版权声明:本文为博主原创学习笔记,如需转载请注明来源。 https://blog.csdn.net/SHU15121856/article/details/83865181
学习《Python3爬虫、数据清洗与可视化实战》时自己的一些实践。
书上这章开篇就说了尽量找JSON格式的数据,比较方便解析(在python里直接转换成字典),去哪儿网PC端返回的不是JSON数据,这里抓取的是它的移动端的数据。
如果是就散落在网页上,我觉得就像上篇学习的那样用BeautifulSoup这样的网页解析器去解析。
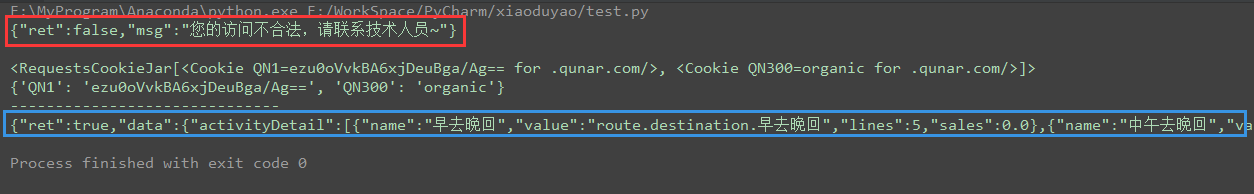
解决"您的访问不合法,请联系技术人员"
在实践这个的时候总是出现上面的问题,检查URL都没有问题,粘贴到浏览器里也可以访问。后来把浏览器缓存清空后,发现也不能访问了,但刷新之后就可以,再清空缓存又不可以…原来是cookies的问题。
这个方法书上没有提及,先访问一次获得cookies(战术访问),同时相应的cookies也推到了服务器上,再把cookies放进请求里再原样访问一次就可以了。
import requests
url = 'https://touch.dujia.qunar.com/list?modules=list,bookingInfo,activityDetail&dep=%E6%BE%B3%E9%97%A8&query=%E6%9D%AD%E5%B7%9E%E8%87%AA%E7%94%B1%E8%A1%8C&dappDealTrace=false&mobFunction=%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95%E8%87%AA%E7%94%B1%E8%A1%8C&cfrom=zyx&it=dujia_hy_destination&date=&configDepNew=&needNoResult=true&originalquery=%E6%9D%AD%E5%B7%9E%E8%87%AA%E7%94%B1%E8%A1%8C&limit=0,16&includeAD=true&qsact=search'
proxies = {
# 'https': 'https://183.129.207.73:14823',
'http:': 'http://61.135.217.7:80'
}
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0; Nexus 5 Build/MRA58N) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/67.0.3396.99 Mobile Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies)
# 第一次访问是失败的
print(response.text)
# 但取到cookie
print(response.cookies)
cookies = requests.utils.dict_from_cookiejar(response.cookies)
print(cookies)
print('-'*30)
# 再次访问就成功了
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies, cookies=cookies)
print(response.text)
运行结果:
实践代码
这里用了fake_useragent库提供伪造的随机的用户代理,另外可以去爬取西刺代理本身提供的代理,构建自己的代理池,然后每次的ip也从代理池里随机取,这样就更保险了。
import requests
import urllib.request # 这里注意不要引成了urllib,否则找不到urllib.request
import fake_useragent
'''
去哪儿网 https://touch.dujia.qunar.com/
西刺代理 http://www.xicidaili.com/
'''
dep_list = [] # 出发地列表
# 用来生成随机的User-Agent
# 禁用服务器缓存,以解决'fake_useragent.errors.FakeUserAgentError: Maximum amount of retries reached'
ua = fake_useragent.UserAgent(use_cache_server=False)
# 代理池
proxies = {
# 'https': 'https://183.129.207.73:14823',
'http:': 'http://124.235.135.166:80'
}
# 生成出发地列表,直接取用户在选择出发地时页面上的数据即可
def gen_dep():
global dep_list
url = 'https://touch.dujia.qunar.com/depCities.qunar'
response = requests.get(url)
dep_dict = response.json()
for dep_item in dep_dict['data']: # 这里是a,b,c...开头字母
for dep in dep_dict['data'][dep_item]: # 每个开头字母又对应了一个列表
dep_list.append(dep)
# 根据不同的出发地获取对应的目的地列表,对每组合理的出发地和目的地寻找产品并存储(存储略,这里采样输出)
# (在自由行中,用户先选择出发地(或者识别当前位置的城市),然后点击搜索框时会出现不一样的目录树)
# (实际上大部分内容是一样的,主要是[周边]不一样)
def gen_arr_and_sto_product():
global dep_list, ua, proxies
# 为了速度,控制循环次数,仅实现功能
i = j = k = 0
for dep in dep_list: # 对于每个出发地
i += 1
if i > 2:
break
# 对应于该出发地的目的地集合(目的地用出发地请求得来,可能存在重复,用集合自动去重)
attr_set = set() # 每个出发地都对应一个目的地集合
# 对每个出发地进行URL编码,再填充到相应的参数位置上去,注意url里去掉callback参数
url = 'https://touch.dujia.qunar.com/golfz/sight/arriveRecommend?dep={}&exclude=&extensionImg=255,175'.format(
urllib.request.quote(dep))
response = requests.get(url, headers={'User-Agent': ua.random}, proxies=proxies)
arrv_dict = response.json()
for data_it in arrv_dict['data']: # 这里得到的是列表中的一项项dict
j += 1
if j > 4:
break
for subMod_it in data_it['subModules']: # 该dict里面subModules列表里的每一项
k += 1
if k > 6:
break
for item_it in subMod_it['items']: # 该项的item字段所示列表的每一项
# print(item_it['query']) # 取其query字段
attr_set.add(item_it['query']) # 添加到目的地集合中
# 接下来获取该出发地dep到若干目的地attr_set的若干产品
# (这也符合用户的行为:先选择出发地,再选择目的地,然后看到若干产品)
for attr in attr_set:
url = 'https://touch.dujia.qunar.com/list?modules=list,bookingInfo,activityDetail&dep={}&query={}&dappDealTrace=false&mobFunction={}&cfrom=zyx&it=dujia_hy_destination&date=&configDepNew=&needNoResult=true&originalquery={}&limit=0,16&includeAD=true&qsact=search'.format(
urllib.request.quote(dep), urllib.request.quote(attr + '自由行'),
urllib.request.quote('扩展自由行'), urllib.request.quote(attr + '自由行')
)
# 两次访问的伪装头需要一致,所以记录下来这次的随机头
now_ua = ua.random
# 这次访问是失败的,但可以把cookies推给服务器,同时自己的这份也能从response中取到
response = requests.get(url, headers={'User-Agent': now_ua}, proxies=proxies)
# 再次访问,把cookies放进去
cookies = requests.utils.dict_from_cookiejar(response.cookies)
response = requests.get(url, headers={'User-Agent': now_ua}, proxies=proxies, cookies=cookies)
# print(response.text)
try:
route_count = int(response.json()['data']['limit']['routeCount']) # 产品数
except:
continue # 没有这条路径说明对应的出发地到目的地没有产品,直接跳过看下一个目的地
# 用户下划时Ajax请求获取新的产品,观察发现受url中参数index=a,b影响
# 其中a表示从哪个产品开始,b表示向后取多少产品
for limit in range(0, route_count, 16): # 观察发现用户下划时每次取了16个
url = 'https://touch.dujia.qunar.com/list?modules=list%2CbookingInfo%2CactivityDetail&dep={}&query={}&dappDealTrace=false&mobFunction={}&cfrom=zyx&it=dujia_hy_destination&date=&configDepNew=&needNoResult=true&originalquery={}&limit={},16&qsact=scroll'.format(
urllib.request.quote(dep), urllib.request.quote(attr + '自由行'),
urllib.request.quote('扩展自由行'), urllib.request.quote(attr), limit
)
# 一样的流程,先'战术访问'拿到cookies,再访问一次
now_ua = ua.random
response = requests.get(url, headers={'User-Agent': now_ua}, proxies=proxies)
cookies = requests.utils.dict_from_cookiejar(response.cookies)
response = requests.get(url, headers={'User-Agent': now_ua}, proxies=proxies, cookies=cookies)
# 这里不妨输出每个产品的到达列表和住宿情况看一下
results = response.json()['data']['list']['results']
for i, it in enumerate(results):
# 为了快速看结果,每5个输出一个就好了(每组16个也就是只输出0号5号10号15号)
if i % 5 != 0:
continue
print(it['arrive'], it['accomInclude'])
# 存储功能略,和之前用MongoDB一样
if __name__ == '__main__':
gen_dep()
# print(dep_list)
gen_arr_and_sto_product()
运行结果:

书上提及的多进程爬虫
其实就是用python的进程池,开多个进程执行某个函数,任务要处理的若干输入数据将被分配给它们执行。
这里干脆就用上篇的有道词典翻译的爬虫为例记录一下,爬这个去哪网旅游数据的也是一样的做法。
from multiprocessing import Pool
import k2 # 那个有道词典翻译的py文件名
words = '''
一
二
三
四
五
六
七
八
九
十
十一
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
pool = Pool()
pool.map(k2.get_translate_data, words.split())
运行结果:
a
The second
three
four
five
seven
six
eight
nine
eleven
ten