题目:
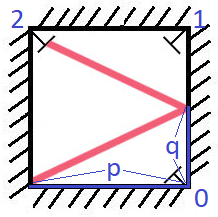
There is a special square room with mirrors on each of the four walls.Except for the southwest corner, there are receptors on each of the remaining corners, numbered
0,1, and2.
The square room has walls of lengthp, and a laser ray from the southwest corner first meets the east wall at a distanceqfrom the0th receptor.
Return the number of the receptor that the ray meets first. (It is guaranteed that the ray will meet a receptor eventually.)
Example 1:Input: p = 2, q = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: The ray meets receptor 2 the first time it gets reflected back to the left wall.
Note:
1 <= p <= 1000
0 <= q <= p
解释:
镜反面射
需要注意一个特点:光线每横向着走了p的距离,纵向必然走了q的距离(因为反射角等于入射角,三角形相似等),所以若经过上下底面镜面折射,虽然光线会到达另一边,但是由于折射前后所走的水平距离之和依旧是p,则折射前后所走的两个纵向距离之和一定是q。
如果没有上下两面镜子,光线只会在左右两面镜子来回反射,一直向上走,所以上下两面镜子的作用是改变光线的方向,如果光线到达接收器时候是向上走,则到达1/2,如果光线到达接收器是向下走,则到达0,如光线向上且向右,则到达1,如果向上且向左,则到达2,需要两个flag,up和right。
如何判断光线到达接收器?
利用上面的例子,不经过上下底面折射的情况下,p减去B点到下方镜子的距离(q)记为verticalDistanceToTarget 再除以q,如果能除尽,则光线到达接收器,否则,光线会经过上方镜子的反射,改变方向,继续向下射,如果光线到达下底面还是没有被接收器接收,则经过下方镜子反射,改变方向,继续向上走。
python代码:
class Solution(object):
def mirrorReflection(self, p, q):
"""
:type p: int
:type q: int
:rtype: int
"""
up,right=True,True
#距离上方墙壁的距离
verticalDistanceToTarget =p
while True:
verticalDistanceToTarget-=q
#到达上面
if verticalDistanceToTarget==0:
if up:
return 1 if right else 2
else:
return 0
#光线反向
if verticalDistanceToTarget<0:
#verticalDistanceToTarget还是表示距离底边的距离
verticalDistanceToTarget=p-(-verticalDistanceToTarget)
up= not up
right=not right
c++代码:
class Solution {
public:
int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
bool up=true,right=true;
int verticalDistanceToTarget=p;
while(true)
{
verticalDistanceToTarget-=q;
if (verticalDistanceToTarget==0)
if (up)
return right?1:2;
else
return 0;
if(verticalDistanceToTarget<0)
{
verticalDistanceToTarget=p-(-verticalDistanceToTarget);
up=!up;
}
right=!right;
}
}
};
总结: