1.变量命名规则
# 中文是可以作为变量名的,但不建议
# 变量名可以由字母,数字或者下划线;
# 变量名只能以字母或者下划线组成;
# 变量名不能是python的关键字: eg: if, elif, else,
# eg: while, for, break,continue,pass
2.定义方式
1)a = "hello"
2)b = 'westos'
3)c = """
用户管理系统
1). 添加用户
2). 删除用户
3). 显示用户
"""
2. 字符串常用的转义符号:
# \n:换行# \t: 一个tab键
# \': '
# \": "
3.字符串特性
s = "hello"
1)索引:
#索引值是从0开始的;
print(s[-1]) # 拿出字符串的最后一个子符;
2)切片:
print(s[0:4:2]) # 切片时规则为s[start:end:step],从start开始,到end-1结束, 步长为step;print(s[:]) # 显示所有子符
print(s[:3]) # 显示前3个子符
print(s[::-1]) # 对于字符串倒序输出;
print(s[1:]) # 除了第一个子符之外, 其他全部显示;
3)重复:
print(s*10)
4)连接:
print("hello "+"world")
5)成员操作符:
in, not in
print('he' in s)
print('aa' in s)
print('he' not in s)
4.字符串函数
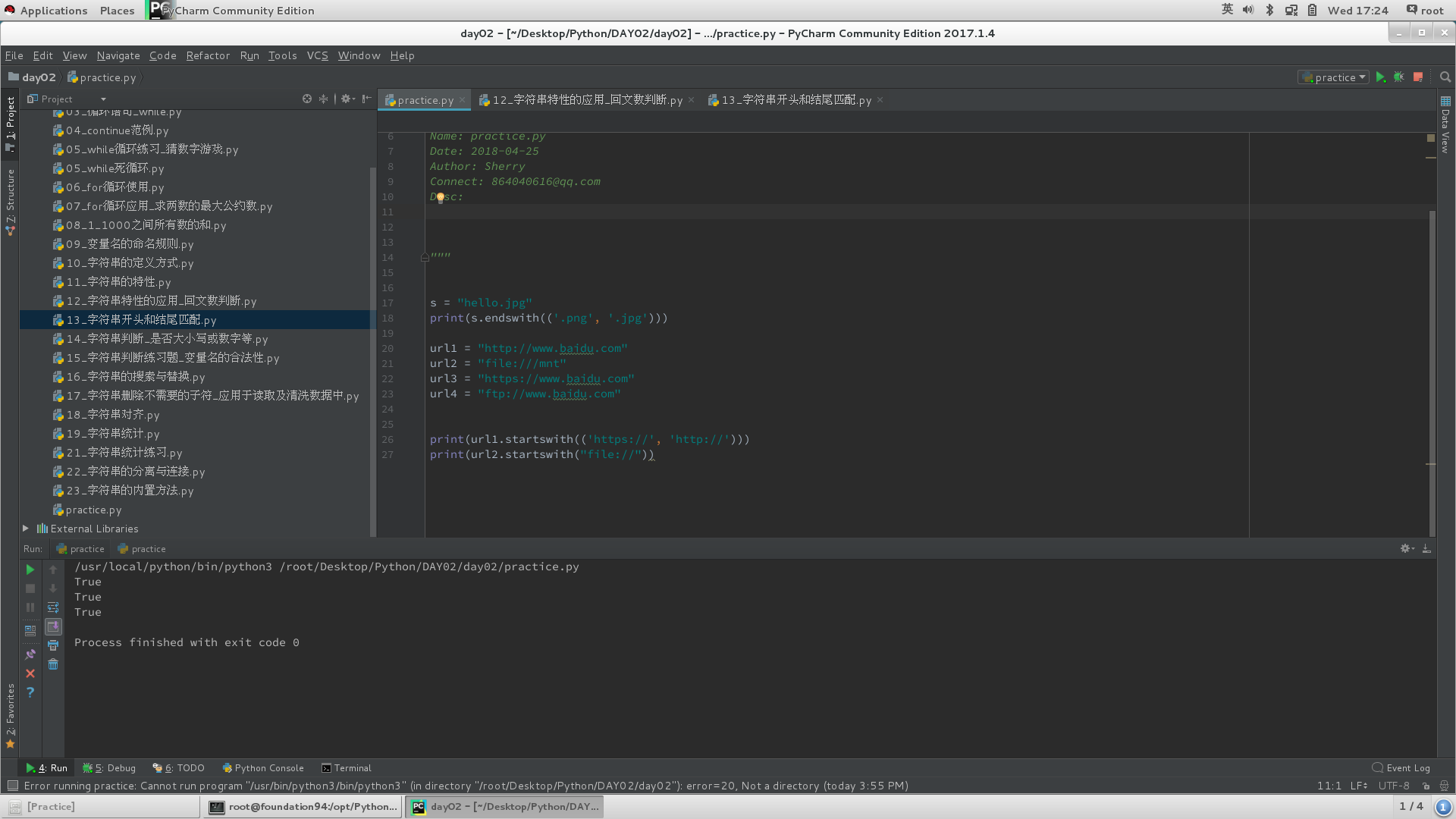
1)开头结尾匹配
#判断是否以xxxx开头或结尾
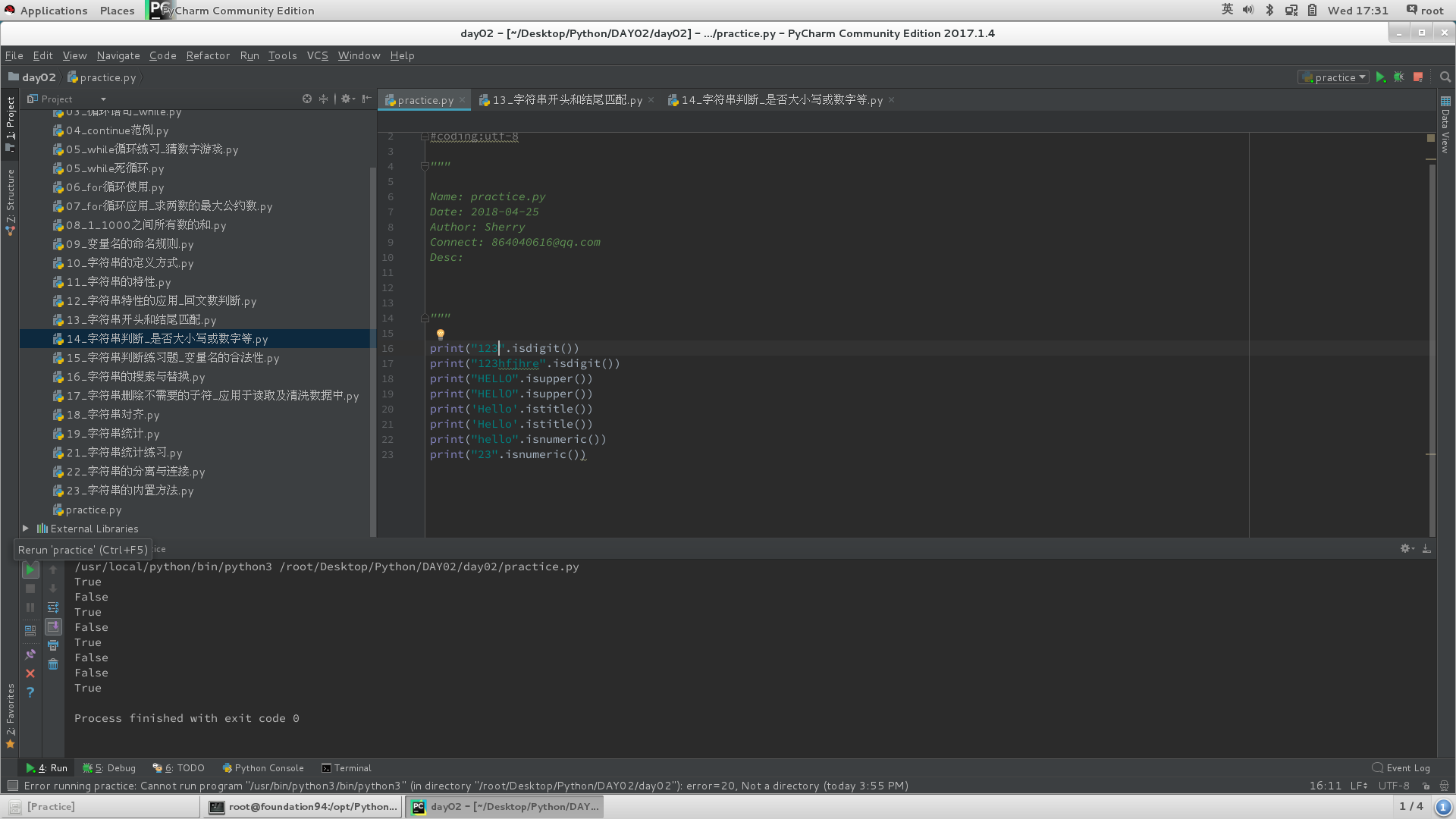
2)字符属性判断
# 判断字符串里面的每个元素是否为什么类型, 一旦有一个元素不满足, 返回False;
#isdigit与isnumeric的区别:isdigit:是否为十进制整数;isnumeric:能否转化成数值类型;
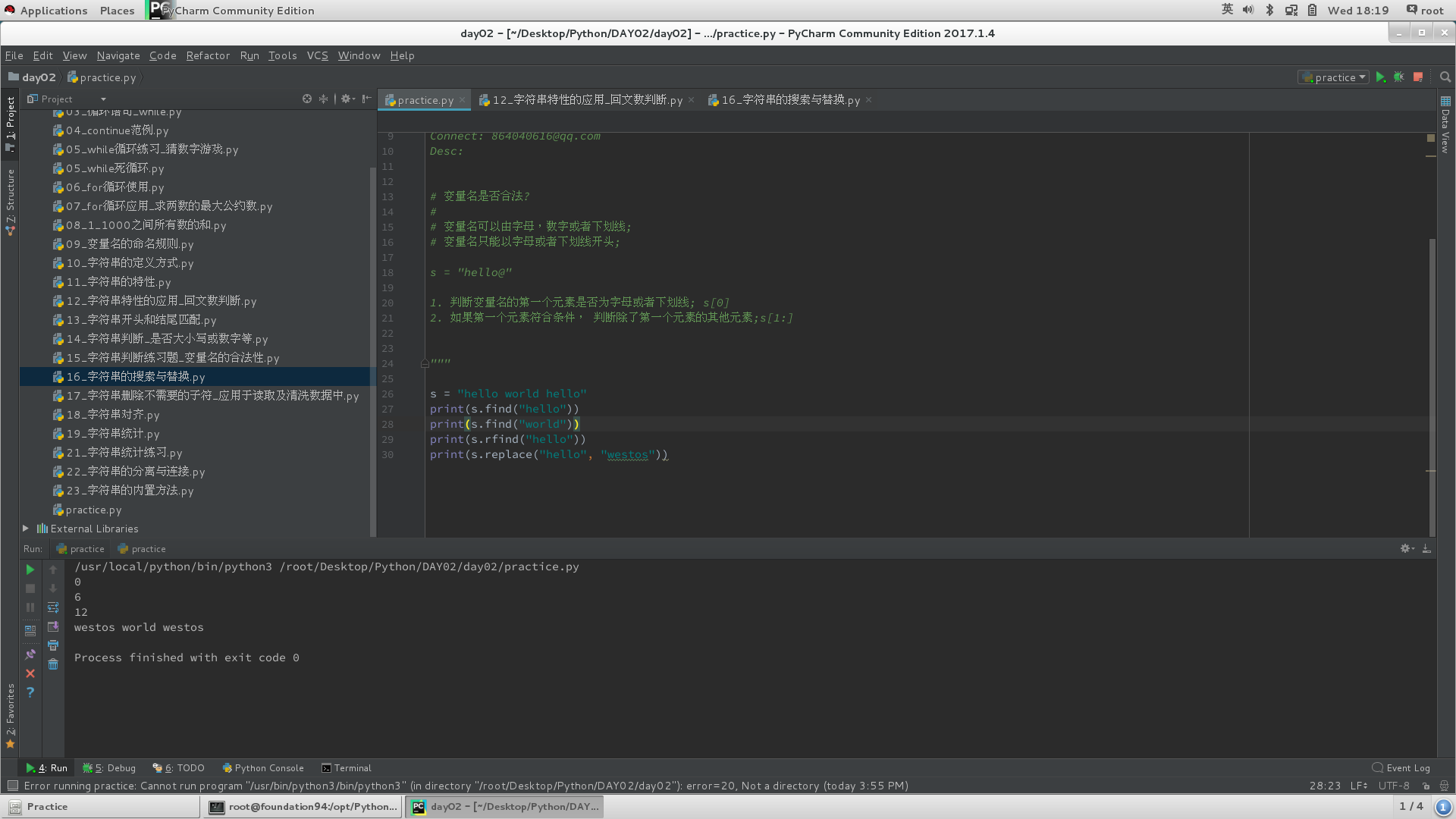
3)搜索与替换
# find找到子串,并返回最小的索引值;
# rfind找到子串,并返回最大的索引值;
# replace替换字符串中所有的“xxxx”为"xxxx"
4)数据清洗
# strip: 删除字符串左边和右边的空格; 在这里空格是广义的: \n,\t,
# lstrip:删除字符串左边的空格;rstrip:删除字符串右边的空格
# 通过replace间接实现删除中间空格
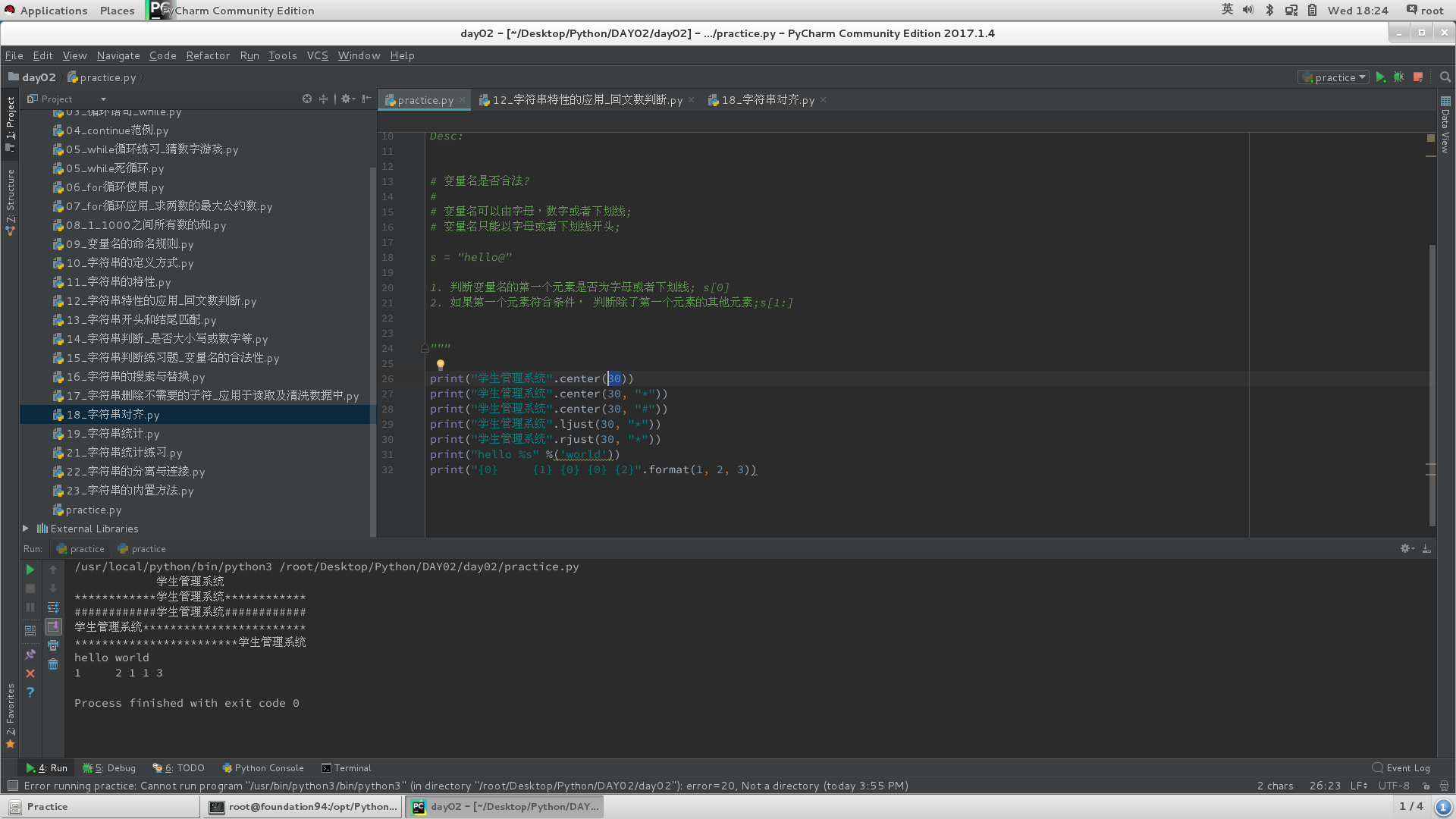
5)格式对齐
# center:居中,可输入填充符号;
# ljust:左对齐,可输入填充符号;
# rjust:右对齐,可输入填充符号;
# format:位置参数,格式制表;
print("{0} {1} {0} {0}".format(1,2))
6)字符统计
# count:回归统计数
print("hello".count('l'))
print("helloll".count('ll'))
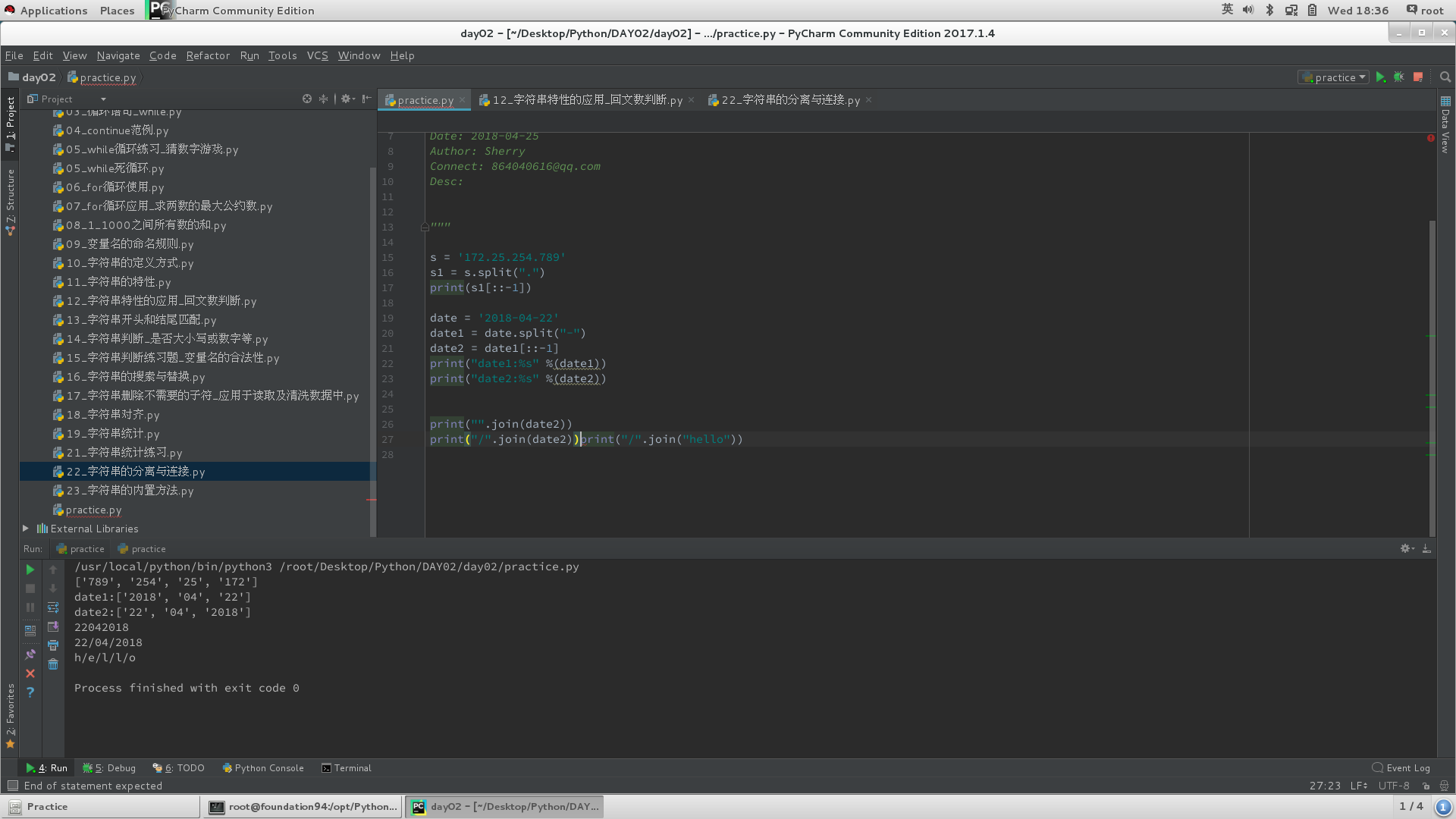
7)分离与连接
# split:分离,通过指定的分割符,分割每个字符串;
# s = '172.25.254.789' 分割为 ['172', '25', '254', '789']列表数据类型;
# join:连接,通过指定的连接符, 连接每个字符串;
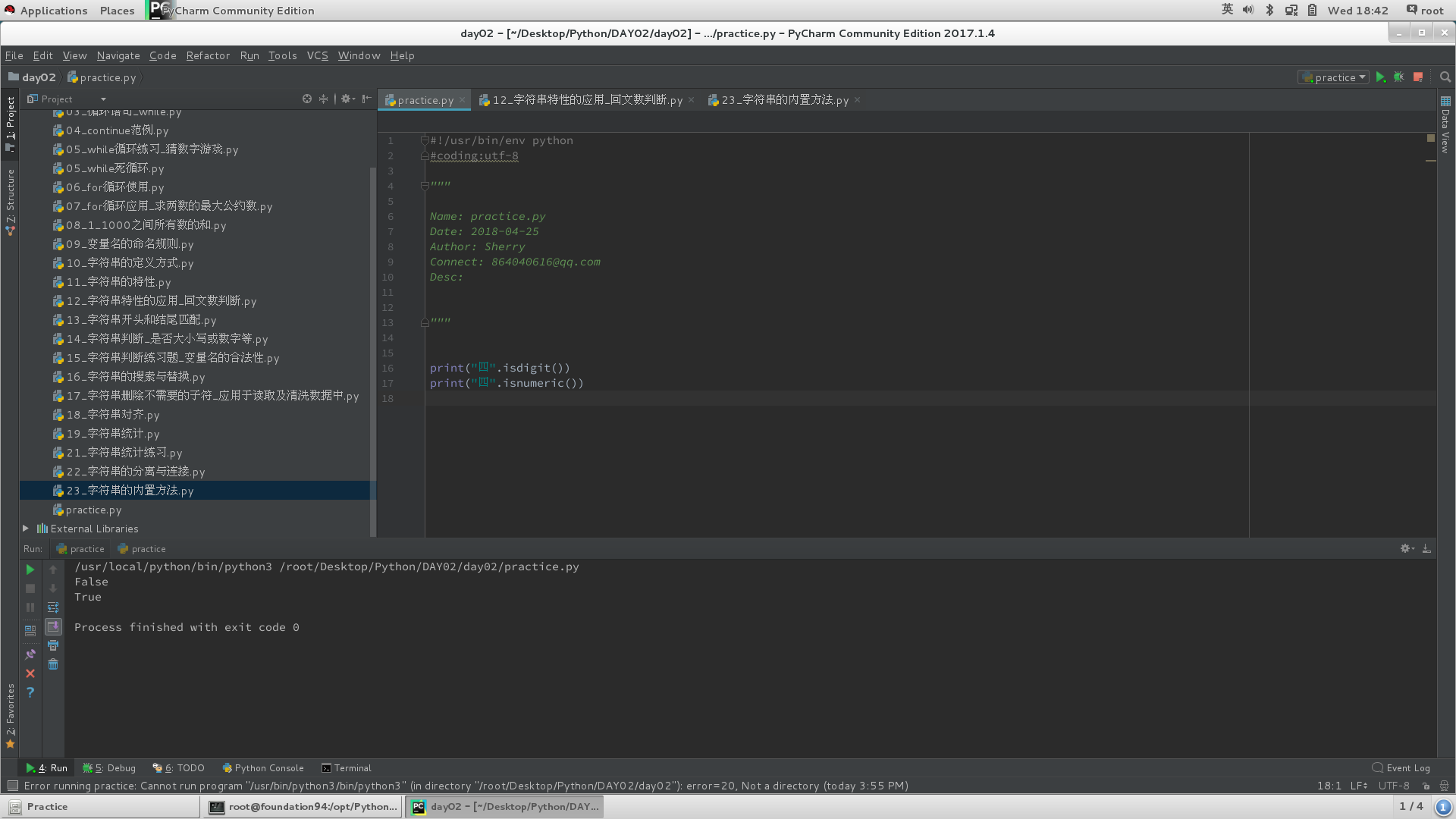
8)内置方法
#字符串与数值通过ASCII码转换;
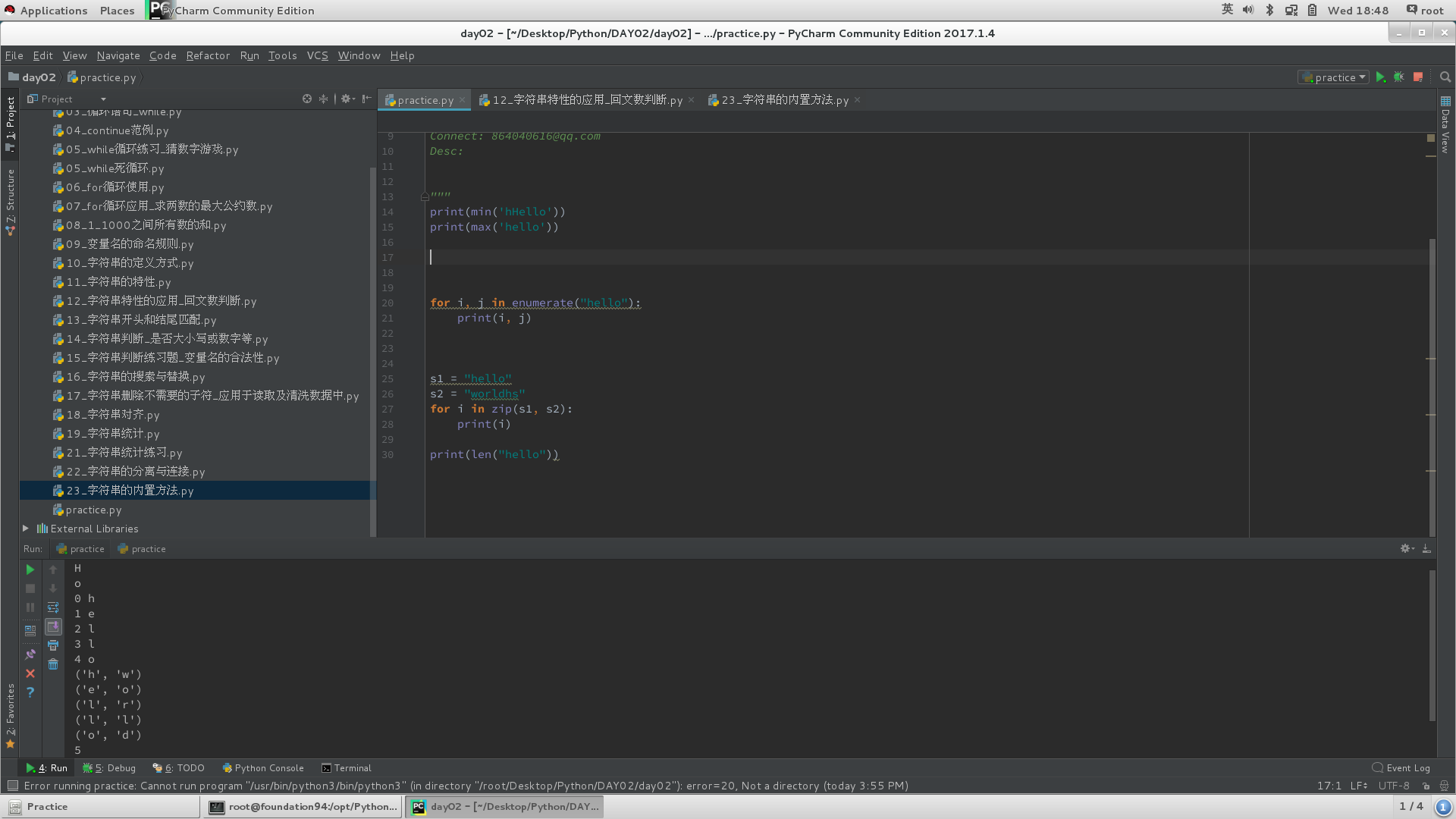
a.比较大小:
print(min('hHello'))
print(max('hello'))
b.字符串内字符遍历:
i为字符对应索引,j为单个字符;
for i,j in enumerate("hello"):
print(i,j)
c.字符串对应:
s1 = "hello"
s2 = "worldhs"
for i in zip(s1, s2):
print(i)
d.字符串长度
print(len("hello"))