实验十一 集合
实验时间 2018-11-8
一 理论知识
一般将数据结构分为两大类:线性数据结构和非线性数据结构。线性数据结构:线性表、栈、队列、串、数组和文件。非线性数据结构:树和图。
线性表按其存储结构可分为顺序表和链表;用顺序存储结构存储的线性表称为顺序表;顺序表将线性表中的数据元素依次存放在某个存储区域中。一维数组就是用顺序方式存储的线性表。用链式存储结构存储的线性表称为链表。
栈(Stack)也是一种特殊的线性表,是一种后进先出 (LIFO)的结构。栈是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除运算的线性表,表尾称为栈顶(top),表头称为栈底(bottom)。栈的物理存储可以用顺序存储结构,也可以用链式存储结构。
队列(Queue)是限定所有的插入只能在表的一端进行 ,而所有的删除都在表的另一端进行的线性表。表中允许插入的一端称为队尾(Rear),允许删除的一端称为队头(Front)。队列的操作是按先进先出(FIFO)的原则进行的。队列的物理存储可以用顺序存储结构,也可以用链式存储结构。
散列表又称为哈希表。散列表算法的基本思想是:以结点的关键字为自变量,通过一定的函数关系(散列函数)计算出对应的函数值,以这个值作为该结点存储在散列表中的地址。当散列表中的元素存放太满,就必须进行再散列,将产生一个新的散列表,所有元素存放到新的散列表中,原先的散列表将被删除。在Java语言中,通过负载因子(load factor)来决定何时对散列表进行再散列。负载因子越高 (越接近1.0),内存的使用效率越高,元素的寻找时间越长。负载因子越低 (越接近0.0),元素的寻找时间越短,内存浪费越多。HashSet类的缺省负载因子是0.75。
JAVA的集合框架实现对各种数据结构的封装,以降低对数据管理与处理的难度。所谓框架就是一个类库的集合,框架中包含很多超类,编程者创建这些超类的子类可较方便的设计设计程序所需的类。
集合框架:JAVA集合类库的统一架构。
集合类的作用:Java的集合类提供了一些基本数据结构的支持。
集合类的使用: Java的集合类包含在java.util包中。
集合类的特点一:只容纳对象。注意:数组可以容纳基本数据类型数据和对象。如果集合类中想使用基本数据类型,又想利用集合类的灵活性,可以把基本数据类型数据封装成该数据类型的包装器对象,然后放入集合中处理。
特点二:集合类容纳的对象都是Object类的实例,一旦把一个对象置入集合类中,它的类信息将丢失,这样设计的目的是为了集合类的通用性。因为Object类是所有类的祖先,所以可以在这些集合中存放任何类的对象而不受限制,但在使用集合成员之前必须对它重新造型。
Vector类类似长度可变的数组。Vector中只能存放对象。Vector的元素通过下标进行访问。 Vector类关键属性:capacity表示集合最多能容纳的元素个数。capacityIncrement表示每次增加多少容量。size表示集合当前元素个数。
Stack类是Vector的子类。Stack类描述堆栈数据结构,即LIFO。
Hashtable通过键来查找元素。Hashtable用散列码(hashcode)来确定键。所有对象都有一个散列码,可以通过Object类的hashCode()方法获得。
集合框架中的基本接口:Collection:集合层次中的根接口,JDK未提供这个接口的直接实现类。
Set:不能包含重复的元素。对象可能不是按存放的次序存放,也就是说不能像数组一样按索引的方式进行访问,SortedSet是一个按照升序排列元素的Set。
List:是一个有序的集合,可以包含重复的元素。提供了按索引访问的方式。
Map:包含了key-value对。Map不能包含重复的key。
SortedMap是一个按照升序排列key的Map。
Collection接口:构造类集框架的基础。
List的明显特征是它的元素都有一个确定的顺序。实现它的类有ArrayList和LinkedList。ArrayList中的元素在内存中是顺序存储的。LinkedList中的元素在内存中是以链表方式存储的。
ArrayList:可以将其看作是能够自动增长容量的数组。利用ArrayList的toArray()返回一个数组。Arrays.asList()返回一个列表。LinkedList是采用双向循环链表实现的。利用LinkedList实现栈(stack)、队列(queue)、双向队列 (double-ended queue )。ArrayList底层采用数组完成,而LinkedList则是以一般的双向链表(double-linked list)完成,其内每个对象除了数据本身外,还有两个引用,分别指向前一个元素和后一个元素。如果经常在 List 中进行插入和删除操作,应该使用LinkedList,否则,使用ArrayList将更加快速。
Set中的元素必须唯一。添加到Set中的对象元素必须定义equals方法,以提供算法来判断欲添加进来的对象是否与已经存在的某对象相等,从而建立对象的唯一性。实现Set接口的类有HashSet,TreeSet。
TreeSet是一个有序集合,TreeSet中元素将按照升序排列,缺省是按照自然顺序进行排列,意味着TreeSet中元素要实现Comparable接口。可以在构造TreeSet对象时,传递实现了 Comparator接口的比较器对象。HashSet是基于Hash算法实现的,其性能通常都优于TreeSet。通常使用HashSet,需要排序的功能时,使用TreeSet。
Map接口用来维持很多“键-值”对,以便通过键来查找相应的值。HashMap基于散列表实现(替代Hashtable)。TreeMap在一个二叉树的基础上实现。
映射(map)是一个存储关键字和值的关联或关键字/值对的对象。给定一个关键字,可以得到它的值。关键字和值都是对象。关键字必须是唯一的。但值是可以被复制的。
Map接口映射唯一关键字到值。关键字(key)是以后用于检索值的对象。给定一个关键字和一个值,可以存储这个值到一个Map对象中。当这个值被存储以后,就可以使用它的关键字来检索它
Map循环使用两个基本操作:get( )和put( )。使用 put( )方法可以将一个指定了关键字和值的值加入映射。为了得到值,可以通过将关键字作为参数来调用 get( )方法。调用返回该值。
Map接口的实现类主要有HashMap,TreeMap,Hashtable,Properties。HashMap对key进行散列。TreeMap按照key进行排序。和Set类似,HashMap的速度通常都比TreeMap快,只有在需要排序的功能的时候,才使用TreeMap。
二、实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API;
(2) 了解java集合框架体系组成;
(3) 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
(4) 了解HashSet类、TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
(5)了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API;
(6) 结对编程(Pair programming)练习,体验程序开发中的两人合作。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API;
(2) 了解java集合框架体系组成;
(3) 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
(4) 了解HashSet类、TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
(5)了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API;
(6) 结对编程(Pair programming)练习,体验程序开发中的两人合作。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第9章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 使用JDK命令运行编辑、运行以下三个示例程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API。
| //示例程序1 import java.util.Vector; class Cat { private int catNumber; Cat(int i) { catNumber = i; } void print() { System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber); } } class Dog { private int dogNumber; Dog(int i) { dogNumber = i; } void print() { System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber); } } public class CatsAndDogs { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector cats = new Vector(); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) cats.addElement(new Cat(i)); cats.addElement(new Dog(7)); for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++) ((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print(); } } |
| //示例程序2 import java.util.*; public class Stacks { static String[] months = { "1", "2", "3", "4" }; public static void main(String[] args) { Stack stk = new Stack(); for (int i = 0; i < months.length; i++) stk.push(months[i]); System.out.println(stk); System.out.println("element 2=" + stk.elementAt(2)); while (!stk.empty()) System.out.println(stk.pop()); } } |
| //示例程序3 import java.util.*; class Counter { int i = 1; public String toString() { return Integer.toString(i); } } public class Statistics { public static void main(String[] args) { Hashtable ht = new Hashtable(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { Integer r = new Integer((int) (Math.random() * 20)); if (ht.containsKey(r)) ((Counter) ht.get(r)).i++; else ht.put(r, new Counter()); } System.out.println(ht); } } |
示例程序一:
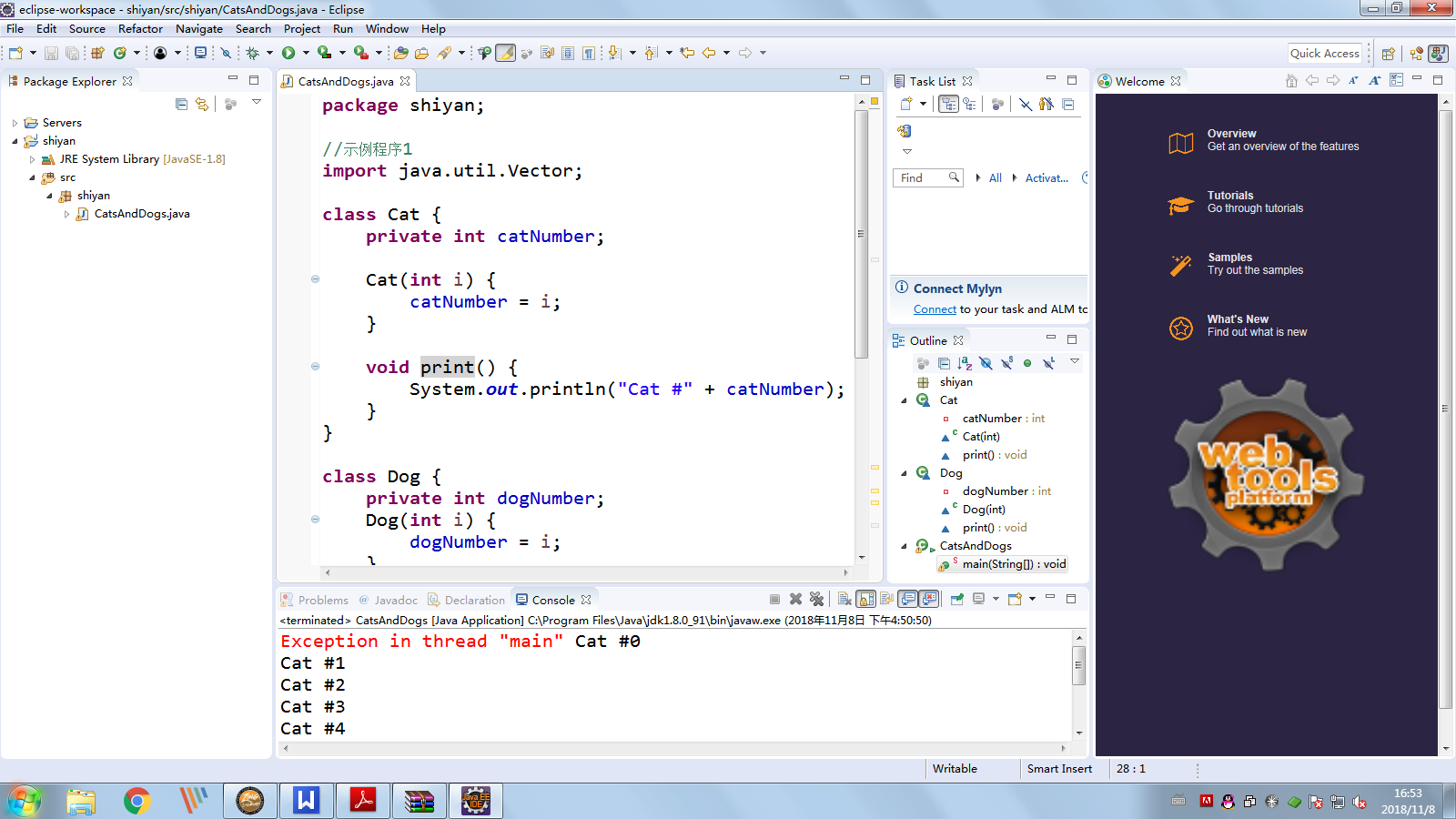
修改程序错误后如下图
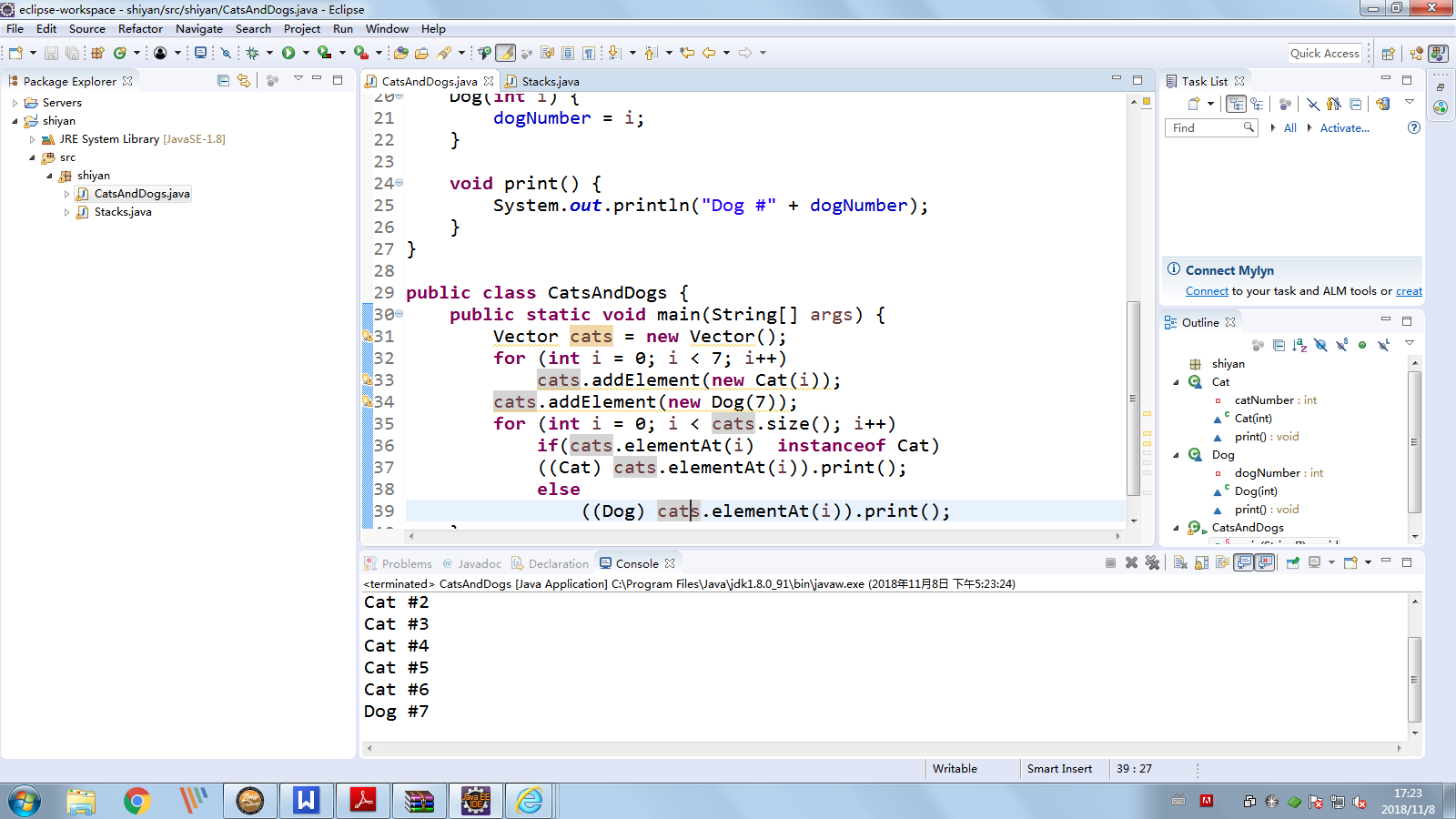

package shiyan; //示例程序1 import java.util.Vector; class Cat { private int catNumber; Cat(int i) { catNumber = i; } void print() { System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber); } } class Dog { private int dogNumber; Dog(int i) { dogNumber = i; } void print() { System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber); } } public class CatsAndDogs { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector cats = new Vector();//生产cats类集合 for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) cats.addElement(new Cat(i)); cats.addElement(new Dog(7)); for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++) //判断是否为cats类型的数据,如果是按Cat输出 if(cats.elementAt(i) instanceof Cat) ((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print(); //若不是cats类型的数据,按Dog输出 else ((Dog) cats.elementAt(i)).print(); } }
示例程序2:
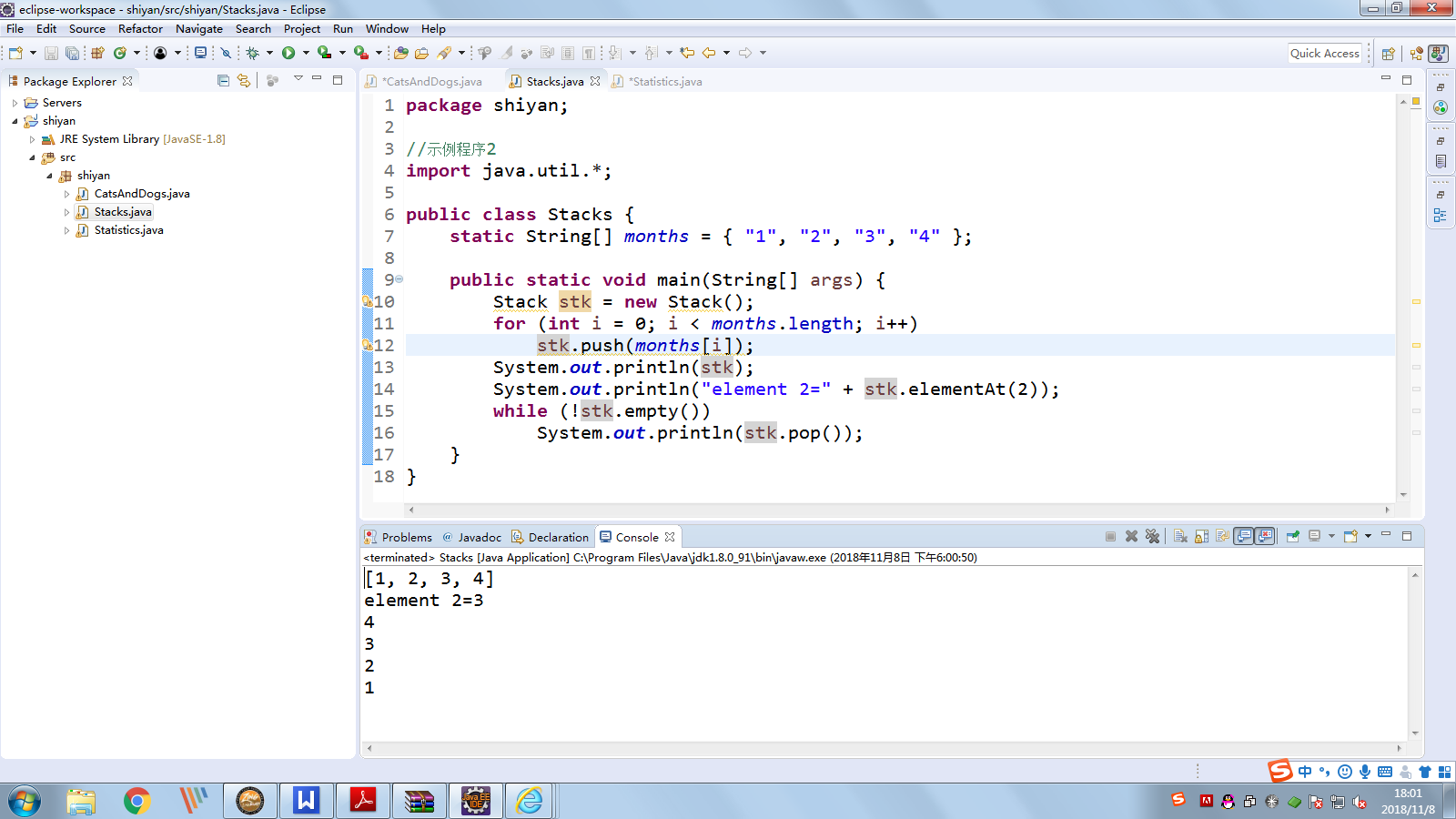

package shiyan; //示例程序2 import java.util.*; public class Stacks { static String[] months = { "1", "2", "3", "4" }; public static void main(String[] args) { Stack stk = new Stack(); for (int i = 0; i < months.length; i++) stk.push(months[i]);//把项压入栈顶 System.out.println(stk); System.out.println("element 2=" + stk.elementAt(2)); while (!stk.empty())//当栈顶元素不为空时,移除栈顶对象并作为此函数的值返回对象 System.out.println(stk.pop()); } }
示例程序3
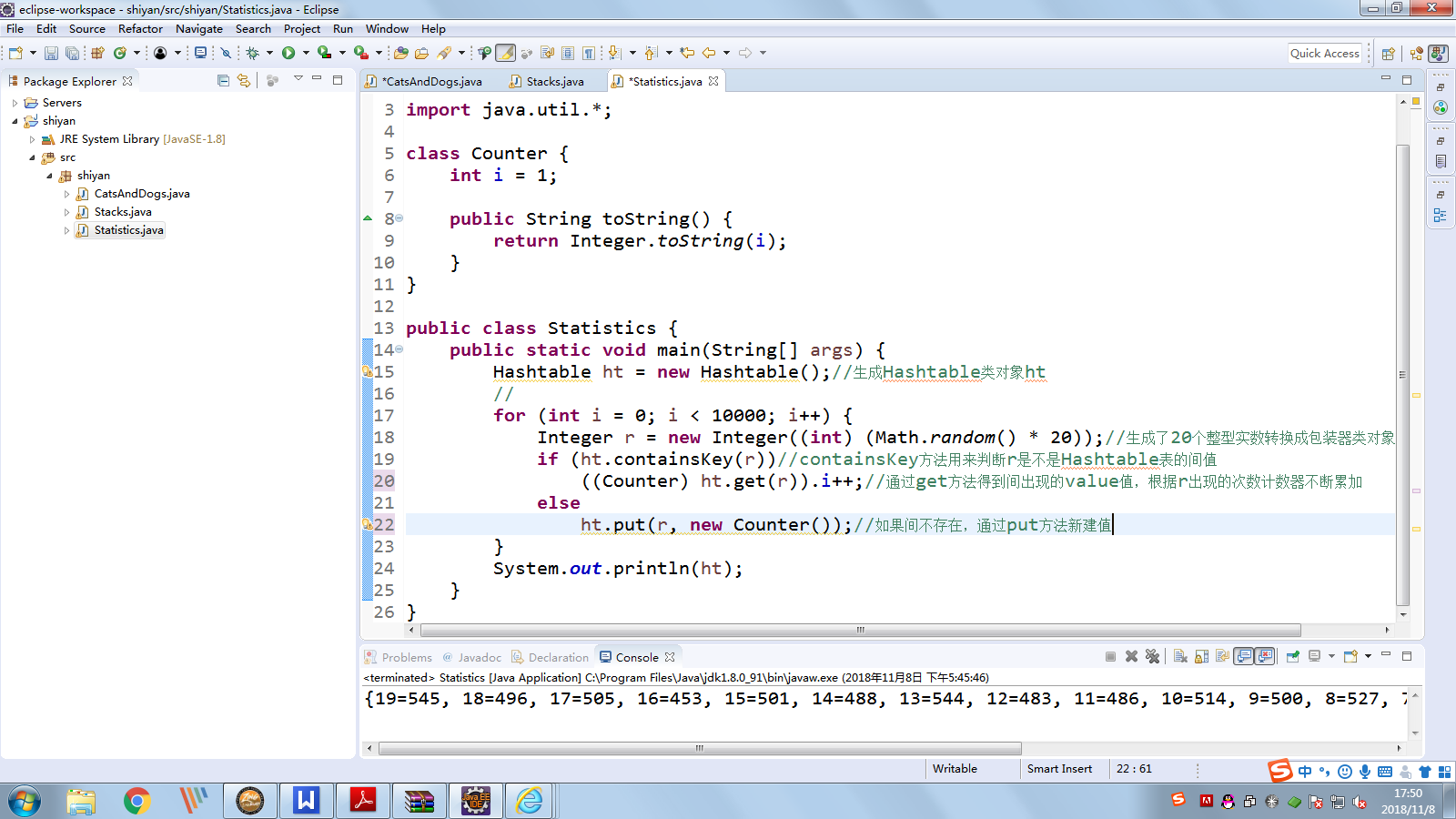

package shiyan; import java.util.*; class Counter { int i = 1; public String toString() { return Integer.toString(i); } } public class Statistics { public static void main(String[] args) { Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();//生成Hashtable类对象ht // for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { Integer r = new Integer((int) (Math.random() * 20));//生成了20个整型实数转换成包装器类对象后用r去引用 if (ht.containsKey(r))//containsKey方法用来判断r是不是Hashtable表的间值 ((Counter) ht.get(r)).i++;//通过get方法得到间出现的value值,根据r出现的次数计数器不断累加 else ht.put(r, new Counter());//如果间不存在,通过put方法新建值 } System.out.println(ht); } }
测试程序2:
l 使用JDK命令编辑运行ArrayListDemo和LinkedListDemo两个程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
| import java.util.*; public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); // Add lots of elements to the ArrayList... al.add(new Integer(11)); al.add(new Integer(12)); al.add(new Integer(13)); al.add(new String("hello")); // First print them out using a for loop. System.out.println("Retrieving by index:"); for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) { System.out.println("Element " + i + " = " + al.get(i)); } } } |
| import java.util.*; public class LinkedListDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { LinkedList l = new LinkedList(); l.add(new Object()); l.add("Hello"); l.add("zhangsan"); ListIterator li = l.listIterator(0); while (li.hasNext()) System.out.println(li.next()); if (l.indexOf("Hello") < 0) System.err.println("Lookup does not work"); else System.err.println("Lookup works"); } } |
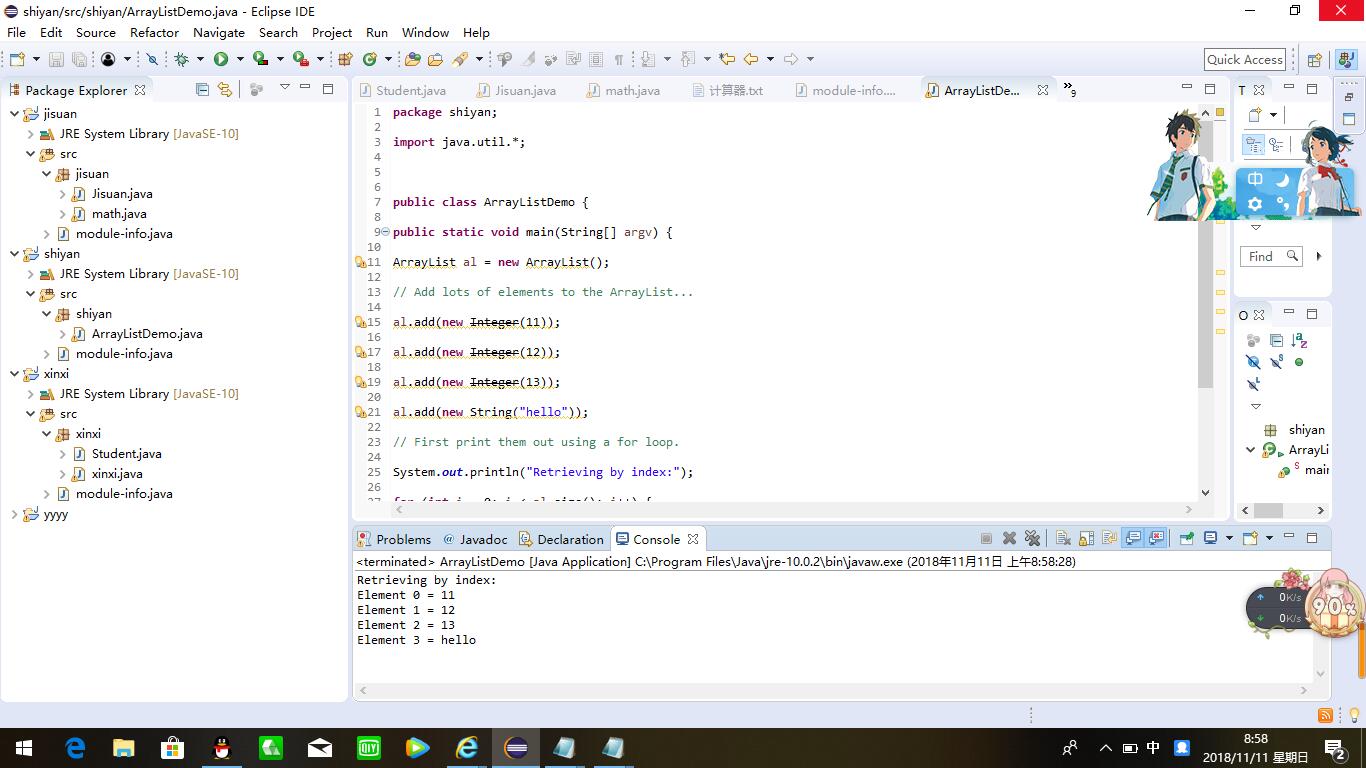

package shiyan; import java.util.*; public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); // Add lots of elements to the ArrayList... al.add(new Integer(11)); al.add(new Integer(12)); al.add(new Integer(13)); al.add(new String("hello")); // First print them out using a for loop. System.out.println("Retrieving by index:"); for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) { System.out.println("Element " + i + " = " + al.get(i)); } } }


package shiyan; import java.util.*; public class LinkedListDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { LinkedList l = new LinkedList(); l.add(new Object()); l.add("Hello"); l.add("zhangsan"); ListIterator li = l.listIterator(0); while (li.hasNext()) System.out.println(li.next()); if (l.indexOf("Hello") < 0) System.err.println("Lookup does not work"); else System.err.println("Lookup works"); } }
l 在Elipse环境下编辑运行调试教材360页程序9-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
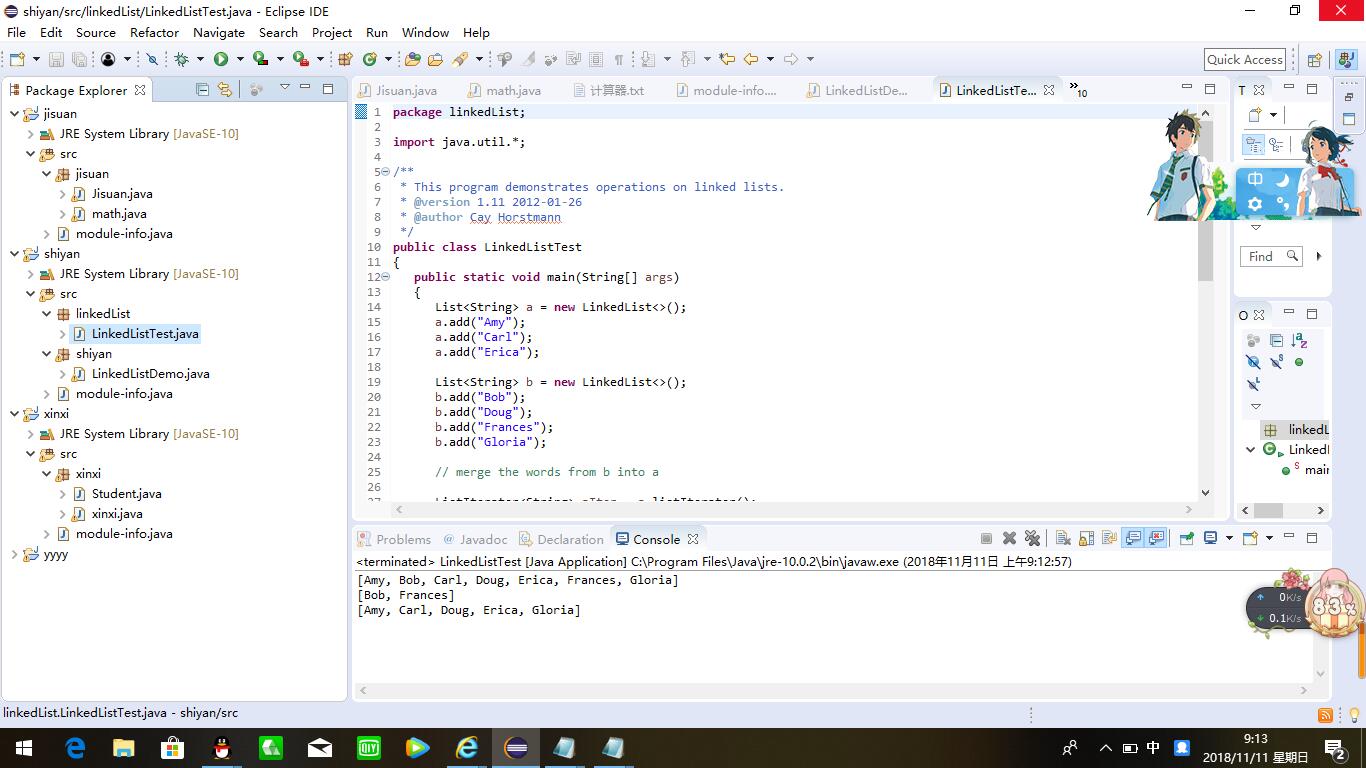

package linkedList; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates operations on linked lists. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class LinkedListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> a = new LinkedList<>(); a.add("Amy"); a.add("Carl"); a.add("Erica"); List<String> b = new LinkedList<>(); b.add("Bob"); b.add("Doug"); b.add("Frances"); b.add("Gloria"); // merge the words from b into a ListIterator<String> aIter = a.listIterator(); Iterator<String> bIter = b.iterator(); while (bIter.hasNext()) { if (aIter.hasNext()) aIter.next(); aIter.add(bIter.next()); } System.out.println(a); // remove every second word from b bIter = b.iterator(); while (bIter.hasNext()) { bIter.next(); // skip one element if (bIter.hasNext()) { bIter.next(); // skip next element bIter.remove(); // remove that element } } System.out.println(b); // bulk operation: remove all words in b from a a.removeAll(b); System.out.println(a); } }
l 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
测试程序3:
l 运行SetDemo程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
| import java.util.*; public class SetDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { HashSet h = new HashSet(); //也可以 Set h=new HashSet() h.add("One"); h.add("Two"); h.add("One"); // DUPLICATE h.add("Three"); Iterator it = h.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } } |
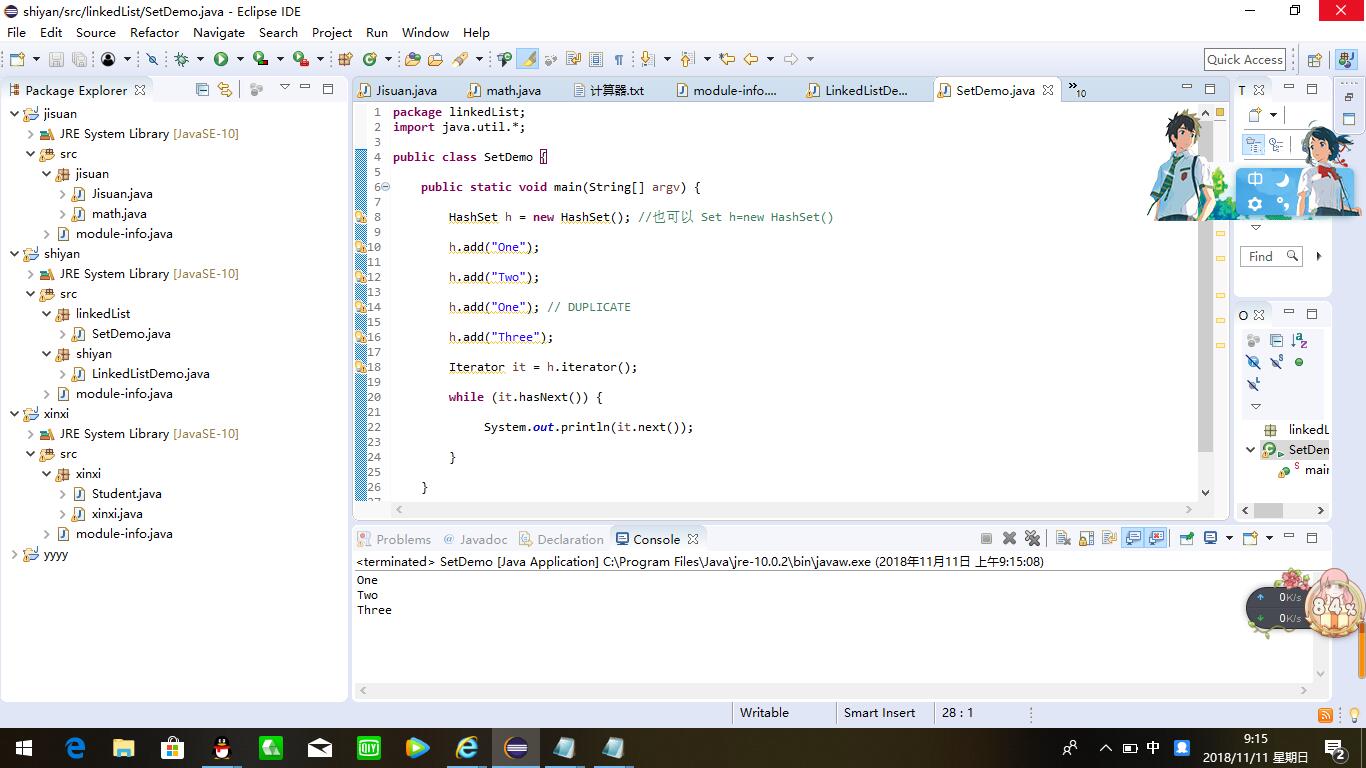

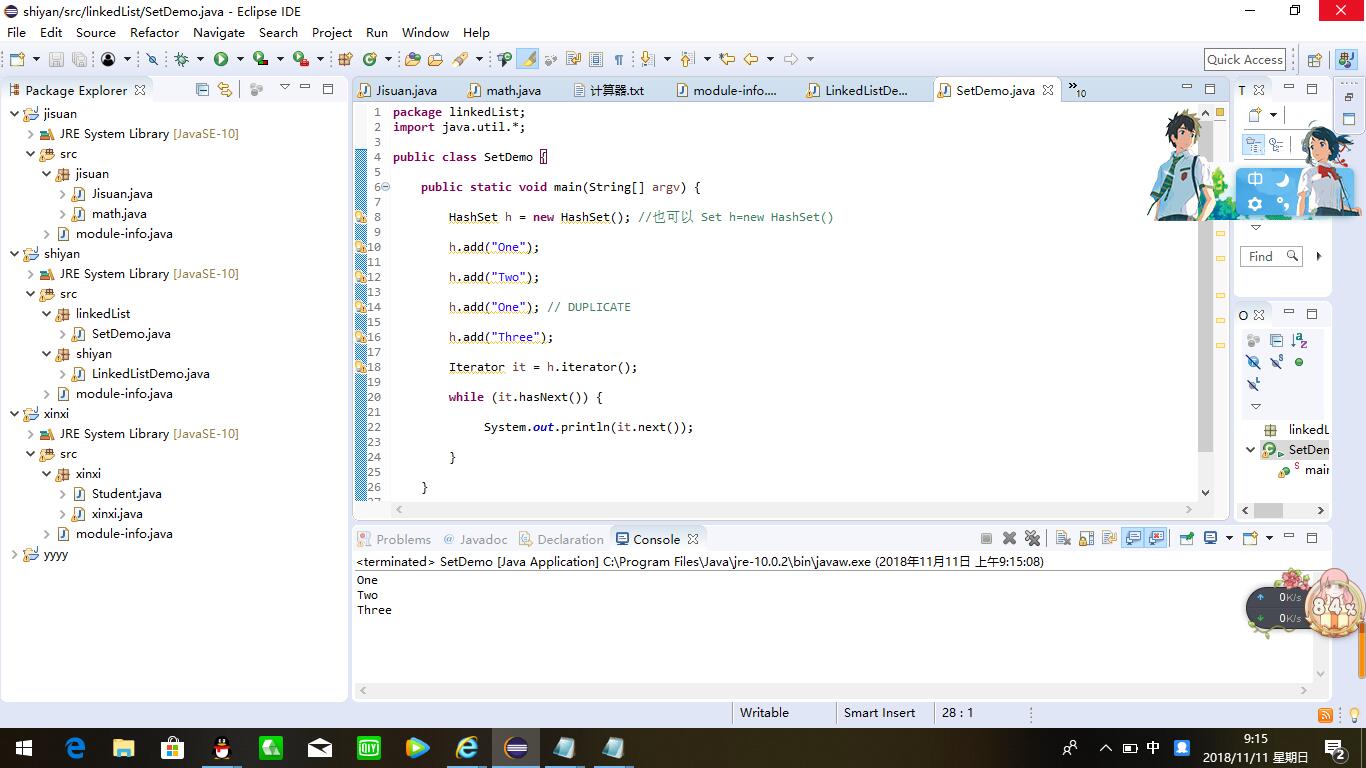
package linkedList; import java.util.*; public class SetDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { HashSet h = new HashSet(); //也可以 Set h=new HashSet() h.add("One"); h.add("Two"); h.add("One"); // DUPLICATE h.add("Three"); Iterator it = h.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材365页程序9-2,结合运行结果理解程序;了解HashSet类的用途及常用API。

package set; import java.util.*; /** * This program uses a set to print all unique words in System.in. * @version 1.12 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<String> words = new HashSet<>(); // HashSet implements Set long totalTime = 0; try (Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in)) { while (in.hasNext()) { String word = in.next(); long callTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); words.add(word); callTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - callTime; totalTime += callTime; } } Iterator<String> iter = words.iterator(); for (int i = 1; i <= 20 && iter.hasNext(); i++) System.out.println(iter.next()); System.out.println(". . ."); System.out.println(words.size() + " distinct words. " + totalTime + " milliseconds."); } }
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材367页-368程序9-3、9-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;了解TreeSet类的用途及常用API。


package treeSet; import java.util.*; /** * This program sorts a set of item by comparing their descriptions. * @version 1.12 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class TreeSetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { SortedSet<Item> parts = new TreeSet<>(); parts.add(new Item("Toaster", 1234)); parts.add(new Item("Widget", 4562)); parts.add(new Item("Modem", 9912)); System.out.println(parts); NavigableSet<Item> sortByDescription = new TreeSet<>( Comparator.comparing(Item::getDescription)); sortByDescription.addAll(parts); System.out.println(sortByDescription); } }

package treeSet; import java.util.*; /** * An item with a description and a part number. */ public class Item implements Comparable<Item> { private String description; private int partNumber; /** * Constructs an item. * * @param aDescription * the item's description * @param aPartNumber * the item's part number */ public Item(String aDescription, int aPartNumber) { description = aDescription; partNumber = aPartNumber; } /** * Gets the description of this item. * * @return the description */ public String getDescription() { return description; } public String toString() { return "[description=" + description + ", partNumber=" + partNumber + "]"; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { if (this == otherObject) return true; if (otherObject == null) return false; if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; Item other = (Item) otherObject; return Objects.equals(description, other.description) && partNumber == other.partNumber; } public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(description, partNumber); } public int compareTo(Item other) { int diff = Integer.compare(partNumber, other.partNumber); return diff != 0 ? diff : description.compareTo(other.description); } }
测试程序4:
l 使用JDK命令运行HashMapDemo程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
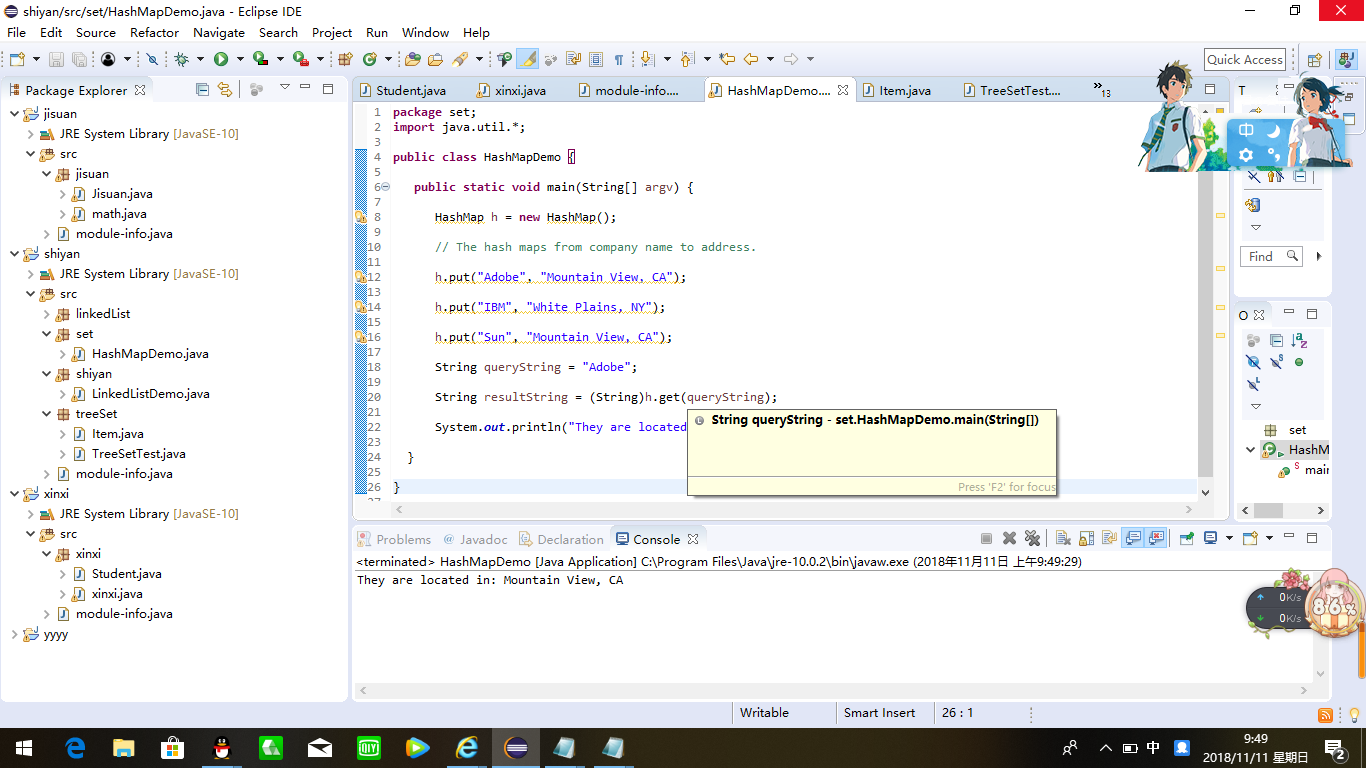
| import java.util.*; public class HashMapDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { HashMap h = new HashMap(); // The hash maps from company name to address. h.put("Adobe", "Mountain View, CA"); h.put("IBM", "White Plains, NY"); h.put("Sun", "Mountain View, CA"); String queryString = "Adobe"; String resultString = (String)h.get(queryString); System.out.println("They are located in: " + resultString); } } |
l

package set; import java.util.*; public class HashMapDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { HashMap h = new HashMap(); // The hash maps from company name to address. h.put("Adobe", "Mountain View, CA"); h.put("IBM", "White Plains, NY"); h.put("Sun", "Mountain View, CA"); String queryString = "Adobe"; String resultString = (String)h.get(queryString); System.out.println("They are located in: " + resultString); } }
在Elipse环境下调试教材373页程序9-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API。
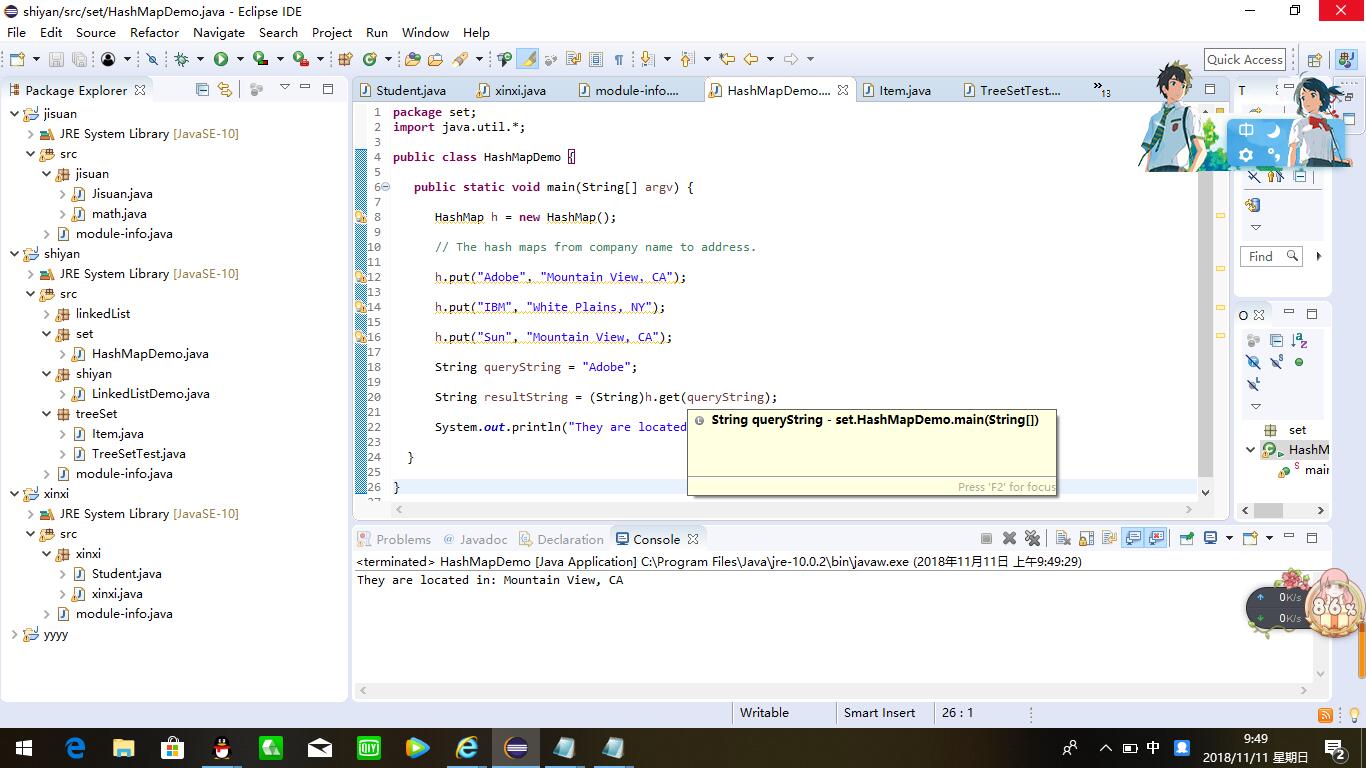

package map; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the use of a map with key type String and value type Employee. * @version 1.12 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class MapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Employee> staff = new HashMap<>(); staff.put("144-25-5464", new Employee("Amy Lee")); staff.put("567-24-2546", new Employee("Harry Hacker")); staff.put("157-62-7935", new Employee("Gary Cooper")); staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Cruz")); // print all entries System.out.println(staff); // remove an entry staff.remove("567-24-2546"); // replace an entry staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Miller")); // look up a value System.out.println(staff.get("157-62-7935")); // iterate through all entries staff.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println("key=" + k + ", value=" + v)); } }

package map; /** * A minimalist employee class for testing purposes. */ public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; /** * Constructs an employee with $0 salary. * @param n the employee name */ public Employee(String name) { this.name = name; salary = 0; } public String toString() { return "[name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]"; } }
实验2:结对编程练习:
l 关于结对编程:以下图片是一个结对编程场景:两位学习伙伴坐在一起,面对着同一台显示器,使用着同一键盘,同一个鼠标,他们一起思考问题,一起分析问题,一起编写程序。
l 关于结对编程的阐述可参见以下链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/08/07/2130332.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pair_programming
l 对于结对编程中代码设计规范的要求参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/11/20/2255971.html
以下实验,就让我们来体验一下结对编程的魅力。
l 确定本次实验结对编程合作伙伴;杨蓉庆
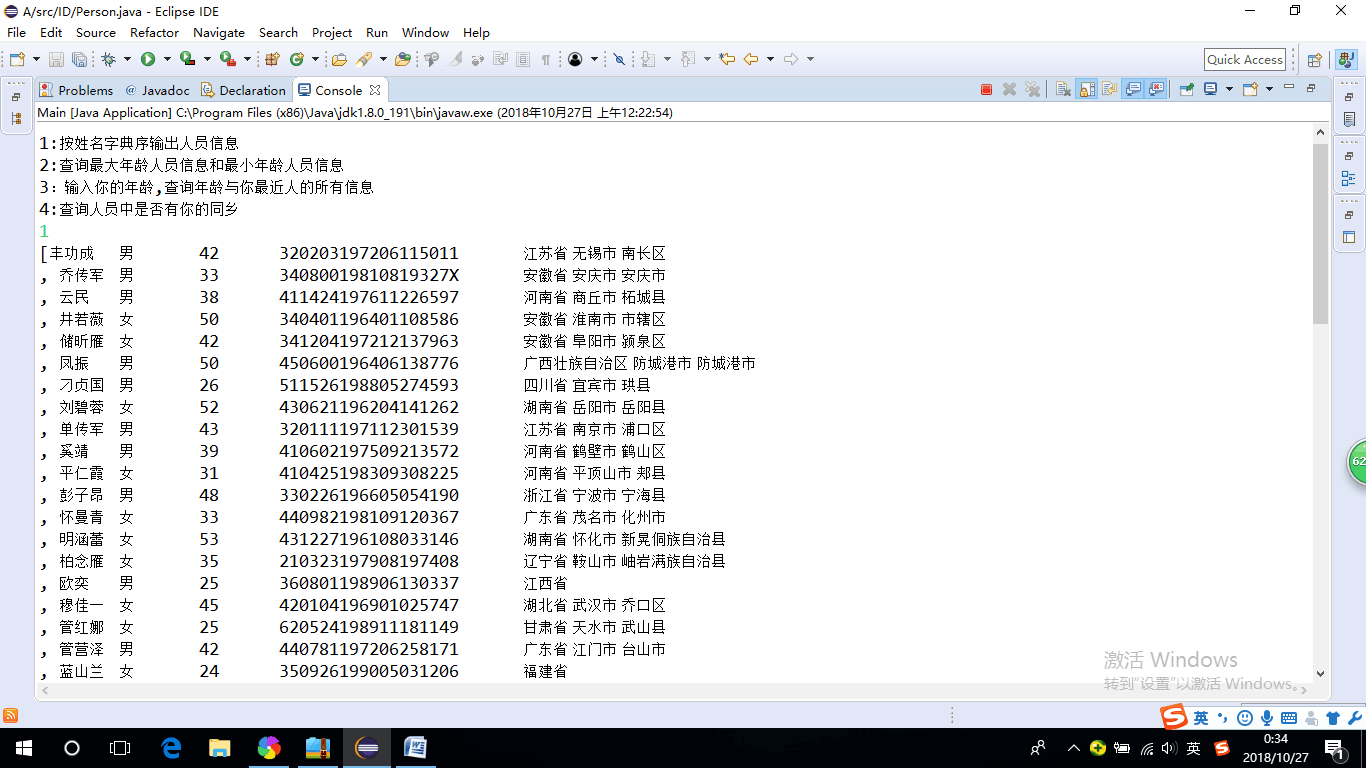
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验九编程练习1,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
l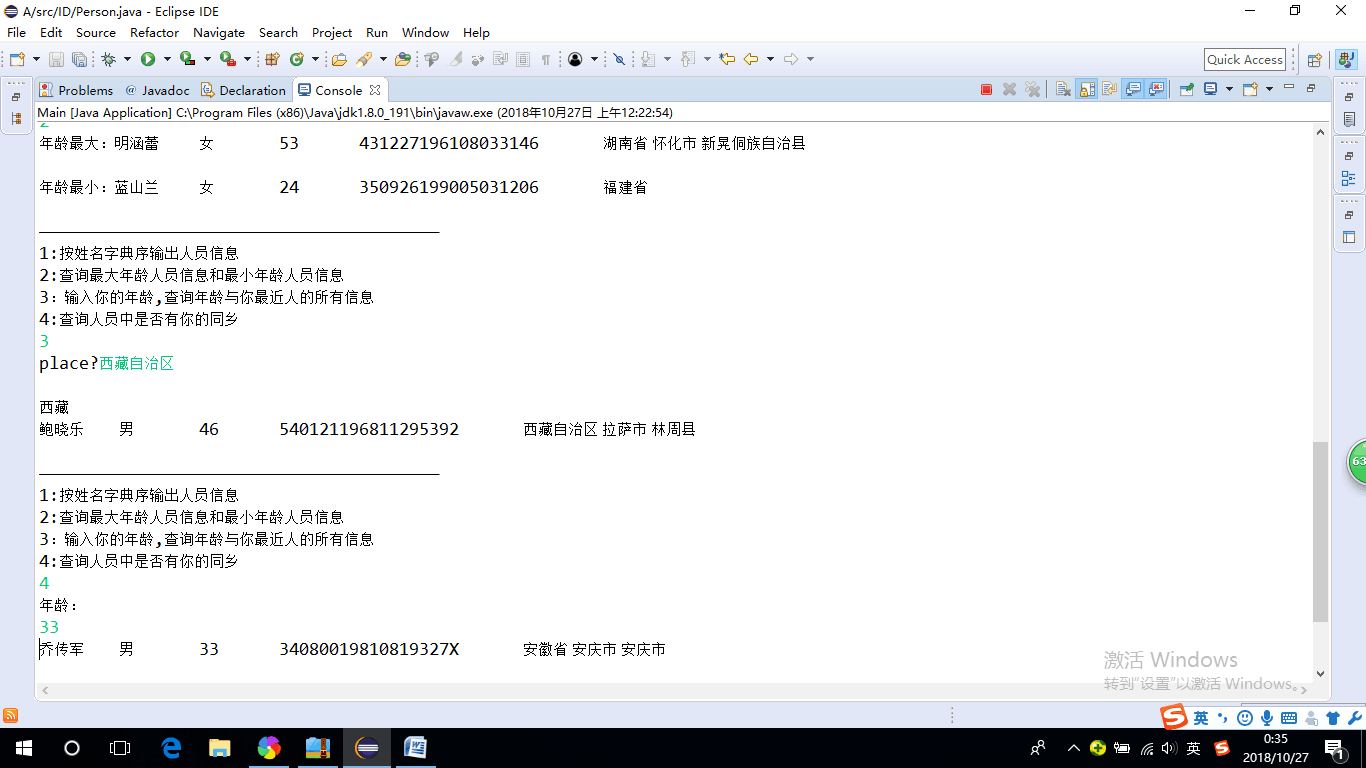

package ID; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; @SuppressWarnings("unused") public class Main{ private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist; @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { Personlist = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("E:\\新建文件夹\\身份证号.txt"); //捕获代码 try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); String name = linescanner.next(); String ID = linescanner.next(); String sex = linescanner.next(); String age = linescanner.next(); String place =linescanner.nextLine(); Person Person = new Person(); Person.setname(name); Person.setID(ID); Person.setsex(sex); int a = Integer.parseInt(age); Person.setage(a); Person.setbirthplace(place); Personlist.add(Person); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("查找不到信息"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("信息读取有误"); e.printStackTrace(); } boolean isTrue = true; while (isTrue) { System.out.println("————————————————————————————————————————"); System.out.println("1:按姓名字典序输出人员信息"); System.out.println("2:查询最大年龄人员信息和最小年龄人员信息"); System.out.println("3:输入你的年龄,查询年龄与你最近人的所有信息"); System.out.println("4:查询人员中是否有你的同乡"); int nextInt = scanner.nextInt(); switch (nextInt) { case 1: Collections.sort(Personlist); System.out.println(Personlist.toString()); break; case 2: int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; for(int i=1;i<Personlist.size();i++) { j=Personlist.get(i).getage(); if(j>max) { max=j; k1=i; } if(j<min) { min=j; k2=i; } } System.out.println("年龄最大:"+Personlist.get(k1)); System.out.println("年龄最小:"+Personlist.get(k2)); break; case 3: System.out.println("place?"); String find = scanner.next(); String place=find.substring(0,3); String place2=find.substring(0,3); for (int i = 0; i <Personlist.size(); i++) { if(Personlist.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(1,4).equals(place)) System.out.println(""+Personlist.get(i)); } break; case 4: System.out.println("年龄:"); int yourage = scanner.nextInt(); int near=agenear(yourage); int d_value=yourage-Personlist.get(near).getage(); System.out.println(""+Personlist.get(near)); /* for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++) { int p=Personlist.get(i).getage()-yourage; if(p<0) p=-p; if(p==d_value) System.out.println(Personlist.get(i)); } */ break; case 5: isTrue = false; System.out.println("退出程序!"); break; default: System.out.println("输入有误"); } } } public static int agenear(int age) { int j=0,min=53,d_value=0,k=0; for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++) { d_value=Personlist.get(i).getage()-age; if(d_value<0) d_value=-d_value; if (d_value<min) { min=d_value; k=i; } } return k; } }

package ID; public class Person implements Comparable<Person> { private String name; private String ID; private int age; private String sex; private String birthplace; public String getname() { return name; } public void setname(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getID() { return ID; } public void setID(String ID) { this.ID= ID; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age) { // int a = Integer.parseInt(age); this.age= age; } public String getsex() { return sex; } public void setsex(String sex) { this.sex= sex; } public String getbirthplace() { return birthplace; } public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) { this.birthplace= birthplace; } public int compareTo(Person o) { return this.name.compareTo(o.getname()); } public String toString() { return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+ID+"\t"+birthplace+"\n"; } }
通过学习合作伙伴的程序,发现他的程序和我的程序相差不大,有些细微的不同可以从他的代码中有所改善。
各自运行合作伙伴实验十编程练习2,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;

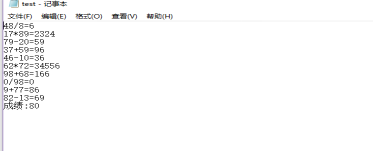

package C; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Suanfa counter = new Suanfa(); PrintWriter out = null; try { out = new PrintWriter("test.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件夹输出失败"); e.printStackTrace(); } int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int m; Random rand = new Random(); m = (int) rand.nextInt(4) + 1; System.out.println("随机生成的四则运算类型:" + m); switch (m) { case 1: a = b + (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); while(b == 0){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } while(a % b != 0){ a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } //若生成的除法式子必须能整除,且满足分母为0的条件,则a一定要大于b,且a模b的结果要为0。 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "/" + b + "="); int c0 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c0); if (c0 == counter.d(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; case 2: System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "*" + b + "="); int c = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c); if (c == counter.m(a, b)) { sum+= 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; case 3: System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "+" + b + "="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c1); if (c1 == counter.add(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; case 4: while (a < b) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } //因为不能产生运算结果为负数的减法式子,所以a一定要大于b。若a<b,则重新生成b。 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "-" + b + "="); int c2 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c2); if (c2 == counter.r(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; } } System.out.println("成绩" + sum); out.println("成绩:" + sum); out.close(); } }

package C; public class Suanfa<T> { private T a; private T b; public int add(int a,int b) { return a + b; } public int r(int a, int b) { return a - b; } public int m(int a, int b) { return a * b; } public int d(int a, int b) { if (b != 0 && a%b==0) return a / b; else return 0; } }
通过观察合作伙伴的这个程序,发现她的比我的程序更为精简,其中有很多可以学习的地方。
l 采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验九编程练习1;

l

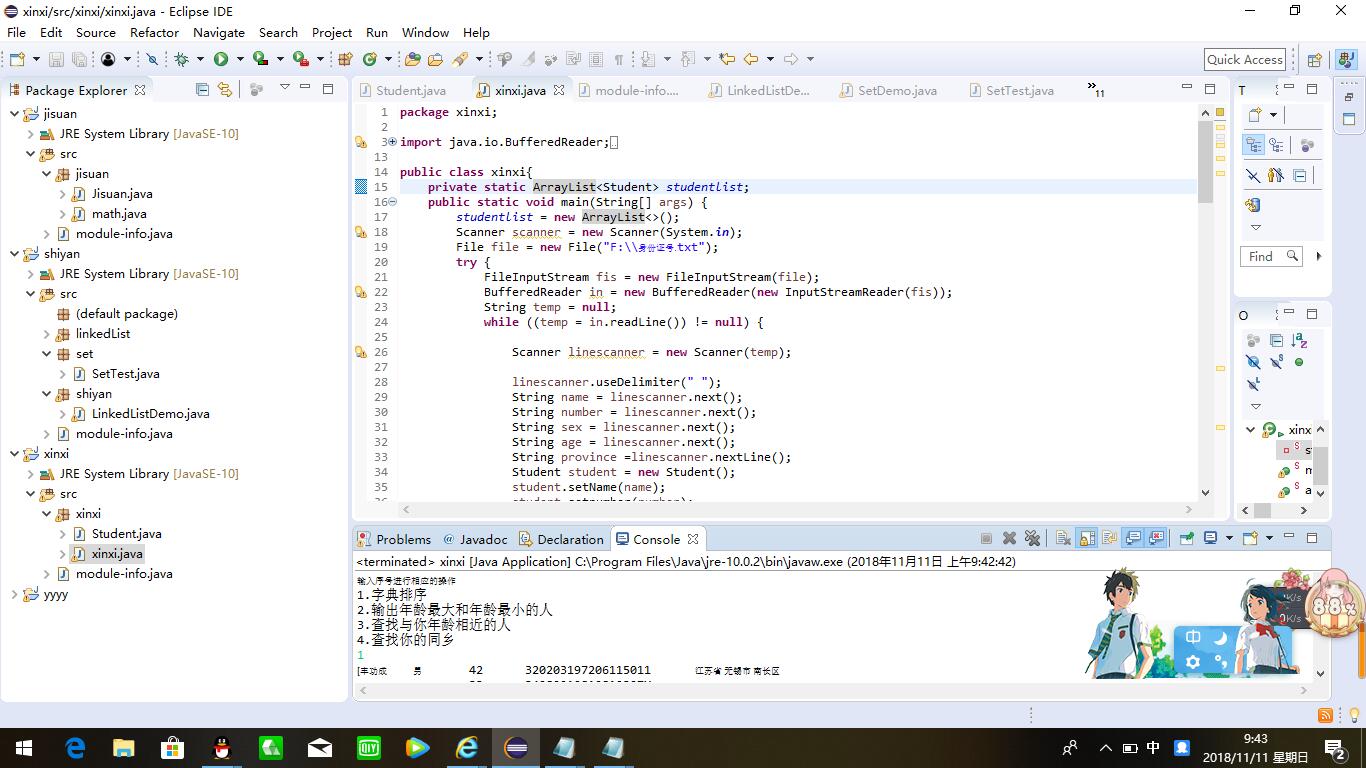
package xinxi; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; public class xinxi{ private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist; public static void main(String[] args) { studentlist = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("F:\\身份证号.txt"); try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); String name = linescanner.next(); String number = linescanner.next(); String sex = linescanner.next(); String age = linescanner.next(); String province =linescanner.nextLine(); Student student = new Student(); student.setName(name); student.setnumber(number); student.setsex(sex); int a = Integer.parseInt(age); student.setage(a); student.setprovince(province); studentlist.add(student); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误"); e.printStackTrace(); } boolean isTrue = true; while (isTrue) { System.out.println("输入序号进行相应的操作"); System.out.println("1.字典排序"); System.out.println("2.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人"); System.out.println("3.查找与你年龄相近的人"); System.out.println("4.查找你的同乡"); String n = scanner.next(); switch (n) { case "1": Collections.sort(studentlist); System.out.println(studentlist.toString()); break; case "2": int max=0,min=100; int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++) { j=studentlist.get(i).getage(); if(j>max) { max=j; k1=i; } if(j<min) { min=j; k2=i; } } System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1)); System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2)); break; case "3": System.out.println("年龄:"); int yourage = scanner.nextInt(); int near=agenear(yourage); int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage(); System.out.println("和你年龄相近的是"+studentlist.get(near)); break; case "4": System.out.println("输入你的家乡"); String find = scanner.next(); String place=find.substring(0,3); for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++) { if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place)) System.out.println("你的同乡是 "+studentlist.get(i)); } break; } } } public static int agenear(int age) { int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0; for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) { value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age; if(value<0) value=-value; if (value<min) { min=value; k=i; } } return k; } }

package xinxi; public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { private String name; private String number ; private String sex ; private int age; private String province; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getnumber() { return number; } public void setnumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public String getsex() { return sex ; } public void setsex(String sex ) { this.sex =sex ; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age) { this.age= age; } public String getprovince() { return province; } public void setprovince(String province) { this.province=province ; } public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); } public String toString() { return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n"; } }
我们在结对编写此程序时,一起交流探索我们各自的程序缺陷和不完美的地方,再统一结合编写出更加精简的程序。
采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验十编程练习2。



package C; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Suanfa counter = new Suanfa(); PrintWriter out = null; try { out = new PrintWriter("test.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件夹输出失败"); e.printStackTrace(); } int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int m; Random rand = new Random(); m = (int) rand.nextInt(4) + 1; System.out.println("随机生成的四则运算类型:" + m); switch (m) { case 1: a = b + (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); while(b == 0){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } while(a % b != 0){ a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } //若生成的除法式子必须能整除,且满足分母为0的条件,则a一定要大于b,且a模b的结果要为0。 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "/" + b + "="); int c0 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c0); if (c0 == counter.d(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; case 2: System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "*" + b + "="); int c = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c); if (c == counter.m(a, b)) { sum+= 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; case 3: System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "+" + b + "="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c1); if (c1 == counter.add(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; case 4: while (a < b) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } //因为不能产生运算结果为负数的减法式子,所以a一定要大于b。若a<b,则重新生成b。 System.out.println(i + ": " + a + "-" + b + "="); int c2 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c2); if (c2 == counter.r(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确!"); } else { System.out.println("错误!"); } break; } } System.out.println("成绩" + sum); out.println("成绩:" + sum); out.close(); } }

package C; public class Suanfa<T> { private T a; private T b; public int add(int a,int b) { return a + b; } public int r(int a, int b) { return a - b; } public int m(int a, int b) { return a * b; } public int d(int a, int b) { if (b != 0 && a%b==0) return a / b; else return 0; } }
我们交流总结出了更为精简的程序。
实验总结
通过本次实验,我掌握了Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API,以及 了解了java集合框架体系组成;此外,这是第一次接触结对编程,体会到了不同于单独编程的优点和乐趣,和合作伙伴彼此交流,借鉴对方的优点,改正自己的不足,互相交流学习,有着很大的收获。
