进程:最小的数据单元
线程:最小的执行单元
一:
1:线程1

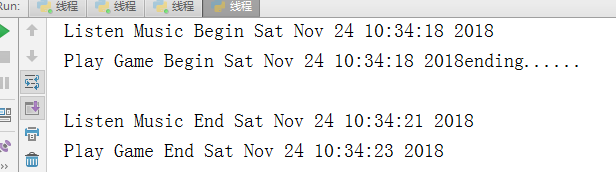
import threading #线程 import time def Music(): print("Listen Music Begin %s" %time.ctime()) time.sleep(3) print("Listen Music End %s" %time.ctime()) def Game(): print("Play Game Begin %s" %time.ctime()) time.sleep(5) print("Play Game End %s" %time.ctime()) if __name__ == '__main__': t1 = threading.Thread(target=Music) t1.start() t2 = threading.Thread(target=Game) t2.start() print("ending......")

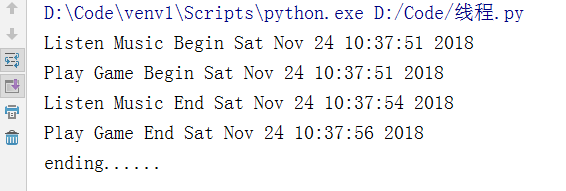
import threading #线程 import time def Music(): print("Listen Music Begin %s" %time.ctime()) time.sleep(3) print("Listen Music End %s" %time.ctime()) def Game(): print("Play Game Begin %s" %time.ctime()) time.sleep(5) print("Play Game End %s" %time.ctime()) if __name__ == '__main__': t1 = threading.Thread(target=Music) t1.start() t2 = threading.Thread(target=Game) t2.start() t1.join() t2.join() print("ending......")

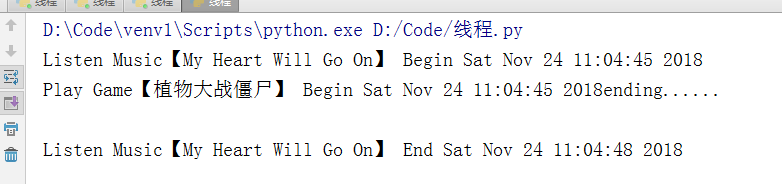
import threading #线程 import time def Music(musicName): print("Listen Music【%s】 Begin %s" %(musicName,time.ctime())) time.sleep(3) print("Listen Music【%s】 End %s" %(musicName,time.ctime())) def Game(playName): print("Play Game【%s】 Begin %s" %(playName,time.ctime())) time.sleep(5) print("Play Game【%s】 End %s" %(playName,time.ctime())) if __name__ == '__main__': t1 = threading.Thread(target=Music,args=("My Heart Will Go On",)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=Game,args=("植物大战僵尸",)) threads=[] threads.append(t1) threads.append(t2) for t in threads: t.start(); print("ending......")


import threading #线程 import time def Music(musicName): print("Listen Music【%s】 Begin %s" %(musicName,time.ctime())) time.sleep(3) print("Listen Music【%s】 End %s" %(musicName,time.ctime())) def Game(playName): print("Play Game【%s】 Begin %s" %(playName,time.ctime())) time.sleep(5) print("Play Game【%s】 End %s" %(playName,time.ctime())) t1 = threading.Thread(target=Music,args=("My Heart Will Go On",)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=Game,args=("植物大战僵尸",)) threads=[] threads.append(t1) threads.append(t2) if __name__ == '__main__': t2.setDaemon(True) for t in threads: t.start(); print("ending......")

# 多线程为什么要使用锁? # 多线程共用一个数据集,不使用可能会造成数据不准确 #1:引入多线程模块 import threading import time # 2:定义一个变量(数据集) num=100 # 3:定义一个方法,操作全局变量 def sub(): global num temp = num time.sleep(0.001) num=temp-1 # 4:创建多个线程 ts=[] for i in range(0,100): t=threading.Thread(target=sub) t.start() ts.append(t) for t in ts: t.join() print(num)
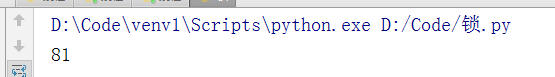

# 多线程为什么要使用锁? # 多线程共用一个数据集,不使用可能会造成数据不准确 #1:引入多线程模块 import threading import time # 2:定义一个变量(数据集) num=100 # 3:定义一个方法,操作全局变量 # 5:创建锁 lock=threading.Lock() def sub(): global num # 5.1 加锁 lock.acquire() temp = num time.sleep(0.001) num=temp-1 # 5.2 释放锁 lock.release() # 4:创建多个线程 ts=[] for i in range(0,100): t=threading.Thread(target=sub) t.start() ts.append(t) for t in ts: t.join() print(num)
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
4209603 查看本文章


