版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/I_do_can/article/details/78083773
结果是最不重要的,重要的是过程
* [问题] 本文主要解决白色背景下,白色的文字看不见的问题
* [解决思路] 给文字加阴影,ios下很好解决,苹果提供了很好 View.layer.shadow**属性,奈何android虽然提供了,但是效果不好, 解决方案是利用TextView在onDraw的时候,获取到画笔,先进行一次比默认大小的文字内容稍微大一点的绘制,然后再进行一次默认大小的文字内容的绘制,这样就产生出了描边效果
* [效果图] 
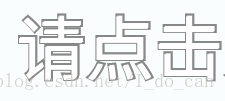
* [核心代码分析] 这个方案可以使用在自定义view时加阴影,如果你画一个矩形,就可以使用这段代码加一圈阴影
// 绘制阴影,使用空心画笔,宽度加宽
mPaint.setColor(mShadowColor);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mPaint.setFakeBoldText(true); // 外层text采用粗体
// todo 此处需要执行绘制操作
// 正常绘制,恢复画笔
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mPaint.setFakeBoldText(false);比如画阴影矩形
private void drawInternal(Canvas canvas) {
drawShadow(canvas, mUpBarRect);
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(mUpBarRect, mBarRoundX, mBarRoundY, mPaint);
}
private void drawShadow(Canvas canvas, RectF rect) {
mPaint.setColor(mShadowColor);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mPaint.setFakeBoldText(true); // 外层text采用粗体
canvas.drawRoundRect(rect, mBarRoundX, mBarRoundY, mPaint);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mPaint.setFakeBoldText(false);
}附上完整代码:
/**
* TextView 文字描边
* 是利用TextView在onDraw的时候,获取到画笔,先进行一次比默认大小的文字内容稍微大一点的绘制,然后再进行一次默认大小的文字内容的绘制,这样就产生出了描边效果
* Created by slack
* on 17/9/6 下午3:43
*/
public class WrapTextView extends AppCompatTextView {
private @ColorInt int mBorderColor = Color.GRAY;
private @ColorInt int mInnerColor = Color.WHITE;
private boolean mBorderText = true;
private TextPaint mTextPaint;
public WrapTextView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public WrapTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, android.R.attr.textViewStyle);
}
public WrapTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mTextPaint = this.getPaint();
mInnerColor = getCurrentTextColor();
}
/**
* onDraw draw border first
*/
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if(mBorderText) {
// 描外层
setTextColorUseReflection(mBorderColor);
mTextPaint.setStrokeWidth(2); // 描边宽度
mTextPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); // 画笔空心
mTextPaint.setFakeBoldText(true); // 外层text采用粗体
super.onDraw(canvas);
// 描内层,恢复原先的画笔
setTextColorUseReflection(mInnerColor);
mTextPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mTextPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mTextPaint.setFakeBoldText(false);
}
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
/**
* 使用反射的方法进行字体颜色的设置
* 其实就是 this.setTextColor(); 但是这个系统方法里会调用invalidate(); 最终的效果导致这段代码无限循环
* 反射部分:
* 1. Class.getDeclaredField(String name); 返回一个 Field 对象,该对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定已声明字段(包括私有成员)
* 2. 获取私有属性的时候必须先设置Accessible为true,然后才能获取
* 3. 通过Field.get(Object obj)获取属性的值,通过Field.set(Object obj,value)重新设置新的属性值
*/
private void setTextColorUseReflection(int color) {
Field textColorField;
try {
textColorField = TextView.class.getDeclaredField("mCurTextColor");
textColorField.setAccessible(true);
textColorField.set(this, color);
textColorField.setAccessible(false);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mTextPaint.setColor(color);
}
}