)
JAVA(tips):
• Every scalar/atomic/basic value in Java is a basic value
• 5, 3.14159, are numbers/literals/values
• Every class in Java is “instantiated” into an object
• Every object is also a memory area
• Every object variable in Java behaves a pointer reference.
• This has complications:
• A basic assignment between objects “=“, only copies the address
• This is a Shallow Copy, only the address is copies
• A more complex assignment uses a “copy constructor”
• This is a Deep Copy, every field must be assigned appropriately
C++ VS Java:
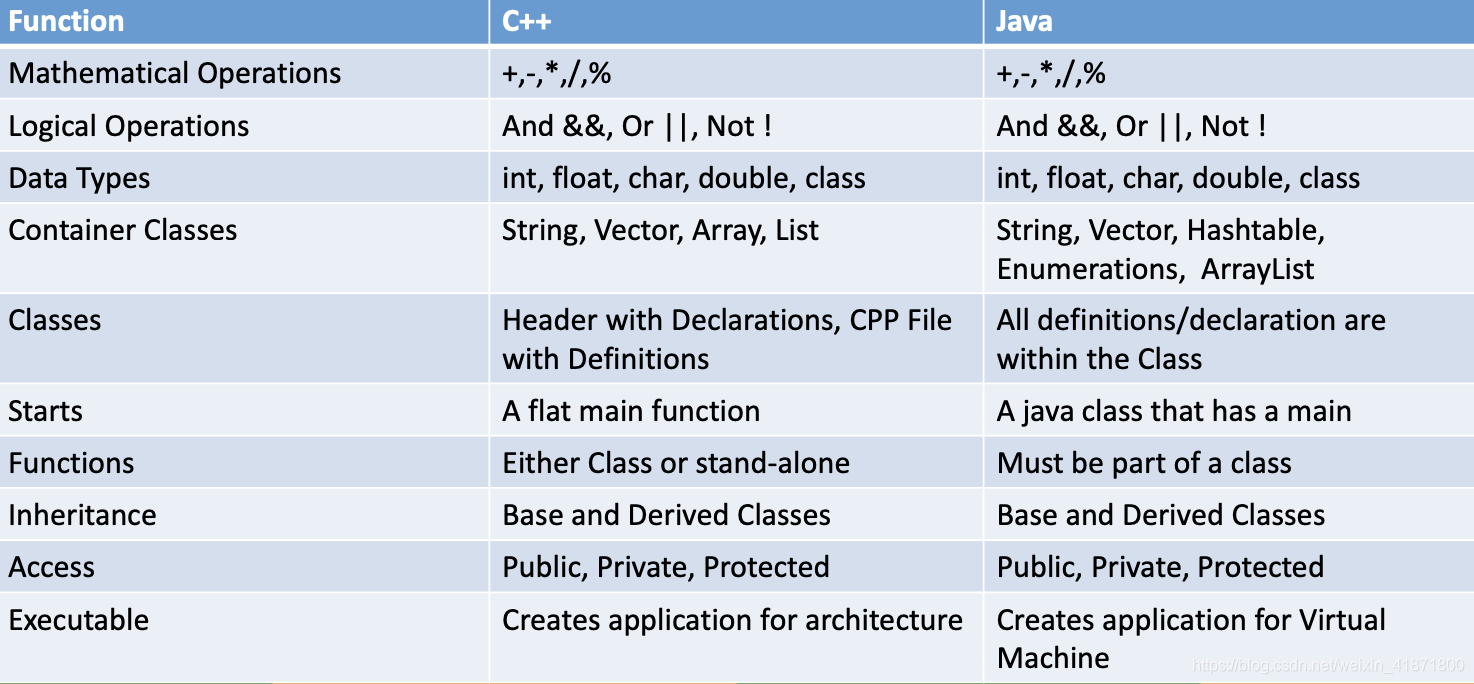
speed of C++ & Java
- C, C++ create code for an architecture
- Java creates code for a Virtual machine.
- Since the Java runs on the virtual machine, by its nature, it will always be slower than C++.
- Optimization makes this go faster and faster, but always just a little lag.
- C++ is faster than Java