注:题目来自于《程序员代码面试指南:IT名企算法与数据结构题目最优解》,该书是左程云老师的著作,值得推荐,这里仅是记录一下该书中题目的解法和个人理解
一:设计一个有getMin功能的栈
题目:在实现栈的基本功能的基础上,再实现返回栈中的最小元素操作
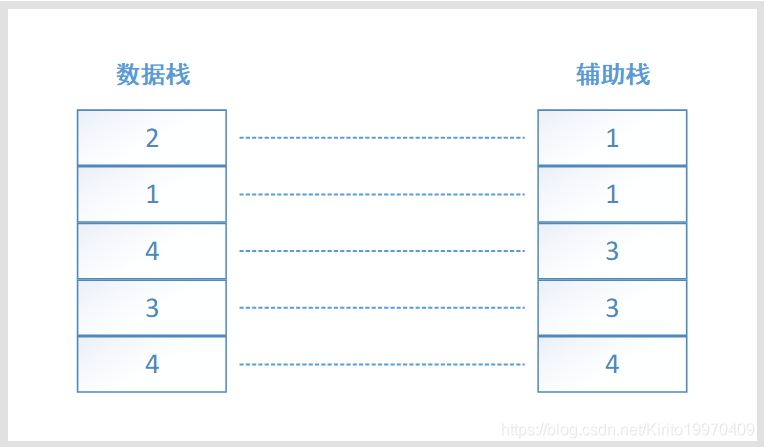
思路:可以创建一个辅助栈,辅助栈保证栈顶值既为最小值。
当入栈的元素小于辅助栈栈顶值,则辅助栈和数据栈都进行入栈操作。
当入栈的元素大于辅助栈栈顶值,则数据栈进行入栈操作辅助栈将栈顶元素复制一份,再将该元素进行入栈
图解:
代码:
class MyStack {
private Stack<Integer> stackData;
private Stack<Integer> stackMin;
public MyStack() {
stackData = new Stack<>();
stackMin = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int num) {
if (stackMin.isEmpty()) {
stackMin.push(num);
} else if (num < getMin()) {
stackMin.push(num);
} else {
int c = stackMin.peek();
stackMin.push(c);
}
stackData.push(num);
}
public int pop() {
if (stackData.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
} else {
stackMin.pop();
return stackData.pop();
}
}
public int getMin() {
if (stackMin.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
} else {
return stackMin.peek();
}
}
}
测试方法:
public class GetMinStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack stack = new MyStack();
stack.push(4);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
System.out.println("min is "+stack.getMin());
}
}
执行结果,亲测可用:
min is 3
二:由两个栈组成的队列
题目:编写一个类,用两个栈实现队列,支持栈的基本操作(add、poll、peek)
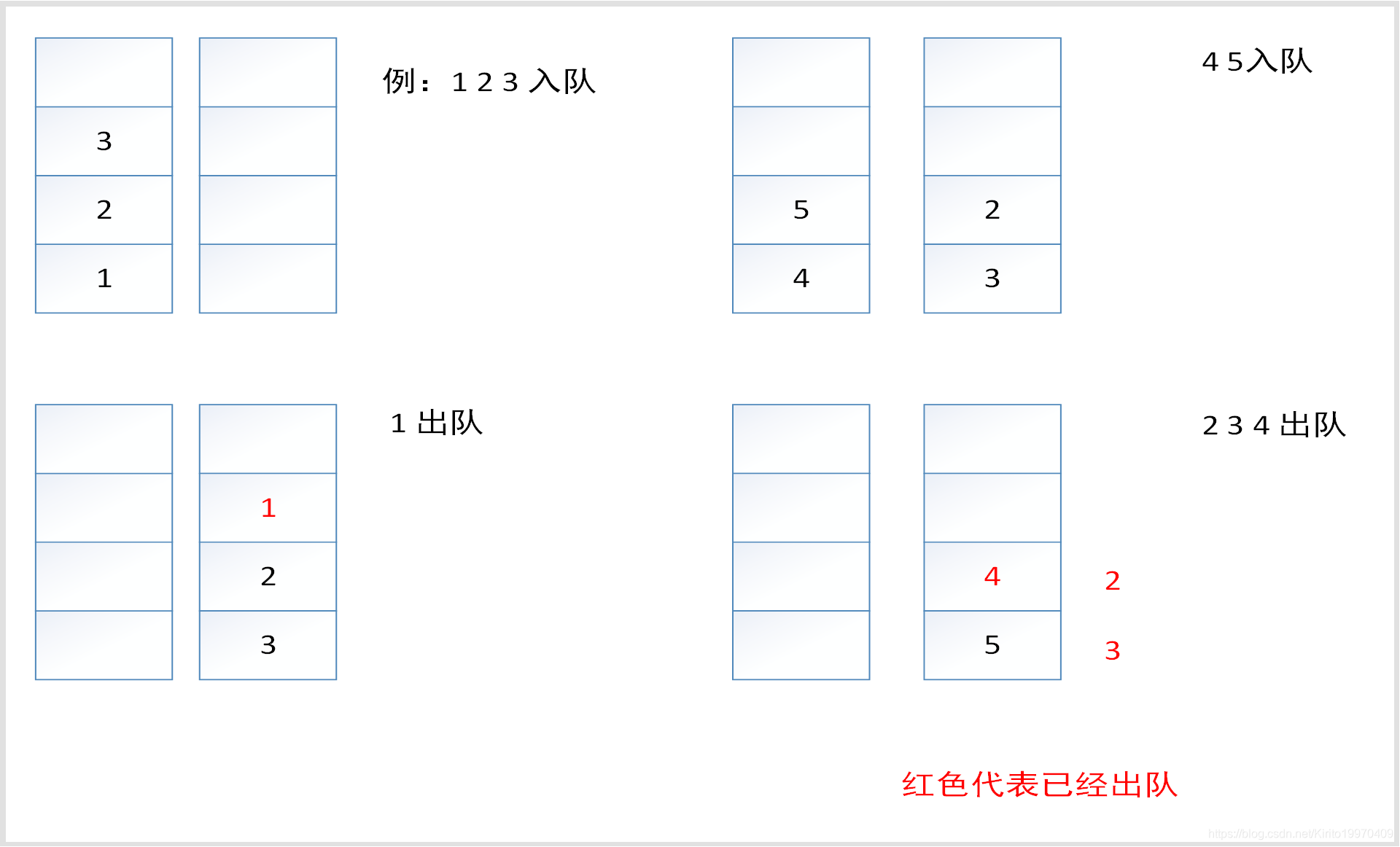
思路:栈是先进后出,队列是先进先出,所以刚好可以用两个栈来实现这种数据结构
但是在数据弹出和压入到另一个栈的时候,需要注意两个点,如果stackPush要往stackPop压入数据,
那么必须保证一次把stackPush中的数据全部压入stackPop。如果stackPop不为空,stackPush不允许向stackPop压入数据
图示:
代码:
class TwoStactQueue {
public Stack<Integer> stackPush;
public Stack<Integer> stackPop;
public TwoStactQueue() {
stackPop = new Stack<>();
stackPush = new Stack<>();
}
public void add(int num) {
stackPush.push(num);
}
public int poll() {
if (stackPop.isEmpty() && stackPush.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty");
} else if (stackPop.isEmpty()) {
while (!stackPush.empty()) {
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
return stackPop.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stackPop.isEmpty() && stackPush.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty");
} else if (stackPop.isEmpty()) {
while (!stackPush.empty()) {
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
return stackPop.peek();
}
}
测试类:
public class StackToQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoStactQueue queue = new TwoStactQueue();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
System.out.println(queue.poll() + "," + queue.poll());
queue.add(4);
queue.add(5);
System.out.println(queue.poll() + "," + queue.peek() + "," + queue.poll());
}
}
执行结果,亲测可用:
1,2
3,4,4
三:如何仅用递归函数和栈操作逆序一个栈
题目:将一个栈中的内容逆序输出,只用递归函数来实现
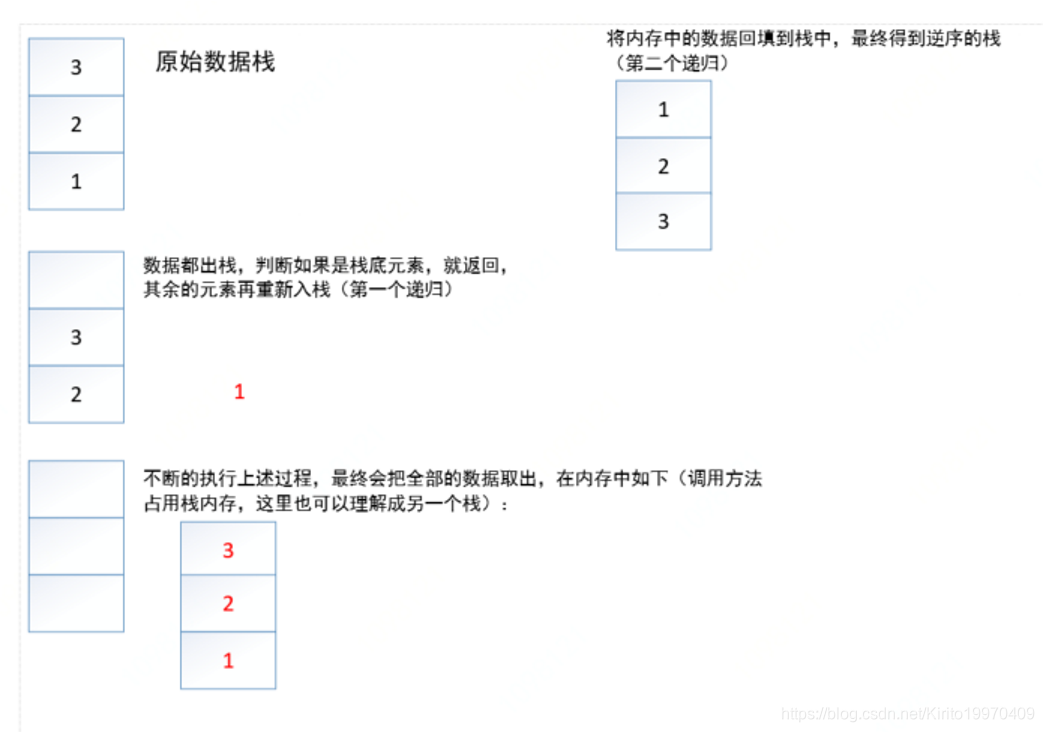
思路:可以用两个递归函数来实现
第一个递归函数用来将栈底数字取出,第二个递归函数用来将数字入栈
图示:
代码:
public class ReverStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(3);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(1);
reverse(stack);
System.out.println(stack.toString());
}
/**
* 将栈stack的栈底元素返回并移除
*
* @return 栈底元素
*/
public static int getAndRemoveLastElement(Stack<Integer> stack){
int result = stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()){
return result;
}else{
int last = getAndRemoveLastElement(stack);
stack.push(result);
return last;
}
}
public static void reverse(Stack<Integer> stack){
if(stack.isEmpty()){
return;
}
int i = getAndRemoveLastElement(stack);
reverse(stack);
stack.push(i);
}
}
测试结果,亲测可用:
[1, 2, 3]