1. 原理介绍
目标检测typical architecture 通常可以分为两个阶段:
(1)region proposal:给定一张输入image找出objects可能存在的所有位置。这一阶段的输出应该是一系列object可能位置的bounding box。这些通常称之为region proposals或者 regions of interest(ROI)。
(2)final classification:确定上一阶段的每个region proposal是否属于目标一类或者背景。
这个architecture存在的一些问题是:
产生大量的region proposals 会导致performance problems,很难达到实时目标检测。在处理速度方面是suboptimal。无法做到end-to-end training。这就是ROI pooling提出的根本原因。
ROI pooling层能实现training和testing的显著加速,并提高检测accuracy。该层有两个输入:从具有多个卷积核池化的深度网络中获得的固定大小的feature maps;一个表示所有ROI(也可以叫GT)的N*5的矩阵,其中N表示ROI的数目。第一列表示图像index,其余四列表示其余的左上角和右下角坐标。
ROI pooling具体操作如下:
(1)根据输入image,将ROI映射到feature map对应位置,映射是根据image缩小的尺寸来的;
(2)按照ROI Pooling输出的数据的坐标,将其映射到上一步中映射的feature区域上,这样就将原来feature map上的ROI映射划分成了几个sections(sections数量与输出的维度(pooled_w*pooled_h)相同);
(3)对每个sections进行max pooling操作;
这样我们就可以从不同大小的方框得到固定大小的相应的feature maps。值得一提的是,输出的feature maps的大小不取决于ROI和卷积feature maps大小,而是取决于该层设置的pooled_h与pooled_w。ROI pooling 最大的好处就在于极大地提高了处理速度。这样不管给定feature map输入的大小,使得输出的数据维度统一,这与SPP-Net的思想类似。
2. ROI pooling的图文解释
考虑一个
大小的feature map,一个ROI,以及ROI Pooling之后的输出大小为
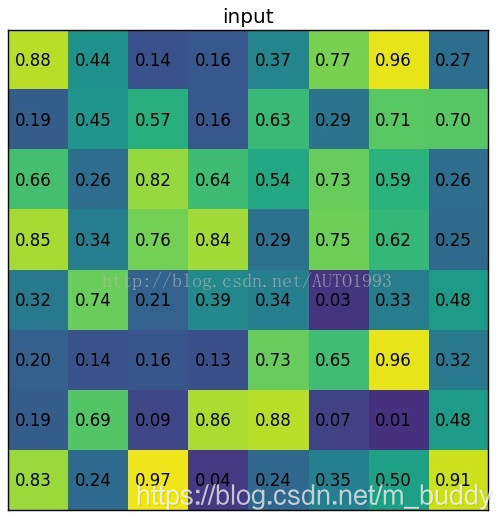
(1)输入的固定大小的feature map
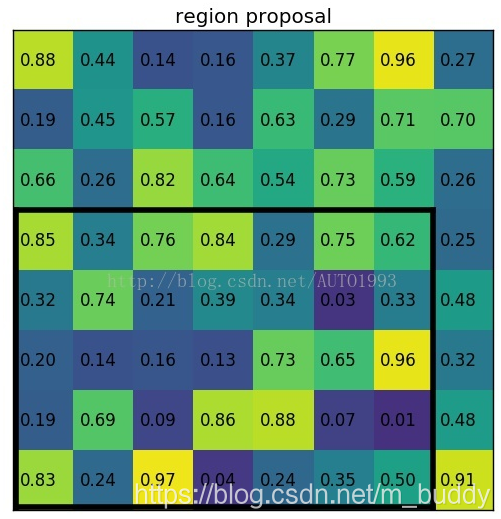
(2)region proposal 投影之后位置(左上角,右下角坐标):(0,3),(7,8)。
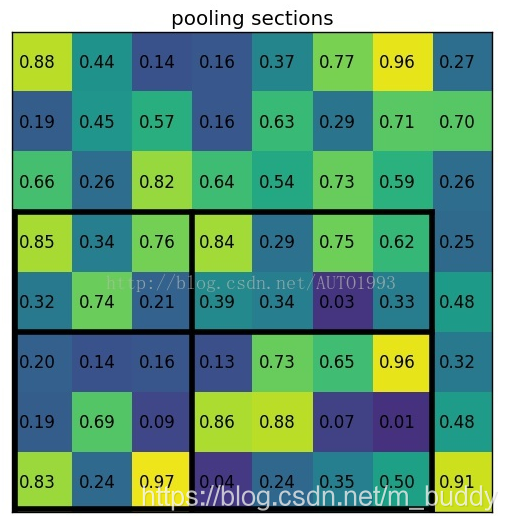
(3)将其划分为(
)个sections(因为输出大小为
),我们可以得到:
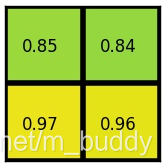
(4)对每个section做max pooling,可以得到:
ROI pooling总结:
(1)用于目标检测任务;
(2)允许我们对CNN中的feature map进行reuse;
(3)可以显著加速training和testing速度;
(4)允许end-to-end的形式训练目标检测系统。
3. Caffe中的使用与实现
对于ROI Pooling层在Caffe的prototxt中是这样定义的
layer {
name: "roi_pool5"
type: "ROIPooling"
bottom: "conv5_3"
bottom: "rois"
top: "pool5"
roi_pooling_param {
pooled_w: 7
pooled_h: 7
spatial_scale: 0.0625 # 1/16
}
}
对应的源代码,这里已经写了必要的注释
template <typename Dtype>
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
ROIPoolingParameter roi_pool_param = this->layer_param_.roi_pooling_param();
CHECK_GT(roi_pool_param.pooled_h(), 0)
<< "pooled_h must be > 0";
CHECK_GT(roi_pool_param.pooled_w(), 0)
<< "pooled_w must be > 0";
pooled_height_ = roi_pool_param.pooled_h(); //Pooling之后的height
pooled_width_ = roi_pool_param.pooled_w(); //Pooling之后的width
spatial_scale_ = roi_pool_param.spatial_scale(); //GT标注的缩放比例
LOG(INFO) << "Spatial scale: " << spatial_scale_;
}
template <typename Dtype>
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
channels_ = bottom[0]->channels();
height_ = bottom[0]->height();
width_ = bottom[0]->width();
top[0]->Reshape(bottom[1]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_, //输出的维度是GT标注的n*channels*Pooling_w*Pooling_h
pooled_width_);
max_idx_.Reshape(bottom[1]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
pooled_width_);
}
template <typename Dtype>
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data(); //卷积的feature map数据
const Dtype* bottom_rois = bottom[1]->cpu_data(); //标注的GT数据
// Number of ROIs
int num_rois = bottom[1]->num(); //标注数据的个数
int batch_size = bottom[0]->num(); //卷积数据
int top_count = top[0]->count(); //输出数据的大小
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data(); //空间初始化
caffe_set(top_count, Dtype(-FLT_MAX), top_data);
int* argmax_data = max_idx_.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, -1, argmax_data);
// For each ROI R = [batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R
for (int n = 0; n < num_rois; ++n) { //遍历每个GT标注数据
int roi_batch_ind = bottom_rois[0]; //取出GT坐标对应当前batch中的index
int roi_start_w = round(bottom_rois[1] * spatial_scale_); //按照图像缩小的尺寸(scale),去计算对应坐标在特征图上的相对位置
int roi_start_h = round(bottom_rois[2] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_end_w = round(bottom_rois[3] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_end_h = round(bottom_rois[4] * spatial_scale_);
CHECK_GE(roi_batch_ind, 0);
CHECK_LT(roi_batch_ind, batch_size);
int roi_height = max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h + 1, 1); //计算特征图上roi的宽高
int roi_width = max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w + 1, 1);
const Dtype bin_size_h = static_cast<Dtype>(roi_height) //计算roi在特征图上的宽高与Pooling之后的宽高的比例
/ static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_height_);
const Dtype bin_size_w = static_cast<Dtype>(roi_width)
/ static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_width_);
const Dtype* batch_data = bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(roi_batch_ind); //取出正在运算的batch
//使用当前GT对应的Pooling结果位置反向到feature map中去做求最大值操作
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
// Compute pooling region for this output unit:
// start (included) = floor(ph * roi_height / pooled_height_)
// end (excluded) = ceil((ph + 1) * roi_height / pooled_height_)
int hstart = static_cast<int>(floor(static_cast<Dtype>(ph) //计算Pooling之后的数据在
* bin_size_h));
int wstart = static_cast<int>(floor(static_cast<Dtype>(pw)
* bin_size_w));
int hend = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<Dtype>(ph + 1)
* bin_size_h));
int wend = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<Dtype>(pw + 1)
* bin_size_w));
hstart = min(max(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), height_); //计算当前Pooling位置对应feature map的区域
hend = min(max(hend + roi_start_h, 0), height_);
wstart = min(max(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), width_);
wend = min(max(wend + roi_start_w, 0), width_);
bool is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart);
const int pool_index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
if (is_empty) {
top_data[pool_index] = 0;
argmax_data[pool_index] = -1;
}
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) { //求出圈定区域的最大值
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
const int index = h * width_ + w;
if (batch_data[index] > top_data[pool_index]) {
top_data[pool_index] = batch_data[index];
argmax_data[pool_index] = index;
}
}
}
}
}
// Increment all data pointers by one channel
batch_data += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1); //当前batch的下一个channel
top_data += top[0]->offset(0, 1); //当前Pooling的下一个channel
argmax_data += max_idx_.offset(0, 1);
}
// Increment ROI data pointer
bottom_rois += bottom[1]->offset(1); //下一个roi区域
}
}