本文为美国卡内基·梅隆大学(作者:Sanjiban Choudhury)的博士论文,共255页。
移动机器人正越来越多地被部署在现实世界中,以适应诸如运输、配送和检查等应用的不断增长需求。移动机器人的运动规划系统在它们所遇到的各种场景中都应该具有一致的性能。尽管可以使用具有可证明的最坏情况保证的最先进的规划器来解决这些规划问题,但是它们在有限时间内应对不同场景的性能是不同的。本文提出的机器人规划模块必须根据所遇到的规划问题的分布来调整其搜索策略,以达到实时性能。我们解决这个问题主要有三个挑战。
首先,我们证明了即使规划问题的分布是固定的,由于规划策略的性能随着环境的微小变化而波动,因此,设计非自适应规划器也是具有挑战性的。我们描述了互补策略的存在性,并提出通过执行不同的规划器集合来实现。
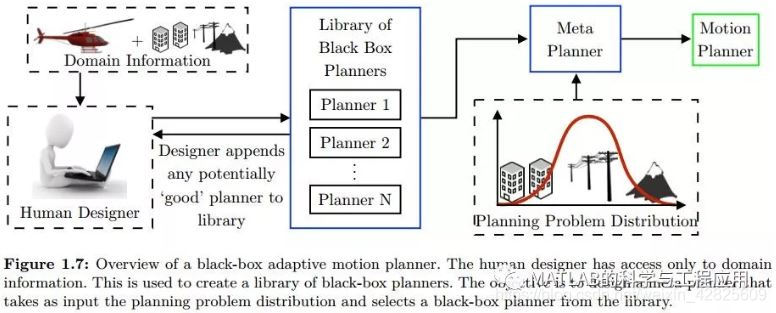
其次,当分布发生变化时,我们需要一个元规划器,它可以从黑盒规划器库中自动选择相应的集合。我们的研究表明,针对失败案例贪婪地训练一个预测器列表,能够实现一个有效的元规划器。对于没有训练数据的情况,研究表明,我们可以通过采用在线寻呼理论中的算法来动态地学习集成。
第三,为了提高效率,我们需要一个白盒规划器,它在规划周期中直接调整搜索策略。我们在数据驱动的模仿学习框架下提出了一个有效的训练自适应搜索的启发方法。我们还提出了一种创新的与贝叶斯主动学习相关的连接方法,并提出了自适应评估图边缘的算法。
我们的方法最终实现了一个鲁棒的实时规划模块,该模块允许无人机无缝地跨环境跨速度导航。我们在当前框架下对一系列规划问题进行了评估,给出了三架无人机(一架全自主无人直升机、一架大型六旋翼无人机和一架小型四旋翼无人机)平台闭环运动的结果。虽然本论文的研究对象是移动机器人,但这些算法可以广泛地应用于其它问题领域,如信息路径规划和操作规划。我们还在运动规划和主动学习、模拟学习、在线寻呼等不同领域之间建立了新颖的联系,为若干新的研究问题打开了大门。
Mobile robots are increasingly beingdeployed in the real world in response to a heightened demand for applicationssuch as transportation, delivery and inspection. The motion planning systemsfor these robots are expected to have consistent performance across the widerange of scenarios that they encounter. While state-of-the-art planners, withprovable worst-case guarantees, can be employed to solve these planningproblems, their finite time performance varies across scenarios. This thesisproposes that the planning module for a robot must adapt its search strategy tothe distribution of planning problems encountered to achieve real-timeperformance. We address three principal challenges of this problem. Firstly, weshow that even when the planning problem distribution is fixed, designing anonadaptive planner can be challenging as the performance of planningstrategies fluctuates with small changes in the environment. We characterizethe existence of complementary strategies and propose to hedge our bets byexecuting a diverse ensemble of planners. Secondly, when the distribution isvarying, we require a meta-planner that can automatically select such anensemble from a library of black-box planners. We show that greedily training alist of predictors to focus on failure cases leads to an effectivemeta-planner. For situations where we have no training data, we show that wecan learn an ensemble on-the-fly by adopting algorithms from online pagingtheory. Thirdly, in the interest of efficiency, we require a white-box plannerthat directly adapts its search strategy during a planning cycle. We propose anefficient procedure for training adaptive search heuristics in a data-drivenimitation learning framework. We also draw a novel connection to Bayesianactive learning, and propose algorithms to adaptively evaluate edges of agraph. Our approach leads to the synthesis of a robust real-time planningmodule that allows a UAV to navigate seamlessly across environments andspeed-regimes. We evaluate our framework on a spectrum of planning problems andshow closed-loop results on 3 UAV platforms - a full-scale autonomoushelicopter, a large scale hexarotor and a small quadrotor. While the thesis wasmotivated by mobile robots, we have shown that the individual algorithms arebroadly applicable to other problem domains such as informative path planningand manipulation planning. We also establish novel connections between thedisparate fields of motion planning and active learning, imitation learning andonline paging which opens doors to several new research problems.
1 引言
2 项目背景
3 探索结构的规划算法
4 专家策划的多元化组合
5 专家策划的自适应组合
6 在线意外规划器
7 基于模仿学习的数据驱动规划
8 贝叶斯主动边缘评估
9 统一的无人机规划体系架构
10 结论
附录A 无人机规划问题
附录B 动态投影滤波器
附录C 无人机专家策划库
附录D 黑盒规划器的特征提取
下载英文原文地址:
http://page5.dfpan.com/fs/2lc4j2221e29416ae17/
更多精彩文章请关注微信号: